Tuberculosis lupus – This is a tuberculous skin disease with a chronic course. Tuberculous skin lesions occur due to the penetration of Mycobacterium tuberculosis into the skin. Predominantly endogenous infection occurs (hematogenous or lymphogenous) from different foci of tuberculosis.
Tuberculous lesions of the skin, in particular lupus, are distinguished by the fact that the patient has practically no subjective sensations that disturb him, despite the fact that the disease develops over a long period and leads to the destruction of bone tissue on the face. Learn more about the symptoms and diagnosis of lupus erythematosus at estet-portal.com.
Tuberculosis lupus – specific skin lesion in tuberculosis
Among patients with skin tuberculosis, lupus erythematosus is detected in 75% of cases. The skin is attached to the process in a metastatic way or per continuitatem. Exogenous autoinoculation of the skin with tuberculosis bacilli of the patient himself with saliva, sputum, urine is also possible if he has active tuberculosis of the lungs or intestines.
Most often, the disease begins in childhood or adolescence. In addition to tuberculous lupus, there are other tuberculous skin pathologies, which you can read about further on estet-portal.com. The first signs of tuberculous lupus appear on the face in the nose area, then the upper lip, gums, cheeks, auricles are drawn into the process.
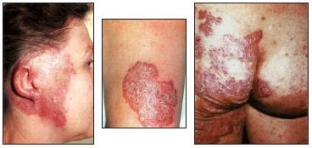
The main morphological element of tuberculous lupus is a tubercle (lupoma) ranging in size from a pinhead to a small pea, yellowish-red color and pasty consistency.
Lupus tuberculosis is easy to diagnose by specific lesions of the skin and mucous membranes.
Clinical signs and symptoms of lupus
Lupomas, merging, create an almost continuous infiltrated focus of inflammation with irregular rounded contours. scar atrophic tissue, resembling crumpled tissue paper, remains at the healing sites with a lupom. When ulcerated with a loop, scars form in their place.
For the clinical diagnosis of lupoma, two research methods are used: diascopy and pressing with a probe. The color of lupoma is composed of a combination of a mild inflammatory color with a brown or yellowish infiltrate. To eliminate hyperemia, glass is pressed on the lesion. At the same time, translucent yellow-brown spots appear (the phenomenon of “apple jelly”).
When pressed, the probe head easily penetrates into the tubercle of a pasty consistency, which turned out to be so due to the melting of collagen and elastin fibers in it. In addition, due to pressing the probe, bleeding can easily occur. Often the patient complains about the pain of the procedure. In addition to the described lupus erythematosus, there are other types of tuberculosis pathology.
Clinical varieties of lupus erythematosus:
- Lupus vulgaris tuberosus is characterized by the formation in the deep layers of the skin of tubercles the size of a pea, protruding above the level of the skin;
- ulcerative lupus erythematosus– characterized by ulcerative decomposition, accompanied by inflammation;
- for impetiginous lupus erythematosus is characterized by banal suppuration;
- in case of psoriasiform lupus erythematosus, the surface of the lupoma is covered with dense silvery-white scales;
- Serpiginating lupus erythematosus is characterized by a propensity for the process to spread. At the same time, a scar is formed on the regressing areas, along the periphery of which new lupomas appear.
The main types of lupus erythematosus according to the localization of the process
According to the prevalence of lupus erythematosus, disseminated and diffuse forms are distinguished.
Some features of the course of lupus erythematosus and its clinical picture are associated with the localization of the process. The lupus process on the face usually stops at the border of the scalp. When the process is localized on the skin of the cheeks and temporal plots, cicatricial changes often cause persistent eversion of the eyelids with the further development of conjunctivitis and dacryocystitis.
If lupus is localized on the nose, then first of all its tip and wings, cartilage and bone tissue are destroyed. Mutilation sets in and the nose takes on the shape of a bird's beak.
Nasal openings narrow and may close completely. There are no subjective sensations even with significant tissue damage. As a result of cicatricial changes, a narrowing of the oral opening may occur – microstomy. Lips, often upper, swollen, thickened, enlarged due to elephantiasis. In the area of the ear lobes, a tumor-like form of the lesion develops more often; in the area of the chin and neck, cicatricial changes can lead to eversion of the lower lip.
The course of lupus erythematosus is torpid, prolonged. In 25-30% of cases, an active tuberculous process develops in other organs. In terms of prognosis, an undesirable complication is the development on atrophic lupus scars of skin cancer and much less frequently – sarcomas. Of course, tuberculous lupus ends with the formation of a smooth, shiny atrophic scar.







Add a comment