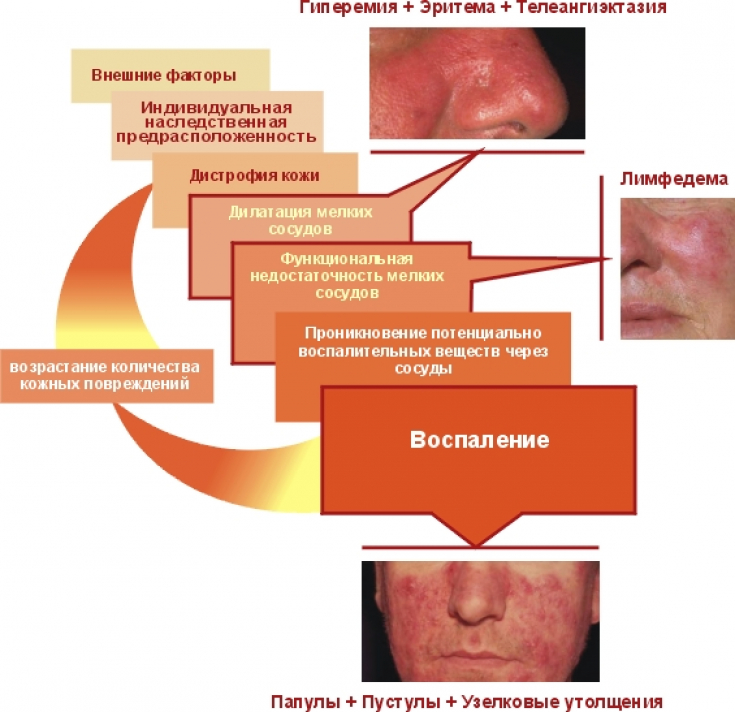
Rosacea – this is a chronic polyetiological progressive disease characterized by the development of centrofascial erythema, telangiectasias, papules and pustules.
The main mechanism of rosacea formation is pathological vascular reactivity, which develops under the influence of vasoactive peptides, circulating immune complexes and other endogenous irritants.
In this article on estet-portal.com you can get acquainted with the most up-to-date ideas concerning pathophysiological aspects of the development of rosacea.
Environmental factors contributing to exacerbation of rosacea symptoms
The clinical manifestations of rosacea are exacerbated by the so-called triggers – environmental factors that contribute to an increase in the severity of the symptoms of the disease.
These include:
1. UV;
2. Long exposure to very low or high ambient temperatures;
3. Sharp temperature fluctuations in the external environment;
4. Consumption of hot drinks, spicy food, alcohol;
5. Mechanical damage to the skin;
6. Psycho-emotional or physical overstrain.
The above environmental factors contribute to the initiation of skin inflammation processes through the activation of Toll-like keratinocyte receptors (translated from English "Toll" - "big").
Rosacea Treatment: Debunking Popular Myths
Pathophysiological mechanisms of rosacea development: the role of keratinocytes
Activation of Toll-like receptors in keratinocytes leads to the fact that they begin to actively synthesize pro-inflammatory substances: kallikrein kinases, metalloproteinases, antimicrobial peptides.
According to the modern view, the key role in the development of rosacea is played by the so-called cathelicidin LL-37 – non-specific inflammatory factor, the level of which is significantly increased in this disease.
In addition to keratinocytes, cathelicidin is also found in the lysosomes of macrophages and polymorphonuclear leukocytes.
One of the main biological effects of cathelicidin is the initiation of angiogenesis processes through the activation of the so-called VEGF – vascular endothelial growth factor.
In turn, neoangiogenesis is one of the main causes of the formation of persistent erythema and telangiectasias characteristic of rosacea.
Thus, the genetic predisposition to over-secretion of the pro-inflammatory peptide – cathelicidin LL-37, promotes the initiation of skin inflammation processes characteristic of rosacea.
Follow us on Facebook
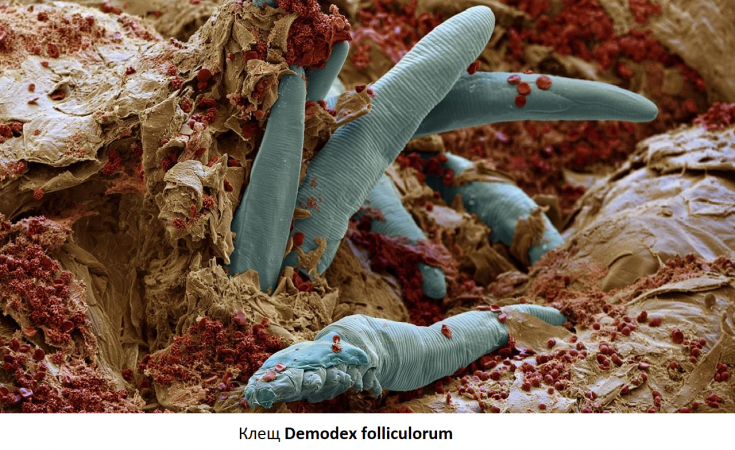
What is the role of Demodex folliculorum in the development of rosacea symptoms
There is strong evidence that Demodex folliculorum mites are associated with the development of papulopustular rosacea.
The Demodex folliculorum mite lives on the skin mainly in the area of the cheeks and forehead.
In patients with rosacea, an increased content of Demodex folliculorum mites on the skin was noted than in the control group of clinically healthy people.
In addition, Bacillus oleronius has been isolated from Demodex folliculorum mites found in patients with rosacea.
Fifty Shades of Red: Nelly Konnikov on Treating Rosacea
Bacillus oleronius – these are Gram-negative bacteria whose antigens stimulate the proliferation of mononuclear cells, thereby contributing to the development of inflammation processes.
Thus, there is a definite correlation between an increase in the level of Demodex folliculorum mites containing Bacillus oleronius and the development of papulopustular rosacea.
Rosacea pathogenesis: increased secretion of pro-inflammatory endogenous peptides
Thus, increased secretion by keratinocytes and mononuclear cells of pro-inflammatory endogenous peptides, in particular cathelicidin, leads to the development of characteristic clinical manifestations of rosacea.
However, aspects of the etiopathogenesis of rosacea, as well as optimal approaches to the treatment of the disease, are still being actively studied.
The treatment of rosacea is aimed at eliminating the processes of skin inflammation, correcting characteristic rashes, restoring the normal structure and tone of the skin.
Therapy should also be aimed at preventing exacerbations and complications characteristic of rosacea.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Cosmetology" section. You may also be interested in Goutta rose: basic approaches to the treatment of rosacea







Add a comment