"Retinoid" is a generic term to describe all forms of vitamin A, including both natural and synthetic derivatives, that have been used regularly in dermatology for over 70 years.
Retinoids have been used to treat various skin conditions such as:
- psoriasis;
- acne;
- epithelial tumors;
- helped fight oily skin and photoaging.
More than 2500 connections are currently available.
At estet-portal.com we will get acquainted with the different forms of topical retinoids, as well as learn how they work and what functions they have.
What are retinoids
There are three generations of retinoids.
They are compounds that have biological activities similar to natural vitamin A (retinol) and cover a huge range of effects, from cosmetic to prescription-only drugs.
It is important to note that vitamin A cannot be synthesized by the body, therefore it must be supplied to the body, for example, as a local product, in a "ready-to-use" form. form.
Retinoids are known to irritate the skin and this limits their use in many patients.
Skin care products commonly use retinol and retinaldehyde as they are a mild but effective alternative to retinoic acide.
How do retinoids affect the skin
Topical retinoids affect cell proliferation differently under different conditions. It has been demonstrated that retinoids can exhibit both immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory activity.
For example, in psoriasis, the use of retinoids has been shown to reduce proliferation, increase differentiation, regulate corneocyte desquamation, modulate lymphocyte function, and inhibit neutrophil migration.
The use of both retinoic acid and retinol has been shown to increase epidermal thickness and show an increase in the expression of procollagen I and procollagen III proteins.
Topical retinoids can act as UV filters because they tend to absorb UV light.
An in vitro study in mice skin after exposure to topical retinyl palmitate demonstrated effects in preventing UVB-induced erythema and DNA photodamage.
The use of retinoids in the treatment of acne: to be or not to be
Vitamin A topical preparations are widely used for wrinkle reduction.
Studies have shown that retinoids increase water content in the dermis by stimulating the synthesis of glycosaminoglycan (GAG), in particular hyaluronic acid (HA), as well as stimulating the synthesis of transforming growth factor (TGF-beta) and procollagen, which leads to an increase in dermal collagen Type I.
Retinoids accelerate epidermal cell turnover by modulating the expression of the corresponding genes, which increases cell differentiation and proliferation.
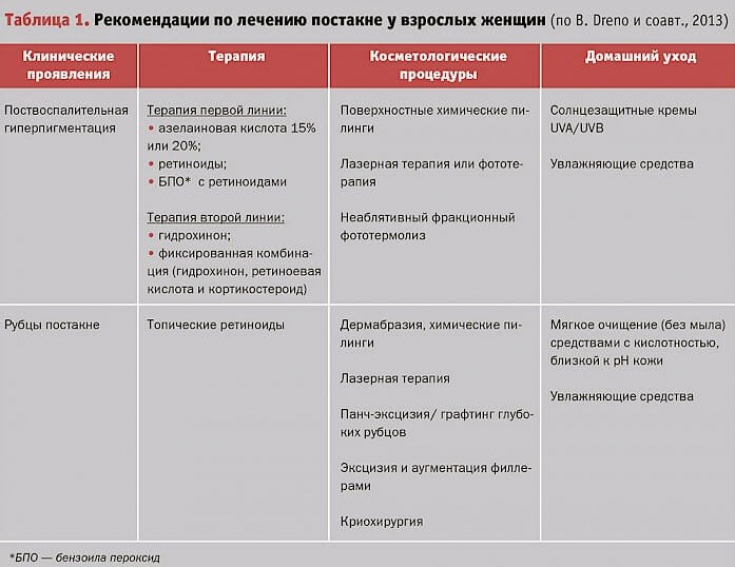
Retinoic acid is used to eliminate hyperpigmentation as it increases cell turnover, which in turn shortens the contact time between keratinocytes and melanocytes, reducing pigmentation through epidermopoiesis, with reduced accumulation of melanin in the basal cells.
Retinoic acid suppresses UVB-induced pigmentation by reducing tyrosinase activity.
It has been found that in patients with acne topical retinoids increase the turnover of the follicular epithelium, displacing mature comedones and suppressing the formation of microcomedones, which creates a negative environment forI Propionibacterium.
Read the most interesting articles in Telegram!
Main types of topical retinoids
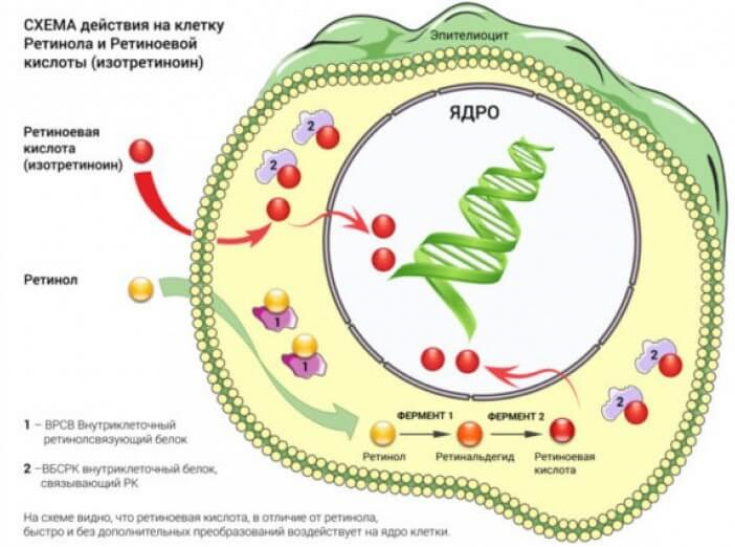
1. Tretinoin in the treatment of photoaging was first demonstrated in 1984. Using an animal model, Kligman et al. noted that 10-week treatment with tretinoin in the skin of mice with photoaging resulted in the synthesis of new collagen in the papillary dermis.
2. Isotretinoin reduces fine lines and wrinkles, as well as pigmentation, sallowness and texture without causing significant irritation.
3. Retinol causes thickening of the epidermis, increases the expression of retinol-binding protein genes. Compared to tretinoin causes less erythema.
Mechanism of action retinol involves conversion to all-trans retinoic acid via retinaldehyde within keratinocytes to act on the epidermis.
Retinol is also associated with less transepidermal water loss, erythema, and skin sloughing than with retinoic acid.
In 2015, Randhawa et al. studied long-term use of retinol, demonstrating that 0.1% retinol significantly reduced signs of photoaging.
4. Adapalene is the first third-generation retinoid to be approved by the FDA for the treatment of acne. It has excellent penetration into the follicles, anti-inflammatory and comedolytic action.
Adapalene is more stable and associated with less irritation than tretinoin. The product does not degrade in the presence of light or air.
5. Tazarotene gel 0.05% or 0.1% is used to treat photodamage and is also indicated for psoriasis and acne.
Tazarotene has the ability to regulate cell proliferation, cell differentiation and inflammation, as well as to suppress the expression of keratinocytes.
Topical retinoids – the gold standard for acne treatment







Add a comment