Rosacea – it is a chronic dermatosis that predominantly affects the middle third of the face (cheeks, nose), but can also affect the central part of the forehead and chin. There are various combinations of typical symptoms of this disease: redness, telangiectasia, swelling, papules, pustules, eye damage, changes in skin texture (enlarged pores, sebaceous hyperplasia and rhinophyma). Diagnosis of rosacea causes certain difficulties, since mild forms of the disease with less severe symptoms are more common in the practice of dermatologists. However, it is very important to recognize the disease in the initial stages in order to prevent its progression. Dr. Rachel Eckel – certified dermatologist – talks about the etiology, diagnosis and treatment of rosacea in adult patients.
Problems associated with the treatment of rosacea in adults
One of the problems associated with rosacea in adults is that the first symptoms of the disease often go unnoticed by a specialist, and this greatly complicates the treatment of rosacea in the future, when the disease becomes severe.
Definition, etiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and control of rosacea – quite controversial issues today. In addition, there are no specific serological or histological markers of the disease.
Another problem is that the patients themselves (in America – about 78%) do not know how to recognize rosacea, therefore they are silent about mild or transient symptoms at a dermatologist's appointment, mistaking them, for example, for sunburn.
Rosacea in adults: the etiology of the disease
Rosacea – an inflammatory process, the exact cause of which has not been established. An important role in the development of the disease is played by excessive production of sebum, but genetic predisposition, hormonal fluctuations and lifestyle are also important factors. Interestingly, rosacea is much less common in adult smokers than in non-smokers.
Inflammation of the skin affects its permeability and weakens its barrier function. The result of these changes is an increased sensitivity of the skin. Since inflammation reduces the elasticity of the skin, rosacea often causes structural changes in the skin. Under the influence of inflammatory processes, the external aging of the skin is accelerated and the production of melanin is enhanced. Therefore, accelerated aging and non-specific skin discoloration – frequent complaints of patients with rosacea.
Also in adult rosacea, there is an excess production of cathelicidin (LL-37), which induces vasodilation of the superficial facial vessels, inflammation and vascular proliferation.
Sebum also promotes rosacea and is immunogenic, as evidenced by characteristic enlarged pores and sebaceous gland hyperplasia. Perhaps, despite the unchanged level of lipids, their composition changes, which makes these substances more pro-inflammatory. Comedones, acne, and seborrheic dermatitis, which also result from excess sebum production, are common in adult rosacea. The anatomical location of the sebaceous glands and rosacea (cheeks, chin, nose, central part of the forehead) also coincide, therefore, hyperproduction of sebum should not be excluded from the list of factors contributing to the development of this disease.
Another factor that contributes to the development of rosacea is the poor selection and use of moisturizers by patients, which leads to:
- thinning of the epidermis;
- accumulation of keratinocytes on the surface of the skin;
- impaired skin barrier function;
- decrease in fibroblast activity, including the production of natural moisturizing factors (NMFs) and glycosaminoglycans (GAGs).
Signs and symptoms of rosacea in adults
Rosacea – a multifaceted disease whose symptoms vary from patient to patient and include:
- oily skin;
- an increase in pores due to a decrease in the elasticity of the skin;
- sebaceous hyperplasia;
- dome-shaped papular lesions of red color on the skin;
- skin sensitivity (burning and tingling sensation);
- tendency to reddening of the face (this sign is more often manifested in more aggressive forms of the disease);
- persistent "blush";
- telangiectasia;
- non-specific skin discoloration;
- conjunctival hyperemia;
- inflammation of the eyelids;
- barley;
- chalazia;
- corneal injury;
- swelling;
- open follicles;
- skin hypertrophy;
- uneven bumpiness of the skin surface;
- rhinophyma.
Interestingly, rosacea patients complain of dry skin. In fact, quite often this disease is accompanied by peeling in the middle third of the face. Such a problem can be due to improper use of moisturizers and a violation of the skin barrier function, as well as seborrheic dermatitis, which is also often diagnosed with rosacea in adults.
According to the author, early diagnosis of rosacea in adults avoids permanent textural and vascular changes that require supportive procedures.
In practice, milder forms of rosacea are more common, the diagnosis of which requires exceptional care and scrupulousness from the doctor during examination (for example, skin stretch marks).
It is also important to remember that symptoms of rosacea can occur intermittently and the disease may be in an inactive stage at the time of examination. Even in the case of remission of the disease, the dermatologist can pay attention to the characteristic markers of rosacea – inflammation and increased oiliness of the skin.
In the author's experience, the most common combination of symptoms in the early stages of rosacea is:
- oily skin;
- enlarged pores;
- sebaceous hyperplasia;
- erythema (including minor);
- telangiectasia;
- acne-like formations.
Adult Rosacea Treatment Program
Although a complete cure for rosacea is currently not possible, the right choice of therapeutic methods in accordance with the symptoms and degree of the disease allows you to control the course of rosacea.
First of all, the dermatologist should tell the patient about the main triggers that contribute to the manifestation of symptoms of the disease, which include:
- alcohol;
- spicy food;
- extreme temperatures;
- exposure to sunlight.
For rosacea treatments, the author uses ZO® Skin Health (Irvine, California), which contain active ingredients (primary and auxiliary) for effective skin treatment. There are two product lines ZO® Skin Health:
- ZO® Medical (used to treat rosacea); and
- ZO® Skin Health (used for daily skin care, prevention, rosacea and anti-aging skin).
The procedures and oral medications that the author uses in her clinical practice are described below.
Topical preparations for the treatment of rosacea in adults
Epidermis correction
These three steps are the basis of daily care for rosacea:
- Oilacleanse cleanser for oily skin removes excess sebum and other impurities that lead to breakouts;
- Vitascrub Exfoliating Scrub removes dead keratinocytes and stimulates the natural exfoliation cycle and supports the skin's barrier function;
- Cebatrol Sponges to remove excess sebum and tighten pores.
Non-disease-specific substances in the treatment of adult rosacea
This optional step includes two subcategories:
- epidermal exfoliation (Glycogent) with alpha hydroxy acids: increases the rate of cell turnover to minimize clogging of the sebaceous glands, softens the texture of the skin, especially in the presence of open follicles and phimosis changes;
- sebum control (Aknetrol) with micronized benzoyl peroxide to remove and control sebum production, ideal for patients with very oily skin; benzoyl peroxide acts as an antimicrobial and micronization technology prevents inflammation.
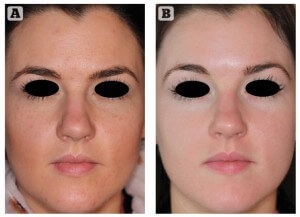
Fig. 1 Patient aged 30 before (left) and after (right) 18 weeks of treatment with ZO Medical (ZO Skin Health, Irvine, CA) in combination with oral isotretinoin (20 mg daily).
Stabilization of the epidermis in the treatment of rosacea in adults
This step is very important when working with the skin: serum (Daily Power Defense) has an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effect, stabilizes melanocytes, promotes DNA repair/protection and renews the skin's barrier function. Also, this drug increases the skin's resistance to UV radiation and inflammation provoked by it.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A Benefits in Treating Rosacea in Adults:
- restoration of the barrier function of the skin;
- thickening of the epidermis;
- normalization of the stratum corneum;
- reduction of acne breakouts;
- pigmentation equalization;
- normalization of vasculogenesis;
- reducing the signs of skin aging;
- improving skin hydration;
- narrowing of pores;
- stimulation of collagen/elastin/NMF/GAG synthesis.
In the treatment of adult rosacea, the author uses retinoic acid. For more effective penetration and action, retinoic acid is combined with Melamix and applied for three cycles of maturation of keratinocytes (18 weeks). After this period, the therapeutic properties of retinoic acid give way to chronic inflammation. Retinoic acid is replaced after 18 weeks with a high dose of Radical Night Repair or Retamax with 1% retinol to avoid irritation. This will help maintain your results and avoid unwanted inflammation.
Pigmentation
Topical vitamin A (retinol or retinoic acid/Melamix) helps to reduce non-specific discoloration in rosacea. If rosacea is accompanied by pigmentation disorders, it is necessary to use additional substances. Brightenex can be used to correct superficial pigmentation. Alternatively, Melamine (4% hydroquinone) is a suitable option for correcting deeper pigmentation disorders (eg melasma).
Sun protection
Sun exposure exacerbates rosacea by triggering an inflammatory response. Patients should apply appropriate sunscreen to their skin to limit this exposure. Interestingly, 88% of rosacea patients report a reduction in redness when using sunscreen. Oclipse-C Broad Spectrum Sunscreen SPF 50 protects skin with physical sun blocking, fractionated melanin and antioxidants and is great for sensitive skin.
Reaction monitoring
In the early stages of an adult rosacea treatment program (using the above medications), reactions such as redness, dryness, and flaking of the skin may occur. Therefore, to soothe the skin, it is also recommended to use Ommerse Daily Renewal Crème, Ommerse Overnight Recovery Crème or Restocalm.
Effective Treatments in the Adult Rosacea Treatment Program
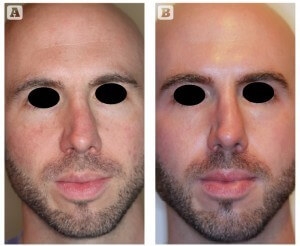
Fig. 2 Male (32 years old) before (left) and after (right) 18 weeks of treatment with ZO Medical (ZO Skin Health, Irvine, CA) combined with oral isotretinoin (20 mg daily)
There are 2 categories of lasers that are suitable for the treatment of rosacea. Rejuvenation lasers improve skin surface texture, tighten pores, eliminate sebaceous hyperplasia and rhinophyma. The author prefers to use fractional ablative CO2-laser for the treatment of adult rosacea. Vascular lasers (dye pulsed) are also suitable for the correction of erythema and telangiectasia.
This kind of procedure should only be carried out in combination with other therapeutic methods. Before laser procedures, it is necessary to first treat rosacea.
Oral medications in the treatment of rosacea in adults
Isotretinoin has been used to treat rosacea since 1981, this drug is:
- reduces sebaceous glands;
- reduces sebum production;
- leads to a decrease in the number of papules and pustules;
- has an anti-inflammatory effect;
- reduces blood flow to the skin;
- reduces the volume of rhinophyma;
- ensures long-term remission after the drug is stopped.
For optimal absorption of isotretinoin, fatty foods are required, but patients often forget how and when to take prescribed medications. New formulas of isotretinoin, developed using Lidose technology, which include a fat component that helps optimize the absorption of the drug, even when taken on an empty stomach.
For the treatment of adult rosacea, the author frequently prescribes oral isotretinoin (20 mg daily). This dose allows the application of topical preparations and is better tolerated by patients. Duration of reception – 3 months or more.
Read also: Mirvaso® – first drug specifically designed for the treatment of erythema in rosacea
The author does not support the use of antibiotics (both topical and oral) for the treatment of rosacea. The limited benefits of antibiotics for rosacea are a result of their anti-inflammatory properties, not their effect on the flora. However, if the doctor decides to prescribe antibiotics (for example, metronidazole) in addition to the indicated treatment program, it can be used after Cebatrol, and then supplemented with other components of ZO Medical. As a rule, if the skin condition does not improve after two cycles of keratinocyte maturation, the drugs are discontinued.
According to Prime magazine.







Add a comment