Botulinum toxin has been perceived as a deadly threat for centuries. In the Middle Ages, guild rules were used to control sausage production as a major source of botulism.
In the 19th century, the German district physician Justinus Kerner published two monographs describing the clinical features of botulism with a precision hitherto unsurpassed. In the 1970s, the perception of botulinum toxin began to change when the first studies of its effects on humans were carried out.
In the early 1980s, attitudes towards neurotoxin completely changed when its therapeutic potential suddenly became apparent.
estet-portal.com about the structure of botulinum toxin, its mechanism of action, as well as the effect of neurotoxin on striated muscles and the autonomic nervous system, dermatovenereologist, specialist of the Beautycom aesthetic medicine clinic (Vinnitsa) Ala’ and Osama Al-Omari.
How does botulinum neurotoxin work: the structure of botulinum toxin

Botulinum toxin is synthesized as a relatively inactive single chain polypeptide with a molecular weight of approximately 150 kDa.
It is activated when the polypeptide chain is proteolytically cleaved into a 100 kDa heavy chain and a 50 kDa light chain. Botulinum neurotoxin exists in seven different serotypes named A, B, C, D, E, F and G.
Although all of these serotypes inhibit the release of acetylcholine from nerve endings, their target proteins and potency differ significantly. To date, the most studied is botulinum toxin type A, known as the drug BOTOX® of the Allergan company.
For more interesting articles visit Facebook!
Molecular mechanism of action of botulinum toxin
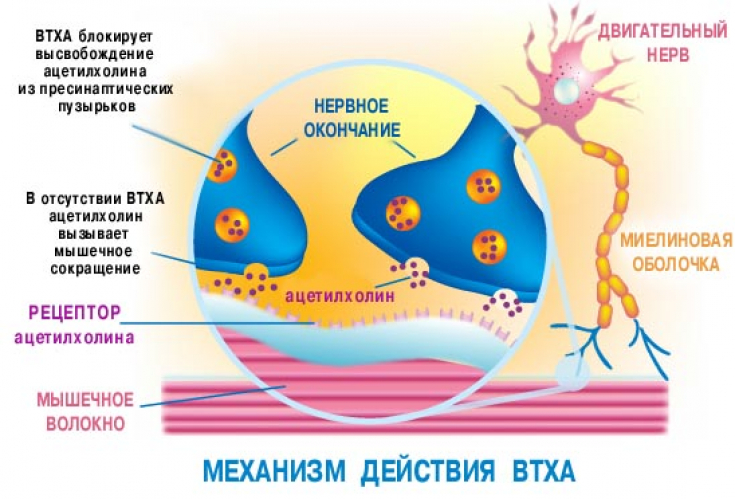
When a motor neuron action potential depolarizes the end of the axon, acetylcholine is released from the cytosol into the synaptic cleft. This release of acetylcholine is carried out by the transport protein chain – SNARE.
When botulinum toxin is injected into the target tissue, the botulinum neurotoxin heavy chain binds to glycoprotein structures specifically found on cholinergic nerve endings.
This specific docking is responsible for the high selectivity of the neurotoxin for cholinergic synapses. After internalization, the botulinum neurotoxin light chain binds with high specificity to the SNARE protein complex.
Cleavage of the transport protein SNARE blocks the release of acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft, and hence neuromuscular transmission.
Proteolytic cleavage of the light chain of the SNARE protein complex prevents docking of the acetylcholine vesicle on the inner surface of the cell membrane and results in blockade of vesicle fusion. When the target tissue is muscle, paresis occurs by chemical denervation. When the target tissue is an exocrine gland, glandular secretion is blocked.
World-wide research: higher doses of BOTOX®
Action of botulinum toxin on striated muscles
After injection of botulinum toxin into the striated muscle, paresis occurs after two to five days and lasts from two to three months. There is a correlation between the amount of neurotoxin applied and the degree of paresis provoked. However, relatively low doses of botulinum toxin already cause significant paresis.
There is also a correlation between the amount of botulinum toxin applied and the duration of its action. However, this correlation seems to exist only when relatively low doses of the neurotoxin are used.
At higher doses, the duration of action saturates to about three months.
When the toxin is injected into an overactive muscle, the induced paresis causes a decrease in the diameter of the target muscle. When the target muscle is hypertrophied due to prolonged hyperactivity, toxin-induced paralysis can normalize its size.
Use of high doses of botulinum toxin in the correction of glabellar wrinkles
Action of botulinum toxin on the autonomic nervous system
Botulinum toxin can be used to treat overactive smooth muscles such as distal esophageal sphincter, sphincter of Oddi, internal anal sphincter, bladder detrusor. Also, the toxin is used to treat hyperhidrosis, hypersalivation, hyperlacrimation. Thus, a neurotoxin can affect the efferent fibers of the autonomic nervous system.
Apparently, the effect of botulinum toxin on the autonomic nervous system does not differ from its effect on striated muscles. Thus, the most studied preparation of botulinum toxin – BOTOX® is a real miracle not only for people with neuromuscular disorders, but also for patients with dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system.
Original drugs of the Allergan company You can only purchase from the official distributor.
BOTOX injections® in different age periods: when and what to correct







Add a comment