Inflammatory diseases of the internal female genital organs is one of the most widespread pathologies in modern gynecology. The penetration of an infectious agent into the pelvic cavity is possible in different ways, and factors such as stress, hormonal imbalances, a general weakening of the body's defense reactions and other important points create favorable conditions for the development of the inflammatory process. With timely diagnosis and effective treatment, inflammatory processes are quite easily and quickly stopped. But quite often, inflammation of the female reproductive organs leads to such complications in gynecology as pelvioperitonitis and parametritis.
Complications in gynecology: causes, main symptoms and diagnostic methods
Pelvioperitonitis and parametritis are complications in gynecology that occur when the infectious process spreads from the reproductive organs to other structures of the small pelvis. With pelvioperitonitis, the peritoneum is affected, with parametritis - the fiber surrounding the uterus. Such conditions often occur even in a hospital, which may be due to the influence of many factors. If such complications occur in gynecology, effective therapy should be started immediately, since the aggravation of the inflammatory process threatens the development of sepsis and a possible fatal outcome for the patient.
Complications in gynecology:
- causes of pelvioperitonitis and parametritis as complications in gynecology;
- clinical picture of pelvioperitonitis: main symptoms;
- what symptoms will indicate the development of parametritis;
- Basic methods for diagnosing complications in gynecology.
Causes of pelvioperitonitis and parametritis as complications in gynecology
The development of such complications in gynecology as pelvioperitonitis and parametritis is due to the following factors:
- pelvioperitonitis - inflammation of the pelvic peritoneum, occurs secondarily as a result of the penetration of infectious agents from the uterus or its appendages into the peritoneum. As a result of the inflammatory process, exudate is formed, according to the type of which two main types of pelvioperitonitis are distinguished: serous-fibrinous and purulent.
- parametritis - inflammation of the tissue that surrounds the uterus. Often this pathological condition occurs when the infection spreads after childbirth, abortion, curettage or surgery on the uterus, and sometimes as a result of improper use of intrauterine contraceptives. The infectious agent penetrates the parametric tissue through the lymphogenous route.
Clinical picture of pelvioperitonitis: main symptoms
Pelvioperitonitis begins acutely. In the clinical picture of this complication in gynecology, pain syndrome comes to the fore. Sharp pains occur in the lower abdomen, accompanied by an increase in body temperature to febrile values, chills, nausea and vomiting, defecation disorders in the form of loose stools. The patient's abdomen is swollen, painful on palpation in the lower sections, but takes part in the act of breathing, which plays an important role in the differential diagnosis of pelvioperitonitis with inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity. Positive symptoms of peritoneal irritation and tension of the anterior abdominal wall may be noted.
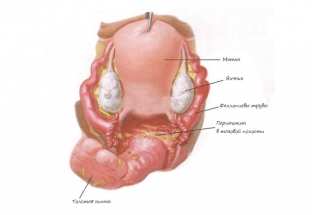
What symptoms will indicate the development of parametritis
The clinical picture of parametritis is primarily due to the inflammatory process and intoxication of the body. There is an increase in temperature, headache, general deterioration of well-being, nausea, dry mouth and pain in the lower abdomen. In the event that infiltration of the parametrium leads to compression of the ureter on the side of the lesion, there may be a violation of the flow of urine through the urinary tract and hydronephrosis may occur. With suppuration of parametric fiber and the development of purulent parametritis, the patient develops chills, fever, and increased symptoms of intoxication. In some cases, at the site of inflammation at the stage of resolution of the inflammatory process, fibrous tissue may form, displacing the uterus. Purulent parametritis may resolve with discharge of pus into the rectum, bladder, or abdomen.
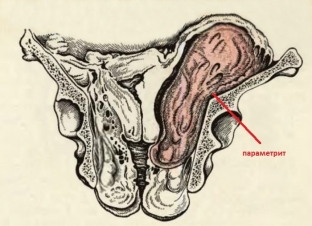
Basic methods for diagnosing complications in gynecology
Diagnosis of complications in gynecology is based on anamnesis data, as well as the results of laboratory and instrumental research methods. In both cases, signs of inflammation are noted in the general blood test: leukocytosis with a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left and an increase in ESR. Palpation with pelvioperitonitis may fail due to pain, or smoothness of the posterior fornix of the vagina is noted. With parametritis, palpation can determine the smoothness of the lateral fornix of the vagina, a dense immovable infiltrate at the site of the lesion of the parametrium. In case of development of fibrinous changes in the parametrial area, a cord is palpated, the uterus is displaced towards the lesion. Ultrasound examination helps to determine the condition of the uterus and appendages, to identify free fluid in the pelvic cavity.






Add a comment