Diabetes mellitus is one of the main risk factors for the development of cardiovascular diseases, which are characterized by functional and structural damage to blood vessels.
Today, diabetes mellitus is recognized as a major risk factor for coronary heart disease, peripheral arterial disease, and cerebrovascular disease. Although there is sufficient evidence of an association between the clinical manifestations of symptomatic atherosclerotic diseases (eg, myocardial infarction) and diabetes mellitus, there is still a lack of understanding of how diabetes mellitus affects long-term outcome in patients with subclinical atherosclerosis.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com about what complications of the cardiovascular system occurt in patients with diabetes mellitus and modern approaches to the diagnosis and prevention of these conditions.
Clinical study of patients with diabetes
Like diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis progresses over many years and often remains asymptomatic and undiagnosed until the first clinical event occurs. Therefore, scientists from Austria conducted a study, the purpose of which was to evaluate the prognosis of mortality in the long term due to a combination of carotid stenosis in patients with diabetes mellitus and asymptomatic carotid atherosclerosis
Follow us on Instagram!
Scientists conducted a study in which 1065 patients with diabetes took part. All participants underwent ultrasound examination of the extracranial carotid arteries. The main indications for ultrasonography were carotid auscultation noise, the presence of cardiovascular risk factors, and known atherosclerotic diseases of other vessels.
Prediabetes – dangerous endocrinological pathology
Patients with diabetes mellitus and current infectious or inflammatory diseases, active malignancies, and symptomatic carotid disease were excluded from the study.
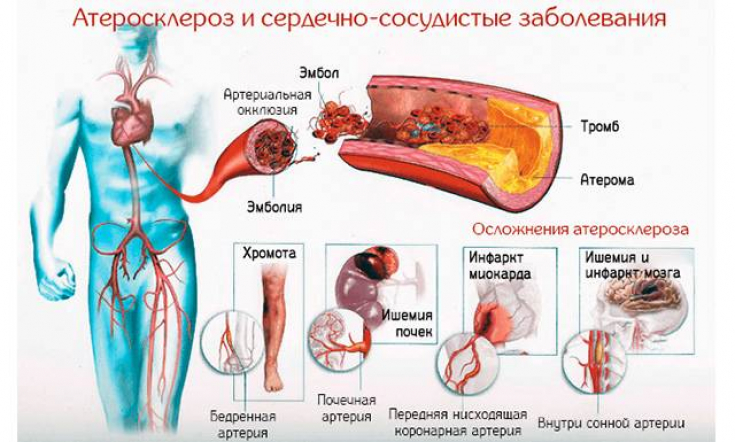
Criteria for vascular lesions in patients with diabetes
The degree of narrowing of the carotid artery in patients with diabetes mellitus was determined by 6 criteria in accordance with the North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial − NASCET classification.
Diabetic ketoacidosis – life-threatening complication of diabetes
Arterial hypertension was diagnosed in patients with blood pressure above 140/90 mm Hg. Art. or in patients taking antihypertensive drugs. Diabetes mellitus was defined as glycosylated hemoglobin > 6.5% and fasting blood glucose > 7.0 mmol/L according to American Diabetes Association criteria.
Results of vascular studies in patients with diabetes mellitus
Over the 11.9 years of the study (6.0-12.4), scientists recorded 548 (51.5%) deaths, among them 367 patients (67%) died from cardiovascular complications, 142 (13 3 %) − from malignant neoplasms, 45 (4.2%) − for other reasons. Diabetes mellitus was detected in 335 (31.5%) people, in the vast majority − Type 2 (95.3%).
The overall mortality rate was 66.9% in patients with diabetes mellitus and 44.4% in those without this pathology, and mortality from cardiovascular complications was 47.5% in patients with diabetes mellitus and 28.5% &minus ; without this pathology.
Mean glycosylated hemoglobin was 6.0% (5.6-6.6%) in the general population and 7.2% (6.4-8.1%) in diabetic patients, and the risk of death from of all causes and cardiovascular complications was higher in patients with high levels of glycated hemoglobin in the blood serum.
Therapeutic Strategies for the Development of Insulin Analogs
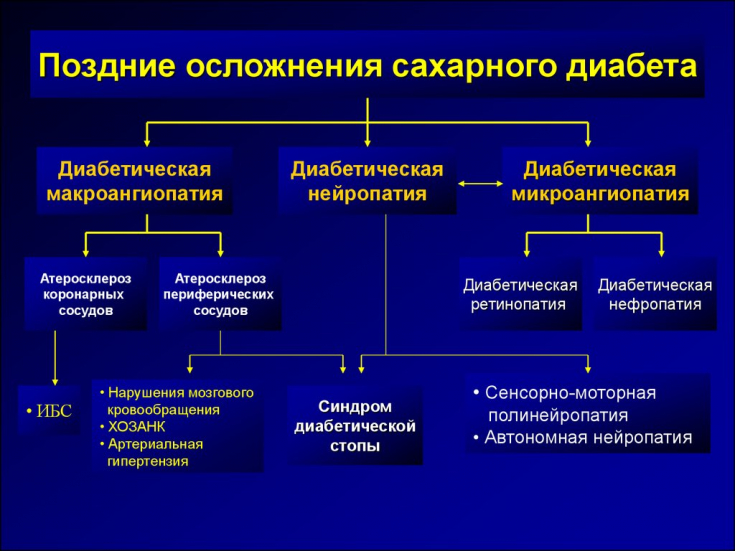
Prevalence of vascular lesions in patients with diabetes
At enrollment, 377 (35.4%) patients had unilateral or bilateral carotid artery narrowing ≥50%. Scientists have found that patients with diabetes mellitus and asymptomatic carotid stenosis ≥50% have a high risk of adverse events.
For example, if a patient was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus and carotid stenosis ≥50% at enrollment in the study, then he had only about a 20% chance of surviving the next 12 years. In addition, patients with diabetes mellitus and carotid stenosis ≥50% risk of death from cardiovascular complications is almost 2.5 times higher compared with patients without diabetes.
Thus, routine carotid ultrasound may be a valuable prognostic tool for diabetic patients.
Neuropathic ulcer as a complication of diabetes







Add a comment