At first, the erosion of the teeth is almost invisible, only the dentist can notice tarnished spots on the tooth enamel during examination. But, if you do not take action and start treating these spots, then very soon the patient will return with complaints of increased sensitivity of the teeth and yellowish or brownish spots on the teeth that have appeared, and the progressive destruction of enamel and dentin will be revealed to the doctor. Tooth erosion is classified as a non-carious disease, but caries can join due to damage to the enamel, so erosion requires immediate treatment of the affected teeth.
Why tooth erosion develops and how to diagnose it
Tooth erosion is not considered a cosmetic defect, but a serious dental problem that requires not delaying the start of treatment. According to the observations of experts, this problem is most often addressed by middle-aged women. Perhaps the explanation for this is the endocrine theory of tooth erosion, since it has been established that hyperfunction of the thyroid gland doubles the risk of damage to tooth enamel, and it is women who are largely susceptible to hormonal fluctuations.
In addition to the endocrine theory, there are other completely equal theories explaining the reasons for the development of tooth erosion. The mechanical theory suggests damage to tooth enamel by hard toothbrushes and abrasive particles of cleaning products, which provokes tooth erosion. Chemical theory blames the destruction of tooth enamel and erosive damage on exposure to acids from foods and drinks such as citrus fruits, juices, sodas, pickles. Of course, work in hazardous chemical industries also plays a role.
The cause of tooth erosion may be the intake of certain medications, especially those with ascorbic acid. Tooth enamel can be destroyed in GERD when gastroesophageal regurgitation occurs.
Tooth erosion can vary in the degree of enamel damage and in the activity of the development of the process. So, the initial stage & nbsp; erosion consists in the surface destruction of the enamel, with an average lesion, the destruction reaches the dentinal border, and the deep degree of tooth erosion is characterized by damage to the enamel to its entire depth and with the capture of the upper dentinal layer. In the active phase of the disease, tooth erosion changes in size every month and a half, and the patient complains of increased tooth sensitivity. In the passive phase, the process can stabilize, and during the year the erosion of the teeth does not bother the patient.
Symptoms suggestive of dental erosion:
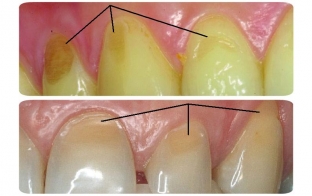
- on the vestibular surface of the tooth appear rounded areas of enamel, devoid of shine;
- with the development of the process, the focus deepens, expands, acquires a whitish color;
- in the stage of deep damage, tooth erosion looks like brownish pigmentation due to the exposed layer of dentin;
- there are complaints of pain when brushing teeth, drinking certain drinks and foods;
- Tooth erosion often occurs symmetrically on incisors or canines.
Gradually adjacent teeth may be involved in the process, the disease has a chronic course.
Dental care and erosion prevention options
Dental treatment for erosion is, first of all, to stabilize the process, to stop the destruction of enamel. For 2-3 weeks, applications with calcium-containing preparations are carried out, the surface of the damaged tooth is covered with fluoride varnish to reduce sensitivity. Calcium electrophoresis is recommended to strengthen the hard tissues of the tooth. In case of severe damage to the enamel, the tooth is subject to restoration or crowning. Pigmentation during tooth erosion can be removed by polishing with toothpaste.
The use of toothpastes with phosphates, as well as the timely treatment of gastroenterological and endocrinological diseases, can prevent the development of dental erosion.







Add a comment