Burns are one of the most dangerous injuries a person can receive. The action of high temperatures in any of their forms and manifestations, for example, exposure to sunlight, flames or hot liquids, can be not only dangerous to the body, but even lead to death. As a result of a burn injury, not only the skin, but also much deeper layers of tissues can be affected, and plastic surgery is involved in their restoration. The best option for treating extensive and deep burn wounds is graft transplantation, read more about it at estet-portal.com.
Assessment of readiness of the burn wound for surgical treatment
Graft transplantation is currently the most effective method of closing burn wounds. It is possible to restore the integrity of the skin, as well as the lost deeper layers of tissues, with the help of this surgical method of treating burns. The essence of the method lies in the fact that from the donor zone, to which certain requirements are imposed, the required size of the graft is taken, which is transferred to the area of a previously prepared burn wound and surgically engrafted. Subsequently, a long-term observation of the graft is necessary, as its rejection is possible.
Burn wound:
- criteria for assessing the readiness of a burn wound for closure;
- basic requirements for donor zones;
- how the donor area is closed after taking a graft for a burn wound.
Criteria for assessing the readiness of a burn wound for closure
It is possible to transplant grafts to a burn wound only after an assessment of its readiness for surgical intervention has been carried out. The evaluation is carried out according to the following criteria:
- the presence of juicy, velvety, bright, fine-grained granulations that do not bleed when touched;
- presence of a clear trace of gauze after removal of bandages;
- presence of pronounced marginal epithelialization;
- less frequently used is the method of quantitative measurement of microorganisms in 1 g of tissues or per 1 sq. see burn wound.
In the event that necrotic masses, hypergranulations with plaque or exposed cartilage and bones are observed at the bottom of the wound, graft transplantation is contraindicated, and local treatment should be continued or osteonecrotomy should be preliminarily performed.
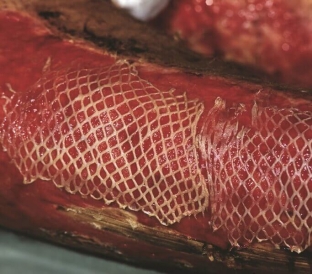
Basic requirements for donor zones
Since the burn wound is closed by transplanting a graft from the donor area onto it, certain requirements are also put forward for the sites for taking transplanted tissues:
- tissues in the donor area should be as close as possible in color and structure to the area to be closed;
- donor areas should be located in areas of the body that can be easily hidden under clothing;
- the donor area should be on the same surface as the burn wound, which is necessary to avoid moving the patient on the operating table;
- donor area should be located in places that will be easily accessible for dressings;
- It is not recommended to collect grafts above the surface of the joints. An exception is the shortage of donor sites for extensive burns.
How the donor area is closed after taking a graft for a burn wound
After taking a graft for a burn wound in the donor area, a thorough hemostasis is performed by irrigating it with warm saline with adrenaline. After that, sterile pressure bandages are applied to the wound in the donor area, which should maintain an optimal microenvironment in it, protect it from mechanical influences and prevent secondary infection of the wound. If the edges of the wound can be matched – they are sutured together and the wound is carried out as standard. Otherwise, a split skin graft is used to close the donor wound, which is fixed along its edges. Under favorable conditions, the epithelium in the donor area is restored by 8-12 days after the graft is taken, and 16-18 days after that, the donor area can be reused.







Add a comment