A prospective, randomized, blinded study of the effects of botulinum toxin preparations was conducted in 30 patients with symmetrical moderate-to-severe forehead lines on a 4-point scale for assessing facial wrinkles.
The aims of the study were to evaluate the efficacy and longevity of using non-reduced incobotulinum toxin A with non-reduced onabotulinum toxin A.
Find out in our article on estet-portal.com the latest research on the action of botulinum toxin, characteristics of neurotoxin types, their differences and subsequent methods to improve the structure and formula of the drug.
- Botulinum toxin applications
- The main constituents of botulinum toxin
- Clinical trials of botulinum toxin
- Results Botulinum toxin action
Botulinum toxin applications
Botulinum toxin (BoNT) is used to treat various neurological disorders and has found wide application in aesthetic medicine as the main weapon in the fight against age-related changes and provides a significant aesthetic improvement in skin condition. There are currently seven different serotypes of the neurotoxin in use. There are serotypes of botulinum toxin: types A, B, C, D, E, F and G.1.
Follow us on Instagram!
Each of these neurotoxins has a unique molecular structure and function, and each is produced from a different strain of Clostridium Botulinum bacteria. Three formulations of botulinum toxin A (BoNT-A) are currently commonly used: Botox, Incobotulinumtoxin A, and Onabotulinumtoxin A.
OnabotulinumtoxinA and incobotulinumtoxinA are the two constituents of botulinum toxin A (BoNT-A) commonly used in aesthetic medicine. Their main differences depend on whether the complexing proteins are included in the active neurotoxin or not.
While OnabotulinumtoxinA has complexing proteins, IncobotulinumtoxinA does not. However, it is unclear if these differences affect their efficacy, longevity, immunogenicity when used.
The main components of botulinum toxin
Each of these drugs has its own unique benefits; however, it is not clear whether their structural and functional differences are clinically significant. Factors that distinguish each neurotoxin include dose efficacy or equivalence, onset of action, duration of action, local diffusion, side effect profile, and differences in immunogenicity. The main difference between these different neurotoxin formulations is the presence or absence of complexing proteins.
10 Interesting Facts About Botulinum Toxin: Everything You Want to Know
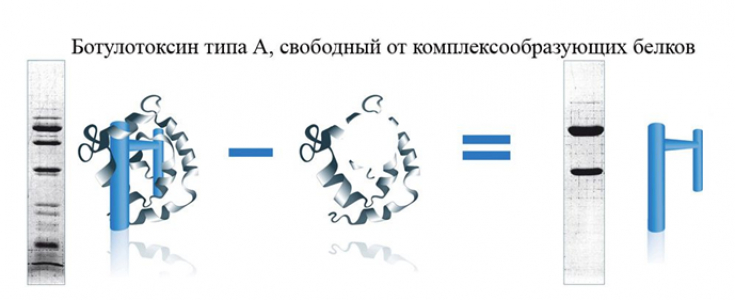
Manufacturers typically produce botulinum toxin as a 150-900 kDa protein that includes both the primary active component (150 kDa polypeptide chain) and complexing proteins. The 150 kDa protein is a neurotoxin and has low toxic activity; however, after cleavage into the 50 kDa (light chain) and 100 kDa (heavy chain) components, the activity of the toxin increases. Complexing proteins consist of hemagglutinin and smaller non-hemagglutinin proteins.
Complexing proteins are sometimes referred to as accessory proteins, protective proteins, or neurotoxin proteins. They are important for protecting toxins in their natural environment (pH range 5-7) but dissociate at physiological pH 6-8.
OnabotulinumtoxinA contains complexing proteins, while incobotulinumtoxinA does not. The amount of botulinum toxin product, along with complexing proteins and residual proteins, determines the foreign protein load on the human body. The human immune system can recognize any part of this protein as part of a neurotoxin, which is recognized as a foreign substance and triggers an immune response, especially after injection.
Clinical trials of botulinum toxin
Several studies, mostly in the clinical literature, have suggested that a higher total protein content of the substance may increase the risk of antibody formation. As a result, botulinum toxin A products began to be produced correspondingly with a reduction in the total protein content. The current formula of incobotulinum A contains only 5 ng of complexing protein per 100 units (E).
Male facial rejuvenation with botulinum toxin type A
Clinically, however, it is not clear whether these molecular differences are significant and whether they affect antigenicity or efficacy. Due to the large number of non-randomised, non-blinded, industry-sponsored trials, it is difficult for clinicians to determine whether a particular botulinum toxin product is more beneficial than another in terms of efficacy and safety. analysis. The study protocol was approved by The Esthetic Clinics Institute.
Botulinum toxin: the hottest news in botulinum therapy
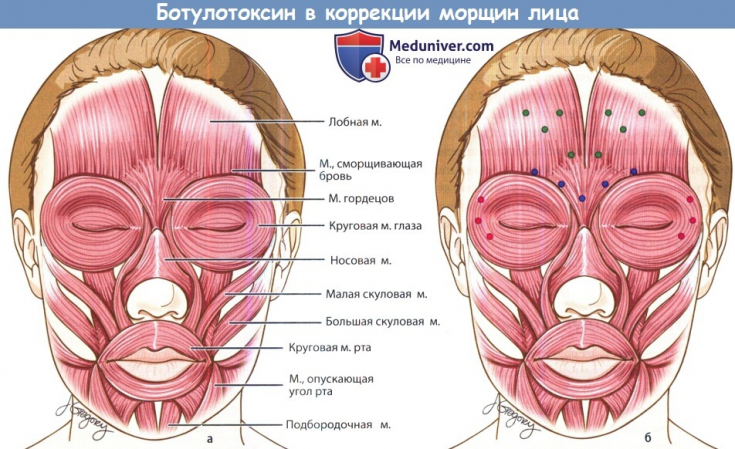
Thirty patients with moderately symmetrical – severe forehead line wrinkles with maximum frown were included in the study. The two groups were matched for age and gender to avoid any confounding results and bias. The international
Carruthers scale was used to assess the wrinkle line.
Botulinum toxin resultsA Clinical Improvement Scale was used to analyze the results of the study, the results of patients were assessed over a period of 24 weeks. In the course of the analysis, it was found that forehead lines reappeared in patients treated with onabotulinumtoxin A after 8.3 weeks compared to 10.1 weeks in patients treated with incobotulinumtoxin A.
Light Head or Botulinum Therapy for Migraine
While improvement in both forehead lines was observed for both toxins after 8 weeks.The effectiveness and improvement of onabotulinumtoxin compared to incobotulinumtoxin A decreased, indicating that incobotulinumtoxin A was more effective in long-term wrinkle reduction.
Botulinum toxin: why poison has no analogues among drugs







Add a comment