Chronic hypertrophic rhinitis (rhinitis chronica hipertrophica) is a pathological condition of the nasal cavity in which hyperplasia of its mucous membrane occurs, often involving the periosteum and bone tissue of the turbinates, and a characteristic clinical picture is manifested. Chronic hypertrophic rhinitis can be diffuse and limited forms, mucosal hyperplasia most often occurs on the lower nasal concha, less often in the middle and in the places of localization of the cavernous tissue. In this regard, there are some peculiarities in the treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis.
Characteristic clinical picture of hypertrophic rhinitis
The clinical picture of hypertrophic rhinitis is quite characteristic: the disease has a long course, in which nasal breathing is constantly difficult, vasoconstrictor drops in the nose do not have a therapeutic effect, mucous or mucopurulent discharge from the nose, periodic headaches, dryness in mouth and in the oropharynx. Due to the fact that the patient's nose is constantly blocked, his voice timbre changes – there is a closed nasality. If hypertrophy of the posterior end of the lower shell occurs, tubo-otitis develops – ear inflammation. With hypertrophy of the anterior sections of the inferior turbinate, the opening of the lacrimal canal is compressed, which can provoke lacrimation, conjunctivitis and dacryocystitis.
Peculiarities of treatment of mild hypertrophic rhinitisThe treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis is surgical and involves the restoration of nasal breathing by reducing or completely removing hypertrophied areas of the nasal mucosa. The volume of surgical intervention depends on how pronounced the hypertrophic process is. With slight hypertrophy, if after lubrication of the nasal mucosa with a drug that has a vasoconstrictive effect, there is a minimal improvement in nasal breathing, it is recommended to use the most sparing surgical interventions, such as:
- cauterization of the nasal mucosa with chemicals (50% lapis, trichloroacetic acid, etc.);
- submucosal ultrasonic disintegration of the inferior turbinates;
- laser destruction.
If the hypertrophy of the mucous membrane is much more pronounced, and the bone base of the turbinates is involved in the process, while nasal breathing is significantly impaired, sparing operations will not be enough to restore the functions of the nose. In such cases, more extensive surgical interventions are recommended, in which partial removal of hypertrophied turbinates is performed. These operations are:
- sparing lower conchotomy;
- osteoconchotomy – submucosal removal of the bony margin of the inferior turbinate.
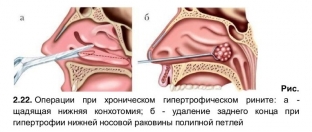
Conchotomy is one of the most effective treatments for hypertrophic rhinitis. During the operation, the patient is in a supine position, he is given local anesthesia of the nasal cavity. Next, a clamp is applied to the entire length of the shell for 1 minute, this is done in order to reduce bleeding during the operation. After removing the clamp or along it, if the clamp is decided to be left, the hypertrophied part of the shell is cut off with special surgical scissors, curved at an angle. At the same time, its hyperplastic posterior end is easily removed with a nasal loop. It is important to remember that the conchotomy should always be performed only sparingly, since the complete removal of the hypertrophied area can lead to atrophy of the nasal mucosa.
Endoscopic treatments for hypertrophic rhinitis
To date, good results in the treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis are also demonstrated by operations using optical systems. Endoscopes make it possible to perform all stages of complex surgical interventions in the nasal cavity under constant visual control, even in the posterior parts of the nasal cavity that are difficult to see.
 One of these endoscopic operations is submucosal vasotomy of the inferior turbinate, which allows to achieve permanent scarring of the cavernous tissue. During this operation, an incision is made at the anterior end of the inferior turbinate, through which soft tissues are separated from the upper surface of the nasal bone. Scarring of the cavernous tissue significantly increases the lumen of the nasal passages and thus is one of the highly effective methods of treating hypertrophic rhinitis.
One of these endoscopic operations is submucosal vasotomy of the inferior turbinate, which allows to achieve permanent scarring of the cavernous tissue. During this operation, an incision is made at the anterior end of the inferior turbinate, through which soft tissues are separated from the upper surface of the nasal bone. Scarring of the cavernous tissue significantly increases the lumen of the nasal passages and thus is one of the highly effective methods of treating hypertrophic rhinitis.







Add a comment