Endocervicosis (pseudo-erosion) – ectopia of epithelium lining canal of the cervix, on the vaginal surface. In most cases, the pathology proceeds without pronounced clinical symptoms. The blurring of the symptomatic picture leads to a chronic process, which sharply worsens the prognosis of the disease, increasing the risk of degeneration into an oncological process. Depending on the cause, endocervicosis is dangerous for malignant degeneration of cervical cells, frequent bacterial infections. Therefore, patients with such a diagnosis are subject to mandatory examination, observation and therapy. On estet-portal.com we will get acquainted with the causes of the development of this pathology, and effective methods of treatment of endocervicosis.
- Endocervicosis: classification and causes of development
- Clinical presentation of endocervicosis
- Diagnostic methods and principles of endocervico therapyfor
Endocervicosis: classification and causes of development
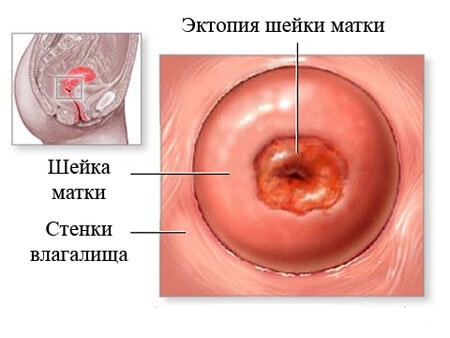
The inner lining of the cervix is represented by two types of epithelial cover. The part adjacent to the vulva is lined with squamous epithelium, the inner part, located in the lower part of the uterus, is covered with glandular epithelial cells that produce mucous discharge. Endocervicosis develops against the background of pathological replacement of secretory cells by squamous epithelial structures.
There are several forms of endocervicosis:
- By cause: congenital and acquired.
- According to pathophysiological changes in the epithelial structure of the cervix: simple endocervicosis, proliferating and epidermizing;
- According to the clinical course: simple and complicated.
Acquired endocervicosis is associated with the following factors:The etiology of the disease is still controversial. Congenital endocervicosis occurs at the stage of intrauterine development, against the background of impaired differentiation of the epithelial cover. This form of pathology proceeds without symptoms and resolves without outside intervention by adulthood.
- mechanical damage to the mucous membrane during medical manipulations, specific sexual games;
- chemical burn when douching with concentrated solutions, using non-traditional methods of contraception;
- tears during delivery;
- infection with pathogenic flora;
- hormonal disorders;
- starting sexual activity at an early age.
The pathogenesis of endocervicosis has not been fully elucidated. Pathological proliferation of the epithelium is associated with a violation of the differentiation of reserve cells located under the cylindrical epithelium of the membrane of the cervical canal and producing the secretion of glands and intended for the regeneration of damaged cells of the cervix.
Metroendometritis: etiology, diagnosis, treatmente
Clinical presentation of endocervicosis
The disease can develop over time and not disturb the patient for years. Often the disease is provoked by inflammatory pathologies, but at the same time, endocervicosis serves as a predisposing factor for the development of viral and bacterial processes. Without the addition of secondary diseases, pseudo-erosion in many cases is asymptomatic, although when collecting an anamnesis, women sometimes complain of:
- occasional discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- small bloody or brownish discharge that continues after the end of menstruation or appears at ovulation;
- Profuse vaginal discharge in the middle of the menstrual cycle.
If another pathology occurs, the symptoms of endocervicosis are masked against the background of clinical signs of the underlying disease. Often, lesions of the cervix are detected during a routine examination or when registering in the early stages of pregnancy.
Read the most interesting articles in Telegram!
Methods of diagnosis and principles of therapy for endocervicosis
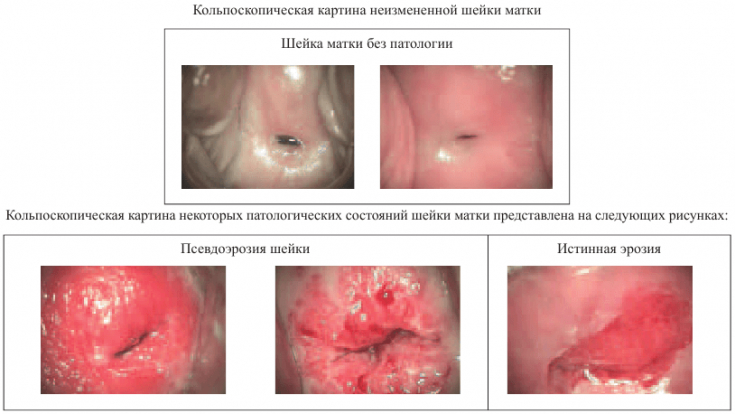
To detect endocervicosis, colposcopy is performed. On examination, areas of the altered epithelial membrane are visible. If there are lesions suspected of atypia, a targeted biopsy is taken.
At the same time, a section of the mucous membrane and underlying connective tissue is captured.
Additionally, analyzes are prescribed using the PCR method for the diagnosis of latent infections.
An integral part of a comprehensive examination of a patient with endocervicosis is a study for a high risk of developing cervical cancer human papillomavirus.
After sanitation of the vaginal cavity and cervix and relief of the inflammatory process, endocervicosis is removed using one of the following methods:
- cryotherapy;
- laser or radio wave exposure;
- thermocoagulation.
If human papillomavirus is detected, consultation with an immunologist and appropriate antiviral therapy is mandatory.
Patients with a highly oncogenic type of human papillomavirus after elimination of endocervicosis need regular (at least 1 time in 6 months) examination by a gynecologist.
You may also be interested in: Atrophic colpitis: hormone replacement therapy of the disease







Add a comment