There can be many processes in the nasal cavity that lead to impaired nasal breathing. These pathological conditions include synechia of the nasal cavity. Synechia can be congenital or acquired. Congenital synechias are formed during fetal development with violations of the formation of the facial skull. Synechias of an acquired nature appear against the background of changes in the nasal cavity of a cicatricial or granulation nature.
Causes of formation of synechia in the nasal cavity
Congenital syphilis is a common cause of congenital synechia. Such synechiae are localized in the posterior parts of the nasal cavity and can be combined with choanal atresia. Changes in the nasal cavity of an acquired nature occur after nasal trauma, chemical and thermal burns, therapeutic coagulations (with bleeding from the nose), after surgical interventions in the nasal cavity (correction of choanal atresia, removal of neoplasms and polyps, operations on nasal conchas). Synechia also appears after inflammatory diseases of an infectious nature (diphtheria, scarlet fever, scleroma, systemic lupus erythematosus, typhus, syphilis).
What can be synechia in the nasal cavity? Classification of synechia
Synechiae of the nasal cavity are divided according to the type of tissue and the place of their localization. Synechia can be from connective tissue, bone and cartilage. More often synechia are represented by connective tissue. Cartilage and bone synechia are congenital.
According to the localization of synechia, there can be anterior, middle and posterior. Anterior synechiae are located in the vestibule of the nasal cavity and lead to occlusion of the nostrils. Middle synechia are localized between the turbinates and the nasal septum. The posterior synechiae are located in the region of the nasal choanae and lead to choanal occlusion. This disrupts the flow of air from the nasal cavity into the pharynx.
What are the symptoms of nasal adhesions?
Synechia in the nasal cavity can be either unilateral or bilateral. Minor synechia usually does not show clinical symptoms and is not detected for a long time. Those synechia that block the lumen of the nasal cavity lead to a violation of air circulation during the act of breathing. The air inhaled through the nostrils normally enters through the choanae into the pharynx. In the nose, the air is warmed and cleaned by the ciliated epithelium. In the presence of synechia, this does not happen, there is a nasal voice.
Patients at the appointment with an otolaryngologist complain of constant nasal congestion, the absence or significant deterioration of the sense of smell and the inability to blow their nose. Synechia may be accompanied by permanent crusting in the nasal cavity.
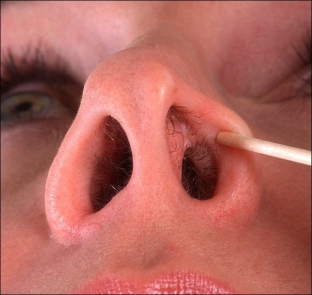
What is the risk of nasal adhesion formation?
When blocking the nasal passages in the nasal cavity with synechia, the risk of inflammatory diseases of the paranasal sinuses and upper respiratory tract increases due to the influx of cold, uncleaned air and impaired ventilation. Such breathing can also provoke the development of otitis media and eustachitis. In children, congenital synechias are manifested immediately after birth by the absence of a normal cry, cyanosis of the skin, and violations of the sucking process. The child refuses the breast, which leads to malnutrition.
At the first signs of a nasal breathing problem, it is important not to postpone a visit to the otolaryngologist and check the nasal cavity for the presence of a cause of nasal breathing difficulties.







Add a comment