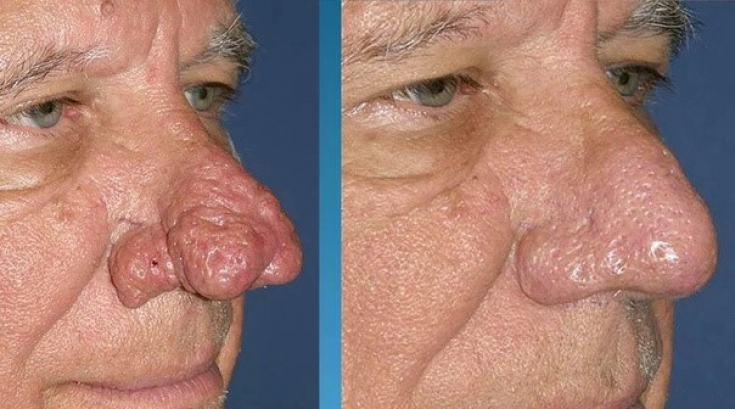
Rhinophyma is the most severe and late stage of rosacea, characterized by severe deformation of the soft tissues of the nose due to hyperplasia sebaceous glands and connective tissue. This deformity needs to be corrected and treated, as the thickening of the nasal alae can block the external nasal valves and significantly affect the patient's quality of life. Rhinophyma is more common in men older than 50: there is a hypothesis about the role of androgens in the development of pathology. Diagnosis is based on clinical findings, however biopsy is also required for
- Pathophysiological and histological aspects of rhinophyma
- Classification of clinical forms of rhinophyma
- Tactics of managing the final stage of rosacea Pathophysiological and histological aspects of rhinophyma
While the underlying bone structure remains unchanged, the soft tissues of the nose hypertrophy with a predominant expansion of the nasal tip and wings, creating a risk of potential
obstruction
of the nasal respiratory ways.
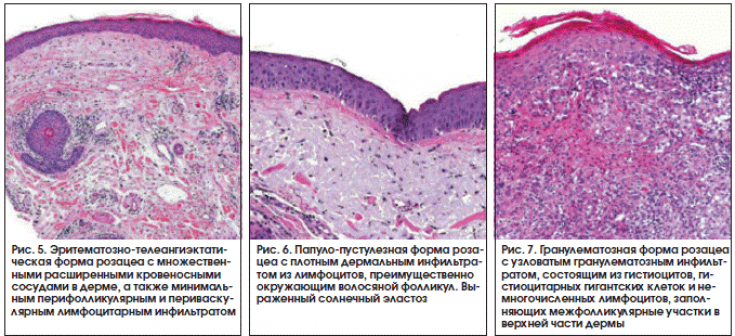
During histopathological examination, hypertrophied sebaceous glands and a thickened dermis containing fibrovascular myxoid stroma and lymphatic cells are observed.
In cases of
severe
rhinophyma, the sebaceous glands are destroyed as a result of
edema and fibrosis
, resulting in the histological xxxx>picture of lymphedema. Classification of clinical forms of rhinophyma Rhinophyma is diagnosed clinically according to the basic criteria
: erythema, telangiectasia, and skin thickening in the nasal area.
The
lower two-thirds of the nose are most commonly affected.
Follow us on Instagram!
Severity and subtypes of rhinophyma are classified differently. There are four clinical variants
: glandular, fibrous, fibroangiomatous and actinic.
Read also: Rules for skin care for rosacea
Glandular rhinophyma, is primarily due to hyperplasia of the sebaceous glands. Fibrous
rhinophyma, in turn, occurs due to hyperplasia of the connective tissue.
Fibroangiomatous rhinophyma includes fibrosis, telangiectasias, and inflammatory lesions. In actinic rhinophyma, elastic fibers grow into nodular masses, causing deformation of the soft tissues.
Starting with
early vascular changes, progressing rhinophyma:
- Moderate diffuse increase,
- Early localized tumor,
- Extensive diffuse increase,
- Extensive diffuse enlargement of a localized tumor.
Follow us on
!
This pathology can also be classified into minor, moderate or major rhinophyma. According to this classification:
Minor: when telangiectasias are present with slight thickening of the skin.
- Moderate: if skin thickening is accompanied by lobes.
- Large: when there are prominent nodules and nasal hypertrophy.
- Management of the final stage of rosacea The foremost goal of surgical intervention
in patients with rhinophyma - is to reduce the volume of hypertrophied sebaceous glands and
restore the contour of the nose
. Secondly, surgical methods are also used to restore nasal epithelialization.
Read also: Adult Rosacea Treatment: Dr. Rachel Eckel's Program
Surgical options:
Full-thickness resection with flap or graft reconstruction
: This approach has the advantage of
immediate
- wound coverage, avoids excessive thermal injury, and eliminates the
- risk of recurrence in connection with the complete removal of pathological tissues. The main types of pathological reddening of the skin of the face
Partial tissue removal: This method preserves the
pilosebaceous complex.
- When only superficial tissues are removed and underlying adnexal structures are preserved,
- re-epithelialization occurs by secondary intention. The disadvantage of this method is the risk of scarring due to hemostasis for a clear field of view.Using a heated Shaw scalpel for partial excision may reduce the severe bleeding seen with a cold scalpel excision, however risks with a hot scalpel excision include scarring, burns, and the possibility of the alae falling off.
Dermabrasion
is used as a
auxiliary
- technique after large volume removal of tissue to provide precise
- contouring of the nose.
TGFb1 and TGFb2
are thought to play a role in the skin thickening seen in rhinophyma. The scientists investigated the in vitro application of the antiestrogen drug "
tamoxifen"
- on TGFb2 producing and secreting fibroblasts in cultured skin with rhinophyma. The results showed both decreased function of
- fibroblasts and suppression of TGFb2. Algorithm for the rehabilitation of patients after rosacea treatment
Rhinophyma is the most severe, last stage of rosacea. Chronic inflammatory lesions
of the skin lead to deformation of the soft tissues and, as a result, deterioration of the patient's appearance. In less severe stages of
rosacea, dermatologists can optimize the treatment of this condition. Upon reaching the point of "no return" surgical and mechanical techniques will be the first-line treatment option. More interesting stuff on our YouTube channel:







Add a comment