Pyelonephritis is one of the most widespread urological pathologies that can develop in people of absolutely different ages. This is an infectious disease in which, as a result of exposure to pathogenic bacteria, the renal pelvis is affected. Pyelonephritis can occur in several forms, and in the absence of adequate and timely therapy, serious complications of this pathology arise. One of these complications is pyonephrosis – purulent destruction of the kidney. Read more about the etiology, main types and characteristic symptoms of pyonephrosis at estet-portal.com.
Clinical picture of pyonephrosis: characteristic symptoms
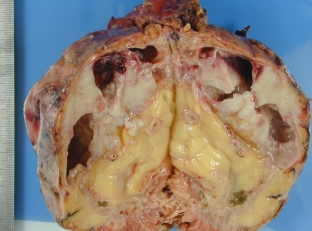
Pyonephrosis – this is the terminal stage of a specific or nonspecific purulent-destructive pyelonephritis. With this pathology, the affected kidney looks like one solid or many small thin-walled cavities that are filled with purulent contents. The disease develops mainly at the age of 30-50 years, and rarely occurs in children. Often in childhood, pyonephrosis can occur against the background of various anomalies of the urinary system.
Such a pathological condition is extremely dangerous for the patient, since the structure of the kidney is completely destroyed and the organ loses its function, resulting in renal failure.
Pyonephrosis:
- etiology of pyonephrosis: main causes of the disease;
- classification of pyonephrosis depending on the etiology and nature of the lesion;
- clinical picture of pyonephrosis: characteristic symptoms.
Etiology of pyonephrosis: main causes of the disease
Pyonephrosis – This is a disease that is caused by infection of the kidney with various microorganisms, most often a mixed microflora, in which Escherichia coli, staphylococcus, streptococcus and Mycobacterium tuberculosis predominate. For the development of this pathology, the presence of two main factors is necessary: the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the urine of the patient, as well as a violation of the outflow of urine. The following main reasons for the development of pyonephrosis can be distinguished:
- purulent acute and chronic pyelonephritis;
- acute purulent or purulent-necrotic process in the parenchyma of the kidney after its traumatic injury;
- pyonephrosis as a complication of a specific kidney disease;
- oncological pathology of the kidneys;
- pyonephrosis of unknown etiology.
Classification of pyonephrosis depending on the etiology and nature of the lesion
Pyonephrosis is characterized by the development of purulent destruction of the renal parenchyma as a result of the formation of purulent foci, both in the kidney cavity and in the "disabled" elements of the pelvic-cup system. In most cases, pyonephrosis is a secondary process that occurs as a complication of pathological processes in the tissues of the kidney. Primary pyonephrosis is extremely rare. Pyonephrosis is classified as follows:
- unilateral pyonephrosis – develops most often, affecting only one kidney;
- bilateral pyonephrosis – occurs extremely rarely;
- closed pyonephrosis – characterized by the presence of completely closed purulent cavities;
- with open pyonephrosis, pus can flow through the ureters into the bladder;
- intermittent pyonephrosis is characterized by the periodic appearance of pus in the urine.
Clinical picture of pyonephrosis: characteristic symptoms
The clinical picture of pyonephrosis depends on the form of the disease and the degree of patency of the urinary tract. Closed pyonephrosis is manifested by hectic fever, heavy sweats, chills, and the presence of acute pain in the lumbar region. If the outflow of urine resumes – sediment, pus, leukocytes and massive bacteriuria appear in it, while the general condition of the patient improves. For open pyonephrosis, the presence of dull pain on the side of the lesion is characteristic, the patient loses weight, body temperature is most often subfebrile. The disease progresses slowly, during periods of exacerbations, severe attacks of pain and hectic temperature are observed. The kidneys are enlarged, tense and very painful on palpation.







Add a comment