The endocrine system has a wide variety of physiological effects on the functioning and structure of the musculoskeletal system.
Diseases of the endocrine glands in their progression always lead to disorders of the bones and joints, muscles, and internal organs. The most common disease in endocrinology is diabetes mellitus, and this pathology has a negative tendency to double every 10-15 years.
Find out in our article on estet-portal.com about such a rare, but no less dangerous complication as diabetic osteoarthritis.
Complications of diabetes
It is the incidence of diabetes mellitus that is one of the most serious medical and social problems of modern endocrinology. In the structure of endocrine diseases, symptoms of damage to the kidneys, retina, arteries (Raynaud's syndrome), and the cardiovascular system often come to the fore.
Follow us on Instagram!
Due to the increase in life expectancy of patients with diabetes, the incidence of diabetic osteoarthropathy (DOA) is increasing. In diabetes mellitus, significant metabolic disorders occur, which cause pathological changes in various organs and systems, including bone-articular and periarticular tissue.
Osteoarthritis as a late complication of DM
Most often, with such an endocrine pathology, retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy and angiopathy of the lower extremities are observed as the causes of a decrease in human performance and disability.
However, as noted by many endocrinologists, most clinicians do not pay due attention to the formation of diabetic osteoarthritis, especially in terms of its early diagnosis.
Diabetic osteoarthritis is a late complication of diabetes mellitus and is noted in history in 42.9-58% of patients with type 1 diabetes and in 24-37.7% of patients with type 2 diabetes. This disease occurs mainly in severe diabetes mellitus after 5-8 years from the onset of the disease, more often in people aged 20-30 years.
Therapeutic Strategies for the Development of Insulin Analogs
The consequences of damage to the musculoskeletal system in DM, in addition to osteoarthritis, are osteopenia, osteoporosis, Dupuytren's contractures (15-35%), humeroscapular periarthritis (8-20%), osteoarthritis (10-14%), flexor tendosynovitis, carpal tunnel syndrome, pyrophosphate arthropathy, gout.

The features of diabetic osteoarthritis are the overwhelming unilaterality of the lesion, the dependence of the progression of the arthritis clinic on timely diagnosis and the adequacy of the treatment of diabetes, the mild pain of the articular syndrome, sometimes its complete absence, associated with concomitant neuropathy.
Neuropathic ulcer as a complication of diabetes
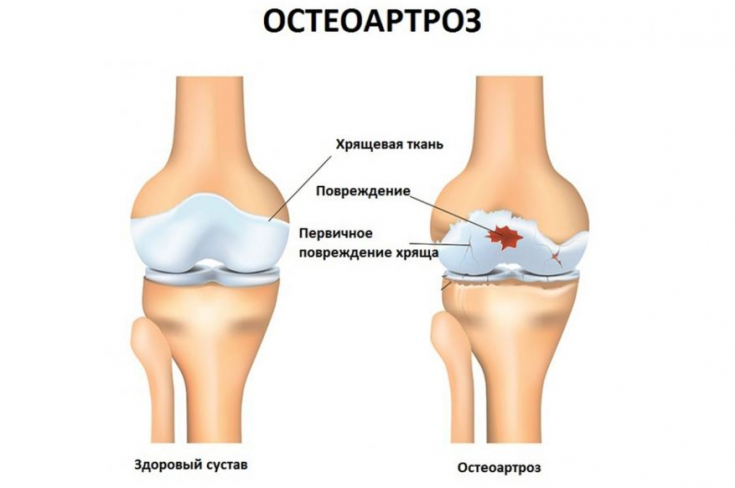
Osteoarthritis formation process
High blood glucose – this is the main factor in the degradation of the joints. With its phenomenon of glucose toxicity on the musculoskeletal system, it contributes to the disruption of the expression of genes responsible for the synthesis of proteoglycans in endothelial cell culture.
Local increase in glucose concentration leads to changes in cartilage tissue due to the formation of glycosylation end products, which, in turn, stimulates chondrocytes and synoviocytes to produce destructive and pro-inflammatory mediators and change the quality of subchondral bone and cartilage, which leads to the formation of osteoarthritis and arthritis.
Advanced Treatments for Diabetes Mellitus
Deterioration of the function of glucose transporters on the surface of chondrocytes contributes to the intensification of destructive processes, which is typical for osteoarthritis. In addition, hyperglycemia causes low-grade inflammation, which deepens the phenomena of osteoarthropathy.
It should be taken into account that the neurotoxicity of hyperglycemia leads to neuromuscular insufficiency of the tissues around the joint and its destabilization.
Impaired blood supply in diabetes
The influence of microangiopathy is manifested in a decrease in capillary blood flow due to changes in the structure and function of blood vessels, as well as connective tissue components, which is the reason for this pathology in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Impaired bone tissue remodeling due to metabolic changes in diabetes is due to insulin deficiency − anabolic hormone of protein synthesis, which stimulates the synthesis of bone matrix, cartilage tissue and ensures normal bone mineralization by stimulating collagen synthesis and moving amino acids into the bone.
Is it possible to achieve remission of type 2 diabetes with weight loss
Even such a negative metabolic situation of these pathogenetic mechanisms, which has been established to this day, can lead to rapid destructive processes in the periarticular structures in severe diabetes.
The above pathogenesis shows that diabetic osteoarthritis has no specificity and can quickly lead to severe disability and permanent disability at a fairly young age.
Statins and diabetes risk: is there a link







Add a comment