Orchiepididymitis occurs when the testicle and the epididymis located in the immediate vicinity are involved in the pathological inflammatory process. Usually diagnosed in men who are sexually active, that is, aged 20 to 40 – 45 years. The main cause of orchiepididymitis is the ingress of pathogenic or opportunistic bacterial flora. Pathology can be treated with antibiotics and with the right choice of treatment regimen, the prognosis is favorable. Otherwise, there is a risk of orchiepididymitis becoming chronic with all the ensuing consequences in the form of impaired testosterone synthesis, infertility, erectile dysfunction. On estet-portal.com read about the causes of orchiepididymitis, methods of diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
- Primary causes of pathology development and provoking factors of orchiepididymitis
- The main directions of diagnosis and treatment of orchiepididymitis
- Epididymo-orchitis: the main clinical symptomatologyka
The etiology of
orchiepididymitis is closely related to the bacterial flora. Any causative agent of a venereal disease can cause an inflammatory process – gonococcus, chlamydia, trichomonas. Orchiepididymitis often occurs against the background of an asymptomatic course of sexually transmitted infections. As a rule, the patient does not seek medical help, and orchiepididymitis develops as a result of an inflammatory process ascending from the urethra.
Sometimes the disease is also caused by representatives of conditionally pathogenic flora: enterobacteria, staphylococcus, streptococcus, Escherichia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus, Klebsiella. Factors predisposing to orchiepididymitis are:
frequent hypothermia;
- presence in the anamnesis of sexually transmitted diseases provoking orchiepididymitis;
- infectious lesions of various parts of the urinary system;
- prostatitis, prostate adenoma;
- immunodeficiency that occurs against the background of systemic chronic diseases, taking a number of medications (corticosteroids, cytostatics, antibiotics);
- injuries of the external genital organs, a separate group is post-traumatic orchiepididymitis;
- impaired blood flow in the pelvic vessels;
- irregular or incomplete bladder emptying;
- an addiction to anal sex and casual sex without the use of a condom.
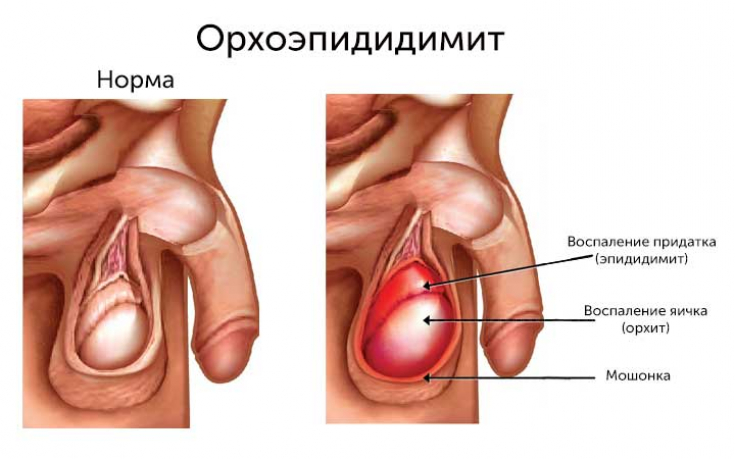
Telegram! Orchiepididymitis: the main clinical symptoms
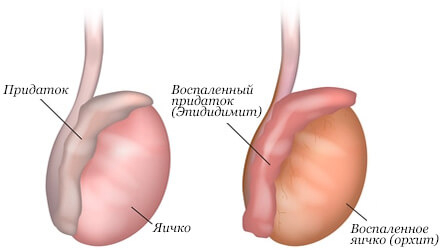
swelling, hyperthermia, redness of the skin of the scrotum; Then the following
orchiepididymitis symptoms:
palpation marks foci of compaction;- acute pain impulses in the scrotum associated with the localization of orchiepididymitis;
- For the late stage of inflammation, a whitish discharge from the urinary canal, sometimes with an admixture of blood, is characteristic.
- If left untreated, orchiepididymitis acquires a chronic course. Pain in the scrotum persists, but they are dull, paroxysmal in nature, their occurrence is associated with physical exertion.
Factors that contribute to the development of infertility in menn The main directions of diagnosis and treatment of orchiepididymitis
A preliminary diagnosis of orchiepididymitis is made after examining the patient.
Orchiepididymitis must be differentiated from torsion of the spermatic cord, which has a similar clinical picture.
Additionally, if orchiepididymitis is suspected, a general urine test and a three-glass sample are taken (in the first portion, an increase in the concentration of leukocytes is detected, bacteriuria is characteristic). To determine the causative agent of orchiepididymitis, specific tests are prescribed by ELISA and PCR.
Treatment of orchiepididymitis is started as soon as possible. Select
antibioticsfrom the group of fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins, macrolides. In the absence of an effect, or after receiving the results of the tests, the treatment of orchiepididymitis is corrected. The duration of the use of drugs is determined by the severity of the symptoms of orchiepididymitis, treatment is continued for 3-5 days after the patient's condition improves.







Add a comment