What could be nicer and more harmless than a small neat mole on a person's face. There are practically no people on the planet whose body did not have at least one mole or pigmented nevus, as it is customary to call such formations on the skin. But from the point of view of dermatology, pigmented nevi – these are extremely dangerous formations that require careful attention, since under certain conditions they tend to degenerate into malignant tumors. Eyelid melanoma – this is a rather rare oncopathology of the face, but every practicing doctor should have the necessary amount of information about this disease.
Why healthy tissues can develop into eyelid melanoma
Eyelid melanoma accounts for no more than 1% of all malignant neoplasms on the skin of the eyelids. The risk of eyelid melanoma increases significantly after the age of 40, with women suffering much more often than men. As you know, melanoma is one of the most aggressive and rapidly progressive cancers. If there are convex moles on the human body – they should always be watched closely. And since the skin of the face – this is an area that is often affected by various traumatic factors, the risk of developing melanoma in the presence of moles on the eyelids is significantly increased.
Melanoma of the eyelids:
- factors contributing to the development of eyelid melanoma;
- clinical picture of eyelid melanoma: characteristics of the tumor;
- what determines the choice of treatment for eyelid melanoma.
Factors contributing to the development of eyelid melanoma
Of course, not every person on the planet is threatened with the development of eyelid melanoma. Since this tumor develops from transformed intradermal melanocyte cells, there are certain factors that increase the risk of developing melanoma, which include:
- availability nevi, especially borderline ones, that is, those whose cells are localized both in the epidermis and in the dermis;
- melanosis – excessive accumulation of melanin in body tissues;
- high individual sensitivity to intense solar radiation;
- light skin color;
- cases of melanoma in blood relatives;
- age over 20.
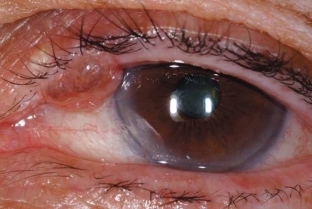
Clinical picture of eyelid melanoma: characteristics of the tumor
Melanoma of the eyelids – it is a flat lesion of the skin of the eyelids, intensely pigmented on the surface and having uneven light brown edges. On the skin of the eyelids, in most cases, a nodular form of melanoma develops, which is characterized by a rapid increase in the size of the tumor, as well as the presence of ulcers on its surface, which can bleed spontaneously. The skin around the tumor is hyperemic due to the expansion of the perifocal vessels; a corolla of sprayed pigment can be observed. Eyelid melanoma quickly spreads to their mucous membrane, conjunctiva and orbital tissue. A characteristic feature of the tumor is that even with a light touch of a cotton swab or napkin to it, a dark pigment remains on their surface. Melanoma of the eyelids metastasizes to the lymph nodes, other areas of the skin, as well as to the lungs and liver.<







Add a comment