When a person's visual acuity decreases even when wearing glasses or lenses, there is a suspicion that he has keratoconus. Keratoconus is called dystrophic processes in the cornea of the eye, which lead to its conical deformation and a progressive decrease in vision. In this case, the image of objects is distorted, areolas and glare appear, double vision (monocular diplopia) and clouding of the cornea. The frequency of detection of keratoconus in ophthalmology ranges from 0.01-0.6%. The disease equally affects people of both sexes and different races. What are the causes and mechanism of development of keratoconus?
What causes keratoconus?
The first signs of keratoconus are detected as early as adolescence or early adolescence. Sometimes keratoconus is detected after 25 years. The progression of the disease leads to a change in the structure and shape of the cornea, it becomes thinned and deformed like a cone. These changes lead to the development of myopia and irregular astigmatism. Keratoconus can be either bilateral or asymmetric.
The question of the causes of keratoconus development remains debatable to this day. There are several hypotheses – endocrine, immunological, hereditary and metabolic. Modern opinions about the causes of keratoconus are more inclined towards the hereditary-metabolic theory. This theory connects the development of keratoconus with hereditary fermentopathy, which is often activated during the restructuring of the endocrine system.
Against the background of the spread of the use of excimer laser vision correction, the frequency of iatrogenic keratoectasias has increased, which leads to the subsequent development of keratoconus.
Studies have been conducted in which a correlation has been established between the development of keratoconus and the following diseases:
- eczema;
- microtraumas;
- bronchial asthma;
- atopic dermatitis;
- hay fever;
- Addison's disease;
- taking corticosteroids;
- pigmentary retinopathy;
- viral or traumatic conjunctivitis;
- Leber's congenital amaurosis;
- Down syndrome and Marfan syndrome.
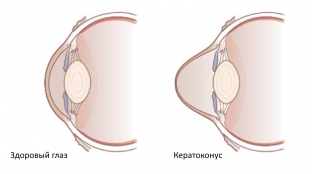
What processes occur in the cornea in keratoconus? Mechanism of development of keratoconus
In the presence of keratoconus, many biochemical changes are detected in the cornea, the concentration of keratin sulfate decreases, the collagen content decreases, the number of non-protein structures increases, and the total protein content simultaneously decreases. Against the background of insufficiency of inhibitors of proteinases and enzymes, gelatinolytic and collagenolytic activity increases. Destructive aldehydes and hieroxynitrites begin to form in the cornea against the background of a decrease in the antioxidant system.
It is believed that the degenerative process of the cornea begins in the basal cells of the corneal epithelium or at the site of its transition to the stroma. Due to the weakness of the corneal epithelium and stroma, the elasticity of the cornea decreases, and its rigidity increases. This is accompanied by persistent stretching and the presence of a cone-shaped deformation. This is how keratoconus develops.
Keratoconus classification. Corneal changes at different stages of keratoconus
Based on the mechanism of development, primary and secondary keratoconus are distinguished. Secondary in most cases provoked by iatrogenic causes. Most often, keratoconus is bilateral. By the nature of the flow, it can be progressive and stationary. A separate form is acute keratoconus.
There are 4 stages during keratoconus:
- 1 stage – characterized by the development of irregular astigmatism, corrected by cylindrical lenses. At this stage, visual acuity is in the range of 1.0-0.5.
- Stage 2 – astigmatism corrected, but more pronounced. Vision within 0.4-0.1.
- Stage 3 – at this stage, the cornea becomes thinned and protrudes, and visual acuity is 0.12-0.02. However, only hard contact lenses can correct keratoconus.
- 4 stage – the cornea becomes cloudy, conical deformation is noticeably pronounced, while visual acuity is 0.02-0.01, which cannot be corrected.
Clinical symptoms and manifestations of keratoconus, as well as diagnostic methods and aspects of treatment, read in our next article.







Add a comment