Any surgical intervention has a kind of prologue and epilogue – preoperative and postoperative period. In aesthetic surgery, as in any other surgical direction, the success of the operation depends not only on the tactics of the surgeon and the quality of the work performed, but also on the correct preparation of the patient for the operation, as well as on the correct management of it in the postoperative period. The latter has some features in plastic surgery, as patients often want to see the final result as soon as possible, which can easily be spoiled if the recommendations of a specialist are not followed. On estet-portal.com read about the features of the postoperative period in plastic surgery.
Peculiarities of postoperative management in plastic surgery
Each surgical operation is associated with damage to healthy tissues, and the postoperative period – This is the time it takes for the surgical wound to heal completely. In plastic surgery, this period of time plays a particularly important role, since it is necessary to achieve the maximum aesthetic effect, and the wound healing process must be as comfortable as possible for the patient.
When planning the postoperative period, the surgeon must answer several fundamentally important questions: when to remove skin sutures for the patient, whether to immobilize the operated area, how to additionally act on the wound for maximum protection?
The correctness of the postoperative period directly affects how good the result of the operation will be.
Postoperative period in plastic surgery:
• timing of suture removal in the postoperative period;
• immobilization of wound tissues in the postoperative period;
• use of fixative coatings in the postoperative period.
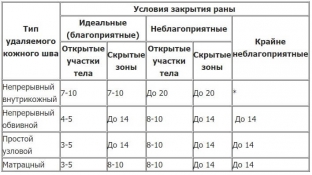
Terms of suture removal in the postoperative period
The removal of sutures is one of the most important moments in the postoperative period. The optimal timing of suture removal is determined by many factors, the most important of which are the type of suture, the location of the wound and the conditions for its closure:
• a continuous intradermal suture that does not injure the skin surface is removed after 7-10 days, subject to minimal tissue tension;
• the continuous suture is removed as soon as possible, as it can compress the surface of the skin along the edges of the wound;
• mattress and simple interrupted sutures are used most often in hidden areas and are removed within one to two weeks after surgery.
Wound tissue immobilization in the postoperative period
Immobilization of the operated area plays an important role, since rest and the absence of any movements in the wound area create optimal conditions for its healing and, to some extent, have an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. Under conditions of rest in the operated area, a scar of a small volume is formed, which has more favorable characteristics. However, immobilization must be carried out within the limb, while in other anatomical zones it is not carried out for the following reasons:
• immobilization is almost impossible on the neck, abdomen, back, face and pelvis;
• the use of bandages necessary for immobilization can cause significant discomfort to the patient and negatively affect his ability to work.
Therefore, in most cases, immobilization is carried out when a soft tissue wound is combined with damage to bones, tendons, joints and other important anatomical structures.
Position of fixative coverings in the postoperative period
It is important to fix the edges of a healing wound in the postoperative period in cases where complex wounds are closed, which have areas that retain great physical exertion. In these places, fixation is performed using strips of an adhesive patch that can well keep this area from stretching for 2-4 weeks. Due to this fixation, the expansion of the scar that is being formed is prevented. The use of the patch should be discontinued when signs of irritation appear on the skin.
Compliance with all these conditions in the postoperative period can significantly improve the results of the operation and prevent the formation of pronounced scars.
Special gels and silicone coatings can be used to further improve wound healing.







Add a comment