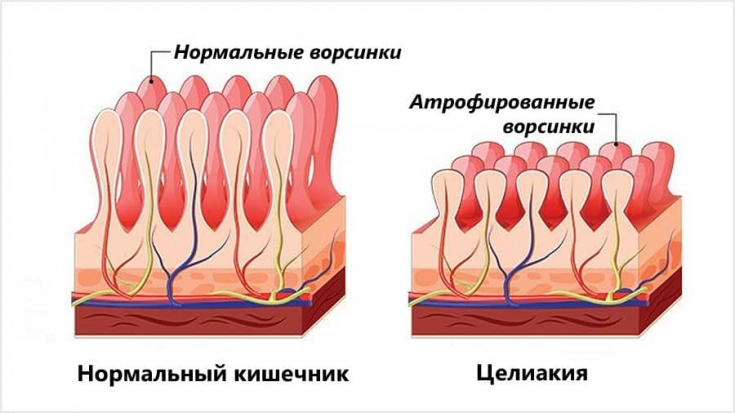
Celiac disease is a disorder of the function of the small intestine due to a deficiency of enzymes that break down gluten and peptide. Celiac disease is a genetically determined pathology. The disease is twice as common in females. Celiac disease is also called celiac disease. An inflammatory process develops in the intestine, which acquires a chronic course and is accompanied by a violation of the absorption of nutrients.
Why is bowel function impaired in celiac disease? What clinical manifestations accompany gluten deficiency? Read about the symptoms of celiac disease in our article.
Properties of gluten. Reasons for the development of symptoms of celiac disease
Gluten – it is a protein found in barley and cereals. The gluten protein contains the substance gliadin, which has a toxic effect on the mucous membrane and leads to malabsorption of nutrients.
Complete exclusion of products containing gluten leads to the restoration of the functional capacity of the small intestine of celiac patients after a few months.
The genetic condition of celiac disease is confirmed by the detection of disorders in the structure and function of the small intestine in first-degree relatives. The dependence of morbidity on the status of the immune system was revealed. Thus, in patients with symptoms of celiac disease, a high titer of antibodies to L-gliadin, endomyosin and tissue transglutaminase is found.

Manifestations of celiac disease. What symptoms of celiac disease reduce the quality of life?
Celiac disease appears towards the end of the first year of a child's life. The main symptoms of celiac disease – malabsorption syndrome, which is expressed by diarrhea, weight loss, steatorrhea and polyhypovitaminosis.
Children with celiac disease lag behind their peers in growth, their body weight decreases. In adults, the symptoms of celiac disease can be triggered by surgery, pregnancy, infections. Subjective symptoms of celiac disease include abdominal discomfort, constant drowsiness, reduced performance, pain and muscle aches.
The stool in celiac disease is liquid, frothy, with undigested food residues. More than 5 stools per day. Prolonged diarrhea leads to dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, which contributes to general dehydration of the body. Patients are pale, thin, the skin is dry, the turgor is reduced.
There are 3 forms of symptoms of celiac disease:
- The typical – develops in the first year of life with characteristic typical manifestations.
- Erased form – manifested by an erased extraintestinal clinical picture. These are anemia, iron deficiency, osteoporosis, bleeding of mucous membranes.
- Latent form – occurs in the elderly. In men, the symptoms of celiac disease develop after 40 years, in women after 30 years.
Effects of symptoms of celiac disease. What are the complications of celiac disease?
Patients with celiac disease are at risk for developing bowel cancer.
A neoplasm in the intestine should be suspected when the symptoms of celiac disease worsen on the background of a long-term gluten-free diet.
Also, with celiac disease, there is a risk of developing ulcerative eunoileitis, in which, against the background of an inflammatory process, ulcers form in the small intestine and ileum, manifested by acute pain in the abdomen and severe fever.
This condition is dangerous by perforation of the small intestine and peritonitis. Long-term malabsorption syndrome in celiac disease leads to the development of hypovitaminosis, increased bone fragility, anemia and impaired fertility.
It is therefore important to follow a strict gluten-free diet when diagnosing celiac disease to prevent intestinal complications.







Add a comment