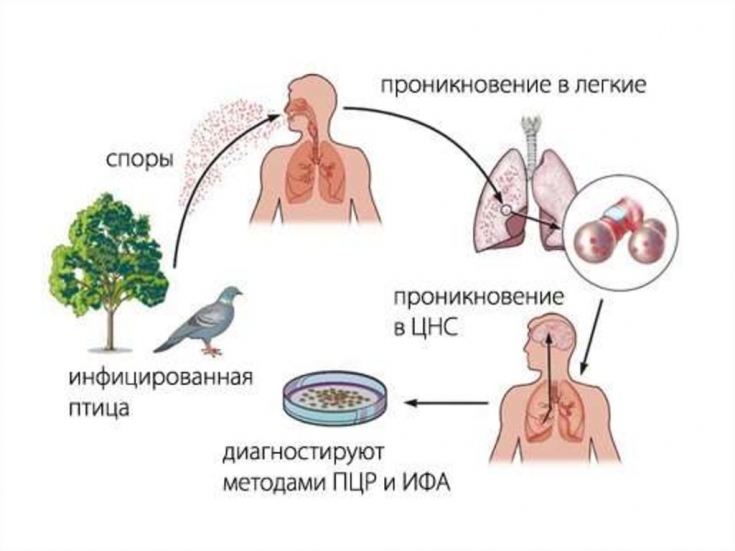
Ornithosis – infectious disease caused by the pathogen Chlamydia psittaci. The peculiarity of this infection is the presence of a specific source: birds.
More than 170 species of birds are known that can be a reservoir and source of ornithosis, but urban pigeons, crows, domestic (ducks, turkeys) and indoor (parrots, canaries) birds are the most important in the spread of infection.
About 20% of cases of community-acquired pneumonia have ornithosis etiology. Therefore physicians of any specialty should be aware of the symptoms and be alert to the diagnosis of psittacosis in such patients.
For more information about the etiology of ornithosis, the mechanism of infection transmission, typical clinical manifestations, as well as modern approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of the disease, read on estet-portal.com in this article.
Ornithosis: mechanisms of infection transmission and classification of the disease
The main transmission mechanism of psittacosis – aerosol. Approximately in 10% of cases fecal-oral mechanism of infection transmission is realized. People become infected with psittacosis through contact with birds.
BLOCKCODE In most cases, a patient with psittacosis does not pose a threat to those around him, although isolated cases of infection among nurses have been described.
The following forms of ornithosis are distinguished:
- Pneumatic;
- Flu-like;
- Typhoid;
- Meningeal.
In some cases, it is impossible to determine a specific form of ornithosis due to the presence of clinical polymorphism of manifestations. Quite often there is a combination of symptoms of different clinical forms in one episode of the disease.
Read more about each of the forms of ornithosis in the article.
Follow us on Telegram
Pneumonic and flu-like forms of psittacosis are most common
The incubation period ornithosis averages 7-10 days, but can last up to 30 days. In approximately 20% of cases, there is a prodromal period of infection, which is characterized by weakness, sleep disturbance, moderate arthralgias and lasts from 1 to 4 days. But more often the disease manifests acutely with symptoms such as fever, severe headache, myalgia, arthralgia.
In virtually every patient with psittacosis, regardless of the form of the disease, an enlarged liver and spleen can be palpated as early as the first week of infection.
Pneumonic and influenza-like forms account for about 85% of ornithosis cases.
In pneumonic form of ornithosis the main manifestation of the disease is lung damage. From the first days of infection, patients may complain of a dry cough. As the disease progresses, the intensity of the cough increases, mucous sputum appears, sometimes with blood impurities.
Painful breathing, shortness of breath and cyanosis may be observed. Objectively, during auscultation, weakened or hard breathing is heard, in some cases crepitus is present, but sometimes there may be no changes at all.
There are such types of pneumonia in ornithosis: interstitial, small-focal, large-focal and lobar.
For flu-like form of ornithosis , pronounced signs of intoxication, sore throat, hoarseness, dry cough are characteristic. At the same time, changes in the lungs are minimal, only an increase in the pulmonary pattern can be determined radiologically.
Read also: The flu season is coming: modern approaches to treatment and prevention.
Typhoid and meningeal forms of ornithosis: characteristic clinical manifestations
The typhoid-like form of ornithosis develops with the fecal-oral mechanism of infection, is characterized by hepatosplenomegaly, bradycardia, intoxication, and prolonged fever of a constant type. At the same time, there are usually no signs of damage to the respiratory system.
When detecting hepatosplenomegaly in a patient with pneumonia, the doctor should first of all think about ornithosis.
Ornithosis meningitis occurs in about 2% of cases. Characterized by meningeal syndrome, severe intoxication. When examining the cerebrospinal fluid, the cerebrospinal fluid is transparent, flows out under pressure. Moderate lymphocytic cytosis is determined: up to 500 cells / μl. Sanitation of the cerebrospinal fluid occurs approximately 5-6 weeks after the onset of the disease.
See also: Infectious mononucleosis: modern methods of diagnosing the disease.
Ornithosis: modern approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of the disease
Since most patients with psittacosis have pneumonia, the need for lung x-rays is obvious.

For specific diagnosis of ornithosis, the PCR method is used, which allows the diagnosis to be made already in the early stages of the disease.
Also widely used is RCC (complement fixation reaction) with ornithosis diagnosticum, but the possibility of obtaining false positive results due to cross-reaction with other chlamydial infections should be considered. Paired sera are examined, the titer is 1:64 and above.
To confirm the diagnosis of ornithosis, methods such as ELISA (enzymatic immunoassay) and RIF (immunofluorescence reaction) are also used. Blood is examined twice: at the beginning of the disease and after two weeks. A four-fold increase in the titer of specific antibodies confirms the diagnosis of ornithosis.
In the case of a mild form of the disease, hospitalization of the patient is not mandatory. The mode is determined by the severity of the patient's condition.
For etiotropic treatment of ornithosis, doxycycline at a dose of 0.1 mg 2 times a day for 10 days, or until the 10th day of normal temperature with a slow regression of the process in the lungs.
Alternative regimen: azithromycin 500 mg qd for 10 days.
Thus, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- Ornithosis – an infectious disease with a predominantly aerogenic mechanism of transmission;
- Birds are the main source of infection in psittacosis;
- For ornithosis, a combination of such symptoms as hepatosplenomegaly and pneumonia is typical, which is rarely determined in other infectious diseases;
- For the diagnosis of ornithosis, methods such as PCR, RSK, RIF, ELISA are used;
- The drug of choice for psittacosis is doxycycline.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Infectology" section. You may also be interested in: Types of influenza viruses and the main clinical symptoms of the disease.







Add a comment