Prediabetes − an intermediate state of hyperglycemia in which blood glucose levels are above normal but below the threshold values for diagnosing diabetes.
Prediabetes as a separate disease was included in the International Classification of Diseases of the 10th revision (ICD-10). The number of recorded cases of the development of prediabetes is growing every year, and its consequences contribute to the rapid development of complications during the transition of this condition to diabetes mellitus.
Learn at estet-portal.com about this pathology and the main diagnostic criteria for prediabetes from the standpoint of evidence-based medicine.
Epidemiology of prediabetes: current trends
Persons with prediabetes are at high risk of developing overt diabetes mellitus and associated complications such as diabetic retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy, and generalized vascular lesions.
Follow us on Instagram!
Better understanding of prediabetes, as well as timely monitoring of glucose levels, can help identify this condition, intervene in a timely manner, and reduce the number of individuals who will potentially have diabetes in the future. The number of people who develop prediabetes is growing rapidly in all countries.
Diabetic ketoacidosis – life-threatening complication of diabetes

In the Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) group, who were at high risk of developing diabetes, the presence of such a complication as diabetic retinopathy was 7.9%. In another study, the prevalence of peripheral neuropathy was higher in patients with prediabetes than in patients with normal glucose tolerance, and was almost identical to the prevalence in participants with newly diagnosed diabetes.
Comorbidity of prediabetes with other diseases
An association between prediabetes and an increased risk of developing chronic kidney disease has also been reported based on the results of a meta-analysis. Another meta-analysis showed that, compared with individuals with normal blood glucose levels, there is an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, coronary heart disease, stroke, and death in individuals with prediabetes.
Furthermore, elevated glucose levels in early pregnancy are associated with an increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes and may also lead to gestational diabetes.
Prediabetes progresses to overt type 2 diabetes in about 25% of patients within 3-5 years, and up to 70% of individuals with prediabetes have overt diabetes mellitus throughout their lives. As a chronic disease, the long-term consequences of diabetes mellitus impair quality of life and significantly increase healthcare costs. Statistics show that a third of Americans have prediabetes and 90% do not know their condition.
Osteoarthritis as a complication of diabetes
Diagnostic glucose levels for prediabetes
Prediabetes − it is a chronic condition that manifests itself as metabolic disorders. It is important to note that the diagnostic criteria and terminology associated with prediabetes varies widely among leading organizations.
Both the WHO and the ADA provide recommendations for screening for prediabetes based on the assessment of glucose tolerance test results and fasting plasma glucose levels. Although certain threshold values for the glucose tolerance test are common to both governing bodies, the ADA recommends a lower threshold for fasting plasma glucose.

The criteria used by the WHO have been proposed to map the relative likelihood of progression from prediabetes to overt type 2 diabetes mellitus. The ADA also recommends a glycated hemoglobin (HbA1C) assessment for detecting prediabetes, but the proposal has not been endorsed by the WHO. HbA1c is considered by many to be a more reliable and convenient test for diagnosing glucose abnormalities because it reflects average blood glucose levels over recent months and requires no preparation. However, the availability of HbA1c testing may be limited in developing countries.
Therapeutic Strategies for the Development of Insulin Analogs
Furthermore, it is worth noting that the key diabetes prevention studies that included patients at high risk of developing diabetes did not use HbA1c as an endpoint; however, additional analyzes of the data have since been performed and HbA1c levels have been confirmed to be a strong predictor of the incidence of diabetes mellitus.
Neuropathic ulcer as a complication of diabetes
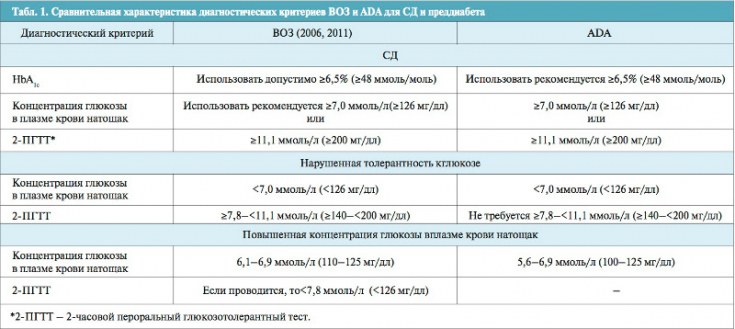
Diagnostic criteria that will be most appropriate for identifying people with prediabetes are still being developed, but the lower fasting glucose threshold in the ADA guidelines compared to the WHO and IDF guidelines improves the level of correlation between the number of people identified by fasting glucose and impaired tolerance to glucose. ADA recommendations are regularly updated with the latest scientific data and can be considered more globally accepted.
Advanced Treatments for Diabetes Mellitus







Add a comment