Almost every inhabitant of the planet is infected with herpes infection. There are over 80 types of herpes. A person can get infected with only 8 of them, but even this is enough to cause a lot of trouble.
Herpes zoster is an actual problem of humanity
Herpes zoster poses a serious threat to humans, as 95% of adults have had chickenpox in childhood. Undoubtedly, this is good. After all, with smallpox infection after 20 years, the course would be much more serious and more difficult.
It follows that almost everyone has the potential to experience the symptoms of herpes zoster. With a decrease in immune forces, hypothermia and excessive mental and physical stress, the virus can move from a dormant state to an active state. It is also observed in people over 55 years of age, in pregnant women, after long-term treatment with antibiotics, cytostatics, glucocorticosteroids.
What is herpes zoster
Herpes zoster is an acute disease caused by the herpes virus. In the process, the intervertebral ganglia are affected, a vesicular rash appears along the branches of the affected sensory nerve. The disease is accompanied by severe intoxication and fever.
Infection is possible from a person who has herpes zoster or chickenpox. Ways of transmission of the virus - airborne, contact, transplacental transmission of herpes zoster is also possible. Adults are prone to the disease, because most of them have already had the initial form of herpes - chicken pox (pathogen varicella). Therefore, adults get herpes zoster upon contact with the patient, and chicken pox in children.
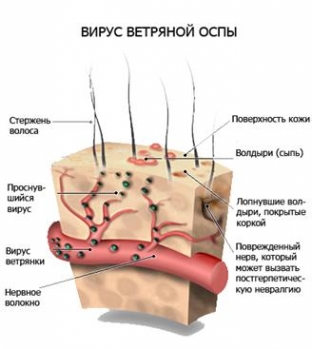
Often the disease develops against the background of viral or bacterial diseases or during them. It is also possible to develop shingles after injuries, treatment with glucocorticosteroids, cytostatics, immunosuppressants, against the background of oncology. That is, for all conditions and diseases in which the protective and adaptive forces of the body are reduced.
Herpes zoster, unlike other types of herpes, does not tend to recur. But in clinical practice, cases of recurrence on the background of diabetes mellitus, lymphogranulomatosis, oncological diseases and HIV infections are described.
The causative agent of herpes zoster is Herpesvirus varicella zoster. This virus causes shingles and chickenpox.
Clinical presentation of herpes zoster
Manifestations begin with pain in the area along the branches of the nerve that are affected. A rash appears later. The pain is very burning, it becomes more intense at night, and also under the influence of certain factors (barometric and cold). At the same time, with herpes zoster, such sensitivity disorders are observed: hypesthesia, hyperesthesia, anesthesia. These changes may apply to all types of sensitivity.
After 3-5 days, and sometimes up to 12 days, skin hyperemia appears in the projection of the passage of the nerve branches on the skin. She becomes swollen. Bubbles appear later. They can appear both simultaneously in all areas, and in waves by 3-7 days of illness. With all this, the patient with herpes zoster is disturbed by a burning pain that persists all the time. The contents of the bubbles are initially transparent, then become cloudy. In their place, yellow-brown crusts form. And after a few weeks, the process ends and pigmentation remains at the sites of the rash. Elements of the rash in herpes zoster, as a rule, are localized asymmetrically. With all these changes in the skin, the pain continues to persist
Possible atypical forms of herpes zoster:
- Abortive form - the process stops at the stage of hyperemia and edema, bubbles do not form;
- Bullous form. With this form of herpes, large blisters with uneven scalloped edges form next to the pustules.
- Hemorrhagic form - the contents of the vesicles become hemorrhagic, and scars remain on the surface after them;
- Necrotic (gangrenous) - ulcers form in place of the vesicles. They are covered with a black scab, later in their place there will be scars. The disease lasts up to 8 weeks.
Often develops in the elderly, in patients with peptic ulcer and diabetes mellitus; - Disseminated (generalized) form - a vesicular rash, localized throughout the body on both sides.
Diagnosis of herpes zoster
As a rule, the typical clinical picture of a herpes infection is enough to make a diagnosis. An increase in body temperature, weakness, a characteristic rash that is accompanied by pain - these symptoms indicate precisely herpes zoster. To confirm the diagnosis, methods of direct and indirect immunofluorescence with specific antibodies, ELISA, PCR can be used.
Modern view on the treatment of herpes zoster
Like other viral infections, shingles should be treated comprehensively. At the beginning, therapeutic measures are aimed at reducing the pain syndrome and preventing the spread of the disease. For this purpose, antiviral drugs are used.
It is recommended to start taking them as soon as possible. It is also mandatory to take human immunoglobulin 5-10 ml once intramuscularly. If the patient took any cytostatics, glucocorticoids or immunosuppressants the day before, they should be immediately canceled. In case of secondary bacterial infection, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used.
You may be interested in: "The role of cytokines in the treatment of non-healing wounds"
If the pain is excessively strong and the person cannot tolerate it, then non-narcotic analgesics are prescribed along with tranquilizers parenterally or orally. For example, diclofenac twice a day, 50 mg.
Ganglioblockers are also used - a 1.5% solution of ganglefan (gangleron), 1 ml per muscle once a day, for up to 10 days. Gangleron is available in capsules, which allows it to be taken on an outpatient basis. K
arbamazepine is prescribed in case of damage to the trigeminal ganglion at a dosage of 0.1 g twice a day, increasing the dose every day, bringing it to a maximum of 0.8 g. This dosage should be divided into 3 doses. After the pain has become less intense or gone, stop taking the drug.
- After the start of treatment, the effect is noticeable after 4 days of treatment. If, after completion, the pain still torments the person, then the following methods can be offered to the patient: The procedure allows you to restore the functioning of the damaged nerve.
Blockade. A substance is injected into the tissues around the affected nerve that blocks the transmission of pain impulses. This makes it possible to eliminate very intense pains for a short time.







Add a comment