Darier's disease (follicular keratosis) is a hereditary disease that has variable penetration, that is, a violation of keratinization. Darier's disease is characterized by rashes in the form of keratotic papules over the entire surface of the skin, as well as dystrophy of the nails. Typically, lesions first appear in patients between the ages of 8 and 15 years of age and rarely before the age of 5 years. Sometimes the disease manifests itself in adults. How Darya's disease manifests itself, and with what pathologies it is necessary to make a differential diagnosis, read in our article.
Causes of Darya's illness. Histological changes in tissue
Until the end, the cause of Darya's illness has not been clarified. An autosomal dominant cause of its transmission suggests a genetic defect in which the primary abnormality is premature keratinization. The disease is characterized by typical histological changes, which are manifested by focal acantholytic dyskeratosis.
Major histological changes in Darier disease:
- Small clusters of cells around lacunae that are not connected to surrounding cells. The cells have dark nuclei and are large, surrounded by bright cytoplasm. They are located in the upper part of the malpighian layer.
- Against the background of suprabasal acantholysis, suprabasal lacunae form.
- There are villi that form from the papillae of the dermis, covered by a single layer of basal keratinocytes.
- Presence of small, granular-shaped dyskeratic cells surrounded by inconspicuous cytoplasm.
- Papillomatosis, acantholysis and hyperkeratosis.
- Chronic inflammatory infiltrate in the dermis.
Clinical presentation and appearance of a patient with Darier's disease
Darier's disease is manifested by the presence of dense keratotic fatty papules that are flesh or brownish in color. They may coalesce into papillomatous masses or large plaques. More often rashes appear on the face, chest, neck, back and in the groin. On the back of the hands and on the feet, the rash resembles Hopf's acrokeratosis verruciformis. Similar changes can be found in close relatives of patients who are absolutely healthy. On the mucous membranes, the lesions are white papules with a depression in the center, more often on the mucous membrane of the soft palate and cheeks.
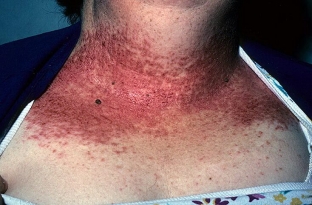
Anomaly of the nails is also characteristic of Darier's disease. It is manifested by the presence of longitudinal white or red lines that run from the base of the nail to the free edge.
Nails are brittle, a V-shaped notch is formed on the free edge of the nail. The nail plates split, which is accompanied by soreness. Fragments of subungual keratosis are present. How the patient's well-being changes with Darier's disease, estet-portal.com knows. Pathology does not affect the general well-being of the patient, manifesting itself only externally. The course of the disease is chronic without remissions. There is a deterioration in the summer months with heavy sweating and ultraviolet exposure.
Differential diagnosis and treatment of Darier's disease
To establish the diagnosis, it is mandatory to conduct a biopsy, which makes it possible to identify focal acantholytic dyskeratosis. Both direct and indirect immunofluorescence results are negative.
Differential diagnosis is with benign familial pemphigus, with acanthosis nigricans and papillomatosis.
There is currently no causal treatment for Darier's disease. Only a third of patients notice an improvement in the condition of their skin and nails with age. It is recommended to avoid overheating and wear cotton clothing.
Thus, Darier's disease is a pathology that is a cosmetic effect, while not worsening the patient's well-being. There is no effective cure for the disease.






Add a comment