When it comes to diseases of the urinary system, the first thing that comes to mind – these are various infectious and inflammatory processes of the kidneys, bladder and urinary tract. However, urology – it is a science that deals with various kinds of pathologies of this system. And in their practice, doctors often have to deal with non-specific diseases, which can be quite difficult to determine. One such disease is Ormond's disease or retroperitoneal fibrosis. This pathology is manifested by disturbances in the functioning of the organs of the urinary system, and information about the methods of its diagnosis and treatment is shared by estet-portal.com.
Clinical presentation and methods of treatment of Ormond's disease
Ormond's disease – This is a nonspecific fibrosclerotic process that develops in the connective tissue areas of the retroperitoneal tissue. This disease is quite rare: about 1 case per 200,000 predominantly in men aged 30 to 60 years. The causes of the disease have not been reliably studied to date. Retroperitoneal fibrosis is thought to be idiopathic in most cases, but chronic surrounding tissue disease, infection, or drug toxicity can also cause it.
Ormond's Disease:
- clinical presentation of Ormond's disease: characteristic symptoms;
- instrumental methods for diagnosing Ormond's disease;
- Conservative and surgical treatments for Ormond's disease.
Clinical presentation of Ormond's disease: characteristic symptoms
In the clinical picture of Ormond's disease, symptoms of urinary tract lesions attract attention, since in this pathology the ureter is compressed and ureterohydronephrosis develops. The characteristic symptoms of pathology include the appearance of dull, paroxysmal pain in the lumbar region, fatigue, increased blood pressure. In the case of the development of a bilateral process and its progression, symptoms of renal failure occur. Depending on the stage of the disease, other specific symptoms associated with ureteral obstruction may occur. A characteristic feature of Ormond's disease is a gradual clinical course with poor symptoms.
In the clinical picture of Ormond's disease, the symptoms of urinary tract lesions attract attention, since in this pathology the ureter is compressed and ureterohydronephrosis develops.
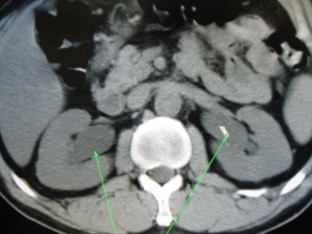
Instrumental methods for diagnosing Ormond's disease
The following instrumental methods are used to diagnose Ormond's disease:
- excretory urography: allows you to determine the expansion of the pyelocaliceal system of the kidney and ureter to the level of its compression, the displacement of the ureter towards the spine;
- antegrade pyeloureterography is performed if excretory urography is contraindicated or renal function is severely reduced;
- radionuclide diagnostic methods allow to determine the anatomical and functional state of the kidneys;
- Computer and magnetic resonance imaging makes it possible to clarify the boundaries of the lesion.
Conservative and surgical treatment of Ormond's disease
Treatment of patients with Ormond's disease depends on the localization of the pathological process, its distribution, the degree of violation of the passage of urine, the condition of the kidneys and upper urinary tract, the activity of the urinary infection. Conservative methods of treatment are recommended in the early stages of the disease and include the appointment of glucocorticosteroids and drugs that promote resorption. But most patients require surgical treatment: ureterolithiasis with relocation of the ureter into the abdominal cavity, resection of the ureter with an end-to-end anastomosis, replacement of the ureter with a segment of the small intestine, or kidney autotransplantation. After surgery, the prognosis for patients is favorable, but a recurrence of the disease is possible.







Add a comment