Ascites is the accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity. This pathology is one of the most common symptoms that occur in the clinic of internal medicine. This is due to the fact that the causes of ascites are very diverse, they are related not only to internal medicine, but also to surgery and oncology. As a rule, the development of ascites indicates the presence of a serious condition of the patient, since in most cases it is a manifestation of the disease in an advanced or irreversible stage. Despite this, the correct and timely identification of the cause of ascites can significantly prolong the life of patients and improve its quality.
Why does fluid collect in the abdomen? Causes of ascites
In most cases, ascites is due to the development of a diagnosed disease. More often it is liver cirrhosis (60-65%) and tumor metastases in the abdominal cavity. The main causes are conditionally divided into common, less common and rare.
Common causes of ascites are cirrhosis of the liver and carcinomatosis of the abdominal cavity. Less common causes are heart failure and nephrotic syndrome.
Rare causes of ascites:
- portal vein thrombosis;
- Budd-Chiari syndrome;
- pancreatitis;
- constrictive pericarditis;
- myxedema;
- Meigs syndrome;
- peritoneal mesothelioma;
- Meigs syndrome;
- biliary ascites;
- pseudomyxoma;
- intestinal lymphangiectasia;
- Whiple's disease.
What is included in the diagnostic examination of a patient with ascites?
Ascites is manifested by an increase in the volume of the abdomen, flatulence and heaviness in the abdomen. The initial examination of a patient with cirrhosis should include an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, a physical examination with the detection of percussion over some places in the abdominal cavity, as well as a symptom of fluctuation, which is detected when the amount of fluid is at least 1000 ml.
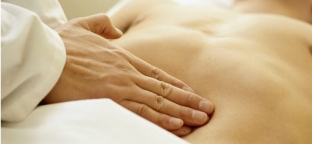
It is also necessary to carry out the procedure for taking ascitic fluid for examination. The presence of bacterial growth in fluid samples, where the level of leukocytes exceeds 250 cells per mm3, lactate dehydrogenase is more than 225 IU/l, glucose is less than 50 mg/dl, total protein is less than 1 g/dl, and multiple microorganisms are detected, indicates the development of secondary bacterial peritonitis.
What are the treatments for ascites?
Treatment of ascites consists of diuretic therapy, non-diuretic therapy represented by hepatoprotectors, and surgical manipulation - paracentesis.
Diuretic therapy. Before starting treatment with diuretics, it is important to assess the gradient of albumin in serum or ascitic fluid. Patients with a small albumin gradient respond poorly to diuretic therapy unless nephrotic syndrome is present.
The main goal of diuretic therapy in ascites is to increase the excretion of sodium in the urine to more than 78 mmol/day.
Effectiveness of using a new class of preparations – aquaretics is currently being studied. These are V2 receptor antagonists of antidiuretic hormone or kappa agonists of opioid receptors.
Aspects of diuretic therapy in ascites
Diuretic therapy consists of spironolactone 100 mg daily plus furosemide 40 mg. If the effect does not occur and body weight does not decrease for several days, the dose of both drugs is increased by 2 times. The maximum daily dose of spironolactone is 400 mg, and furosemide 160 mg. Monotherapy may be effective only in the case of a small amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
Cancellation of diuretic therapy for ascites should be based on the following indications:
- detection of metabolic acidosis and hyperkalemia;
- serum creatinine concentration greater than 2 mg/dl;
- serum sodium concentration less than 120 mmol/l despite fluid restriction;
- presence of side effects of diuretics;
- development of encephalopathy.
In cases where the tension provoked by ascites leads to the appearance of severe clinical symptoms, paracentesis is performed with the removal of a large amount of fluid under hemodynamic control.
Paracentesis is not a first-line treatment and is reserved for patients with tense ascites.






Add a comment