Today, the incredible possibilities of cells are still being explored, among which the intracellular signaling system occupies an important place.
The response of the cell to internal or external stimuli is quite complex. It is a so-called intracellular cascade of signaling molecules, consisting of many biochemical transformations. Some fragments of this system support cell survival, others are involved in apoptosis.
Understanding the features and mechanisms of functioning of signaling pathways is important for doctors of all specialties, especially for endocrinologists, immunologists and dermatologists.
Read on estet-portal.com about the mechanisms of intracellular transmission, the main types of signaling molecules and pathways that transmit information between body cells.
Varieties of molecules involved in the implementation of signaling pathways
In order to understand the mechanisms of formation of intracellular pathways of information transfer, it is necessary to understand what are the mediators – signaling molecules.
Signal molecules – these are various chemicals and their compounds that are capable of transmitting signals inside the cell from the external and internal environment of the body.
Currently, there are two types of signaling molecules: primary and secondary messengers.
Primary messengers are usually extracellular signals. These include:
• hormones;
• cytokines;
• neurotransmitters;
• growth factors
Second messengers are characterized by low molecular weight and high cleavage rate. These include:
• calcium ions;
• cAMP and cGMP;
• inositol triphosphate;
• lipophilic molecules;
• nitric oxide.
Signal molecules are also divided into lipophilic and lipophobic according to their physicochemical properties.
The role of cytokines in the treatment of non-healing wounds
Mechanism of intracellular signal transduction: classical signaling pathways
There are several classic ways of signaling between cells, among which the most studied is the MAPK (mitogen activated protein kinase) pathway.
The mechanism of the MAPK pathway is implemented as follows: first, transmembrane activation of cell receptors occurs with the help of cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins, which subsequently affects gene transcription, metabolism, cell proliferation, apoptosis, and other processes.
The signals from the first messengers are recognized by tyrosinase receptors or G protein-coupled receptors that activate the Ras and Rho families of GTPases. Protein kinases phosphorylate target proteins and transcription factors that determine specific cell responses.
Damaging influences such as oxidative stress, in addition to destroying cell components, increase the expression of a number of signaling and protective proteins.
Follow us also on Instagram
Main types of humoral regulatory effects of signaling molecules
Signal transmission between molecules has several options:
mediated signal transmission (membrane receptors) and direct reception (intracellular receptors).
Target Cells – these are cells that have specialized receptors on their surface for a particular type of signaling molecule.
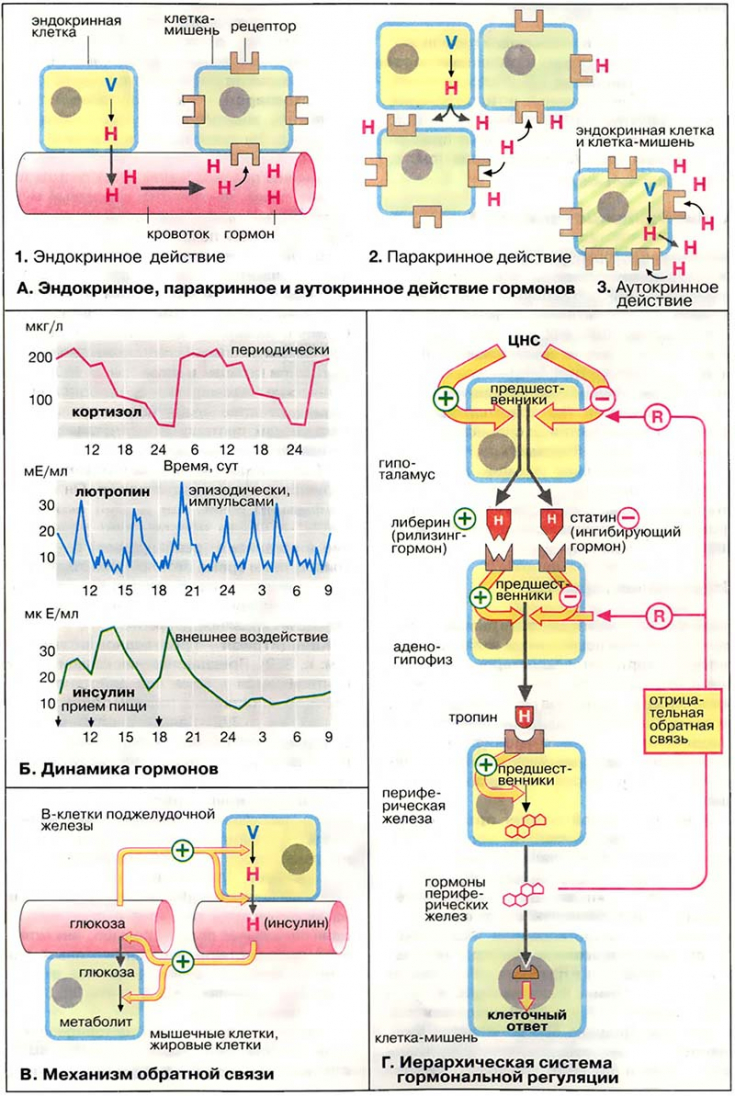
Regulation of signaling molecules is carried out by such systems as endocrine, paracrine and autocrine.
1. Endocrine regulation is that the mediators come to the target cells from the gastrointestinal system with the blood flow. This mechanism is typical for most hormones;
2. Paracrine regulation is carried out with the help of signaling molecules that are produced within the same organ;
3. Autocrine regulation is characterized by the fact that the substance affects the same cell in which it is formed, thereby changing its functional activity.
Nervous and humoral regulation is coordinated by the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
The action of hormones: everything is predetermined!
Consequences of hyperactivity of some signaling pathways for the body
Using the example of permanent activation of the signaling cascade of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), we can consider the consequences of this process for the cells of the body.
The RAS gene family is of great importance for the RAS signaling pathway. The normal RAS is predominantly in an inactive, GDP-bound form. RAS activation is regulated by receptor tyrosine kinase EGFR.
After binding of the receptor extracellular part of tyrosine kinase with a growth factor, mutual phosphorylation of its intracellular domains occurs. The formation of the active RAS-GTP complex occurs in the presence of the GAP protein activating the GTPase, which accelerates hydrolysis hundreds of times. After the hydrolytic conversion of GTP to GDP, RAS is again inactivated. The signal is interrupted. To accept a new signal, if it still exists outside the cell, the reactivation cycle must be repeated.
Thus, the RAS signaling pathway cascade acts as a switch that determines the regulation of gene expression required to effect cell division or differentiation. Constant activation of the RAS system leads to gene mutations and malignant transformation of cells.
Thank you for staying at estet-portal.com. You may also be interested in: What do we know about immuno-oncology and its role in melanoma treatment







Add a comment