Polycythemia develops gradually, over a long period of time, and can be detected quite by accident during a blood test. Symptoms that are present in the initial stages of polycythemia are often attributed to other chronic ailments and advanced age: dizziness, tinnitus, heaviness in the head, chilliness of the limbs, blurred vision and sleep disturbance.
You can find the reasons for the development of polycythemia and the stages of the course of the process in the previous article. Read about the symptoms of development, methods for diagnosing and treating this form of leukemia at estet-portal.com.
What are the clinical manifestations of polycythemia?
A characteristic sign of polycythemia is the development of plethoric syndrome, which is caused by pancytosis and an increase in circulating blood volume. Plethora can be detected during an objective examination, revealing telangiectasia and cherry coloration of the skin of the hands, face and neck, as well as mucous membranes.
The main diagnostic sign of polycythemia is Cooperman's symptom, in which the color of the hard palate remains unchanged, and the soft palate acquires a stagnant cyanotic hue.
Also characteristic of polycythemia is skin itching, which becomes more intense after water procedures. Polycythemia-specific manifestation - erythromelalgia. This is hyperemia and painful burning in the fingertips.
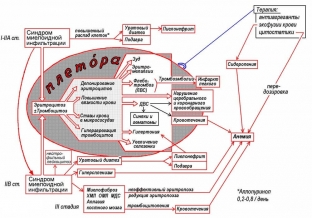
Key specific features of polycythemia
Advanced polycythemia is often accompanied by migraine attacks, cardialgia, bone pain and hypertension in patients. Patients complain of increased gum bleeding, prolonged bleeding after tooth extraction, and bruising of the skin after minor trauma.
Violation of the process of erythropoiesis is accompanied by a violation of purine metabolism and the synthesis of uric acid. Therefore, patients with polycythemia develop conditions such as gout, renal colic, and urolithiasis.
Against the background of violation of the trophic processes of the skin and mucous membranes, trophic ulcers appear on the legs, ulcers form in the stomach – intestinal tract. The most common and dangerous complication of polycythemia is deep vein thrombosis, cerebral and coronary arteries, mesenteric vessels and portal veins. The cause of death in patients with polycythemia is often pulmonary embolism. At the same time, patients with polycythemia are prone to hemorrhagic syndrome with the development of spontaneous bleeding of different localization.
How to detect polycythemia? Aspects of the diagnostic process
Hematological changes are of primary importance in the diagnostic process of polycythemia. A blood test reveals erythrocytosis, increased hemoglobin levels, thrombocytosis and leukocytosis. The shape and size of erythrocytes does not change. An increase in the mass of erythrocytes over 36 ml/kg is a reliable sign of polycythemia. In order to study the bone marrow, a trepanobiopsy is performed, which is more informative for polycythemia than sternal puncture. Histological conclusion for polycythemia – panmyelosis. In the later stages, secondary myelofibrosis is detected.
Additional laboratory tests are performed to assess the likelihood of developing complications of polycythemia:
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck;
- echo-KG;
- general urinalysis;
- Liver tests.
Methods of treatment of chronic leukemia and indications for their use
The first and most important in the treatment of polycythemia is the bloodletting procedure, which significantly improves the patient's well-being for a certain period of time. Blood excisions are carried out in a volume not exceeding 500 ml at a time. The procedure is carried out 2-3 times a week, followed by replenishment of the circulating blood volume with rheopolyglucin or saline. Against the background of such manipulations, the development of iron deficiency anemia is possible. Blood excisions in the treatment of chronic leukemia can be successfully replaced by an erythrocytopheresis procedure, which allows you to extract only the erythrocyte mass from the bloodstream.
The presence of clinical and hematological disorders, the development of visceral and vascular complications are an indication for myelodepressive treatment of chronic leukemia with the help of cytostatics or radioactive phosphorus. In order to normalize the aggregate state of the blood, heparin, chimes or aspirin preparations are prescribed under the control of a coagulogram. For hemorrhages, platelet transfusions are performed.
Polycythemia has a progressive course. The disease is not characterized by the presence of spontaneous remissions and self-healing. Therefore, patients should be under the dispensary observation of a hematologist for life and undergo a course of treatment. The frequency of transformation of polycythemia into leukemia in patients treated with chemotherapy is higher than in patients who did not receive such treatment.







Add a comment