In most cases, bacterial acute cystitis is diagnosed in women of premenopausal age in the absence of anatomical and functional changes in the urinary tract and concomitant pathology.
Outpatient acute cystitis − most common reason for prescribing antibiotics and urology − one of the specialties with a high rate of outpatient antibiotic prescribing.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com what are approaches to the management and treatment of patients with acute infectious diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Acute bacterial cystitis
- Acute cystitis diagnosis
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
- Modern approaches to the treatment of infections of the genitourinary systemwe
Acute bacterial cystitis
Half of the women in the world have had at least one episode of acute cystitis during their lifetime. Approximately 1 in three women develops one episode of cystitis before age 24.
Follow us on Instagram!
Risk factors for developing acute cystitis include:
- sexual contact;
- use of spermicides;
- having a new sexual partner;
- genitourinary tract infections (UTIs) in childhood and mother;
- hypothermia.
, as in pyelonephritis, is the same and is represented by E. coli in 70-95% of cases, and in 5-10% - Staphylococcus saprophyticus. OtherEnterobacteriaceae are sometimes isolated, in particular P. mirabilis and Klebsiella spp. Diagnosing "acute cystitis"
The diagnosis is most likely to be based on a history ofurinary disorders
(dysuria, pollakiuria) andabsence of vaginal discharge. In older women, urinary symptoms are not necessarily due to cystitis.
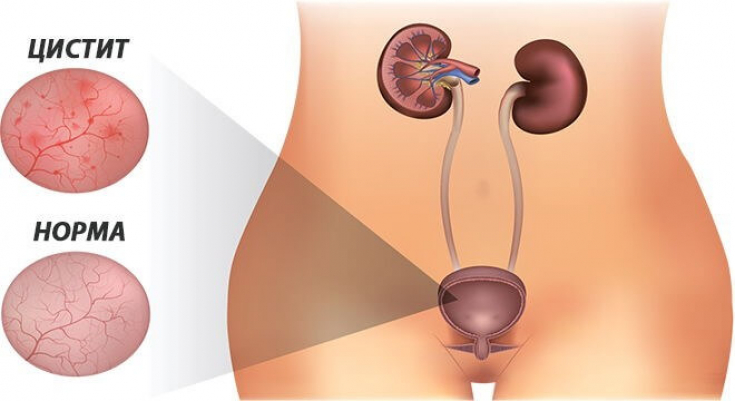
Bacterial culture is recommended
in the following situations:suspicion of acute pyelonephritis;
- Symptoms persist or reappear 2-4 weeks after treatment ends;
- atypical symptoms in female patients;
- pregnancy;
- Suspicion of UTI in male patients.
In women with symptoms of uncomplicated cystitis, bacterial titer of 103 cfu/ml
of uropathogens is considered diagnostically significant. If the patient hasatypical symptoms, as well as in case of ineffectivenessof the prescribed adequate antimicrobial therapy, an additional examination is necessary. Recurrent urinary tract infections
According to the American Urological Association (AUA) as well as the Canadian Urological Association (CUA), recurrent urinary tract infections are defined as culture-confirmed UTIs that are caused by bacterial pathogens and areassociated with acute symptoms
, in in particular dysuria associated with an increased frequency of urination, hematuria, and new cases or worsening urinary incontinence.
Recurrent urinary tract infections
− a very common pathology that occurs in women of any age, race and ethnic groups, regardless of socioeconomic status or educational level.In general, symptomatic acute bacterial cystitis
occurs in approximately 60% of women during their lifetime. About 20-40% of women who have had one episode of cystitis are more likely to have an additional episode, 25-50% of them experience multiple recurrent episodesModern approaches to the treatment of infections of the genitourinary systemAccording to modern foreign and domestic guidelines for the treatment of uncomplicated infections of the genitourinary system (and they are mostly uncomplicated), in adults
it is antibiotic therapy
that is indicated, and a specific drug is chosen empirically. The therapeutic potential of many antibiotics is now almost exhausted, and the doctor is faced with the question of choosingan alternative way to resist uroinfection. Modern original herbal medicines
based on the latest technologies often effectively replace antibiotics or perfectly complement the therapeutic treatment regimen.Modern possibilities and features of clinical urinalysis
Modern research has shown that in many cases the microbiome present in uncomplicated genitourinary infections may also be present in healthy people and does not lead to the development of the disease
and the appearance of clinical symptoms. In addition, its protective effect in the prevention of the development of superinfection has been proven.Taking into account the data of a number of studies, it can be found that the routine use of antibiotic therapy in the treatment of UTI does not always lead to a positive result, especially in the treatment of recurrent pathologies.
Kidney pathology in heart failureModern concepts are changing the paradigm of antibiotic therapy and offering more balanced treatment approaches with multipurpose herbal therapy
.Watch the latest news in the world of medicine on our
YouTube-channel:







Add a comment