A link between chronic inflammation and the process of aging.
is now commonly identified.The central role of inflammation in the context of skin health is a subject of great interest, and a growing body of evidence supports multiple causal links between inflammation and skin aging.
On estet-portal.com read which processes underlie skin aging, how it is the cascade of inflammation that develops that leads to aging, and what preventive measures should be taken to counter them.
- What factors cause chronic inflammation leading to skin aging
- Production of reactive oxygen species caused by inflammation
- Skin Aging Preventionand
What factors cause chronic inflammation, what leads to skin aging
Skin aging is a multifactorial process, the causes of which have been simplified to internal and external factors associated with inflammation.
External aging is due to a combination of environmental factors including:
- ultraviolet (UV) radiation;
- environmental pollution;
- smoking.
It is believed that external factors alone are more than 95% responsible for skin aging.
A correlation between chronic inflammation and skin aging was first postulated by Kligman and Loveker in 1988 and the association has been confirmed.
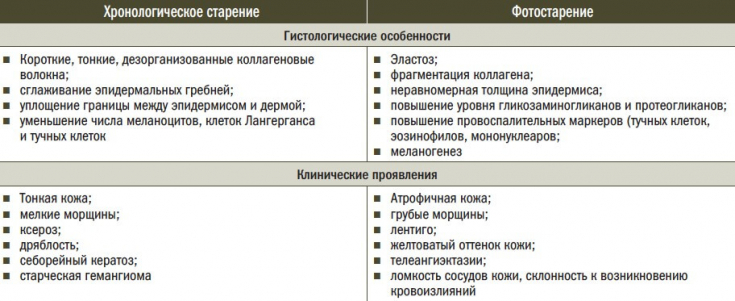
on the skin, known as "photoaging" and is considered the main cause of skin aging. This effect is mediated primarily by the
inflammatory processand its by-products. Evidence is emerging that other external factors, such as pollution, also have their detrimental
things, generating a pro-inflammatory cascade.
How to slow down skin aging: epigenetic possibilities of cosmetology Production of reactive oxygen species caused by inflammation
One of the key mechanisms of aging caused by inflammation is the formation of reactive oxidative species or
reactive oxygen species(ROS). ROS are highly reactive molecules that are considered unstable due to the presence of an unpaired electron.
They are a
by-product of oxygen metabolismand can cause oxidative damage to nucleic acids, proteins and lipids, and contribute to the regulation of intra- and extracellular signaling and gene expression. ROS can be generated from both intrinsic and extrinsic causes, but UV radiation is the most common source of ROS in the context of skin aging.
Photoaging caused by inflammation from exposure to ultraviolet radiation is mediated in several ways.
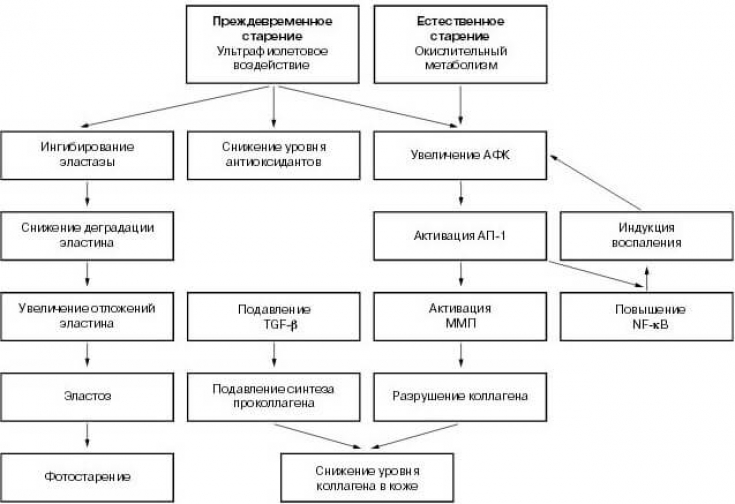 UVA is taken up by cellular chromophores (chemicals capable of absorbing ultraviolet radiation) or photosensitizers in the dermis.
UVA is taken up by cellular chromophores (chemicals capable of absorbing ultraviolet radiation) or photosensitizers in the dermis.
Absorption of this light results in an
excited state of the chromophores, which subsequently leads to DNA damage or ROS formation. ROS generation can attack cellular components such as cell membranes, proteins and lipids, as well as nuclear and mitochondrial DNA.
UV radiation can alsoact on dermal cells
, including keratinocytes, to form pro-inflammatory cytokines, which in turn attract phagocytic immune cells such as macrophages and neutrophils. These
phagocytic cellsgenerate ROS and nitrous oxide (NO) as part of their defense mechanisms, and secrete cytokines including TNF-α, interleukin 1 (IL-1), interleukin 6 (IL- 6) and interleukin 8 (IL-8) which further increase inflammatory cell recruitment and create a smoldering inflammatory environment. Another key structural component of healthy inflamed skin is
elastin. Phagocytic cells, including macrophages and neutrophils, that enter after environmentally induced inflammation release various
elastase enzymesresulting in increased degradation of elastina.
Read the most interesting articles inTelegram! Prevention of skin aging
Inflammation from both endogenous and exogenous sources is recognized as one of the
central principles of skin aging. Much of the attention of aesthetic medicine professionals is focused on addressing the effects of inflammation on the skin using a range of techniques, including therapeutic skin care, hyaluronic acid fillers, microneedles, etc.
But don't forget about
prophylaxis:
use of sunscreen;- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- a diet rich in antioxidants.
- The saying "prevention is better than cure" should become a philosophy in the management of skin aging caused by inflammation.
Inflammation plays a critical role in skin aging throughROS production
. Understanding the mechanism of action of inflammation allows the potential development of new therapeutic strategies to minimize its effect. A holistic approach should now be advocated, focusing not only on the treatment of the effects of skin aging caused by inflammation, but also on lifestyle factors, in order to provide an optimal
comprehensive approach for the treatment ofpatients.
Read also:How to slow down the aging of facial skin: 3 important steps to care







Add a comment