Chronic oophoritis rarely occurs as an independent disease. Migration of the pathogen occurs from the organs located nearby, for example, with infectious inflammation of the fallopian tubes, or less often — with appendicitis. Diagnosis of oophoritis is a rather complicated process, since the pain syndrome, which is the main feature of oophoritis, can accompany any diseases of the abdominal region. Read more about chronic oophoritis, its diagnosis and treatment on estet-portal.com in this article.
Clinical picture and diagnostic methods of chronic oophoritis
Chronic oophoritis can be primary chronic, with the disease characterized by a latent onset. Secondary chronic oophoritis develops as a result of incomplete treatment of acute oophoritis.
Pain syndrome for a long time may be the only sign of chronic oophoritis.
Pain in chronic oophoritis is usually constant, pulling, occurs on the background of stress, colds or during intercourse. The pain syndrome is most pronounced on the eve of menstruation. Another important sign of chronic oophoritis is a change in the menstrual cycle, which occurs due to a violation of estrogen synthesis by the ovaries. key causes of chronic oophoritis;
• modern methods for diagnosing chronic oophoritis;
• chronic oophoritis: the main complications of the disease.
Key causes of chronic oophoritis
Many factors can contribute to the development of chronic oophoritis, such as hypothermia, poor personal hygiene, infections of the genitourinary system, and various endocrine diseases. Smoking has a negative effect, since tobacco smoke affects the composition of cervical mucus: it makes it less thick, which makes it easier for the infection to spread. An unhealthy lifestyle, poor diet, fatigue and stress are factors that can contribute to the development of chronic oophoritis by reducing the protective properties of the immune system.
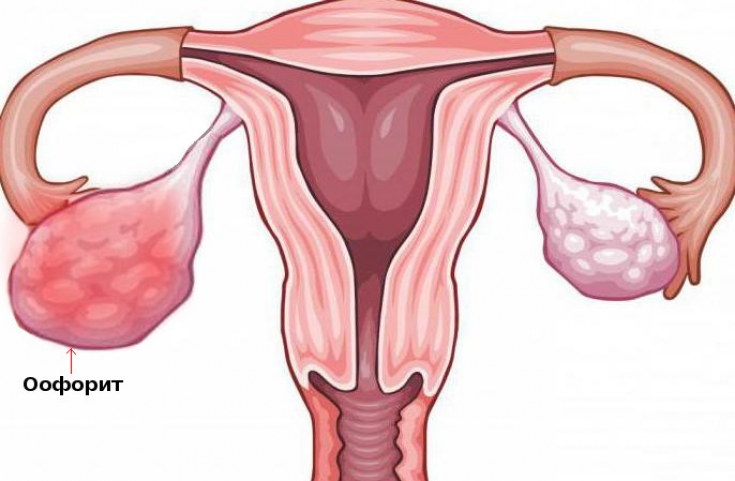 For the diagnosis of chronic oophoritis, a gynecological examination with a study of the vaginal flora is mandatory. Also an informative diagnostic method is ultrasound, which allows you to get an image of the fallopian tubes and ovaries. Among invasive methods, culdocentesis is often used, puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix followed by bacteriological examination. If most of the diagnostic procedures do not give a satisfactory result, a diagnostic laparoscopy is performed.
For the diagnosis of chronic oophoritis, a gynecological examination with a study of the vaginal flora is mandatory. Also an informative diagnostic method is ultrasound, which allows you to get an image of the fallopian tubes and ovaries. Among invasive methods, culdocentesis is often used, puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix followed by bacteriological examination. If most of the diagnostic procedures do not give a satisfactory result, a diagnostic laparoscopy is performed.
Treatment of chronic oophoritis should be carried out consistently and persistently, using antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. The main efforts should be directed to the prevention of the development of adhesions, which can cause
infertility
. For this, the appointment of fibrinolytics is recommended.






Add a comment