Age-related changes in the skin are associated with the destruction of fibroblasts under the influence of exogenous and genetic factors, hormonal changes and metabolic processes, during which reactive organic compounds, active oxygen, sugars and aldehydes are formed. The combination of these factors leads to structural changes in the skin and disruption of physiological processes in the skin. The combined use of carboxytherapy and retinoids can restore youthfulness to the skin by, among other things, acting on fibroblasts.
Age-related changes in the structure of fibroblasts and degradation of collagen
The process of skin aging is characterized by a change in the structure of fibroblasts, the linear dimensions of which increase, while the cells themselves become flatter and more rigid.
Due to increased rigidity, the rate of fibroblast migration to damaged or inflamed areas of the skin slows down, their contact with the collagen fibers of the intercellular matrix worsens.
The hallmarks of skin aging are a decrease in synthetic activity and viscoelastic properties, as well as a violation of the homeostasis of the collagen matrix.
After the age of 40, the amount of collagen fibers decreases by about 1% per year, after menopause – by about 2%.
"Young" skin (18 & 29 years old)
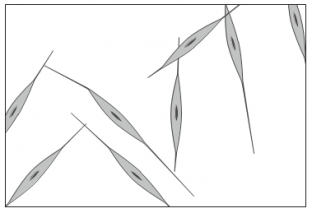
"Old" skin (80+ years)
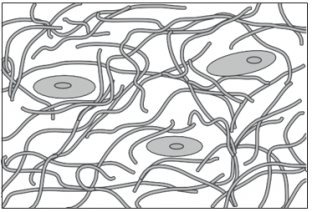
collagen degradation – the result of the activation of factor AP-1 in fibroblasts, resulting in increased activity of expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-1, MMP-2 and MMP-3).
Under the influence of metalloproteinases in the dermis, the level of procollagen types I and III decreases.
During aging collagen:
- becomes rigid and its fibrils are randomly arranged;
- undergoes irreversible modification due to the formation of cross-links between collagens – AGEs.
Reduction of mechanical stretching of fibroblasts exacerbates the decrease in collagen synthesis and increased activity of matrix metalloproteins.
All of the above processes lead to the appearance of visible signs of aging, which can be significantly reduced by the combined effect on the skin of carboxytherapy and retinoids. For this it is important to know:
- classification and mechanism of action of retinoids;
- features of the combined use of carboxytherapy and retinoids.
Cascading retinoids: classification and mechanism of action
Retinoids – lipophilic derivatives of vitamin A, which easily penetrate the epidermis through:
- transepidermal pathway (stratum corneum);
- transfollicular route (excretory ducts of the sebaceous glands).
Retinoids, the concentration of which decreases towards the dermis, control the processes of keratinization and pigmentation in the epidermis and contribute to the restoration of the extracellular matrix in the dermis.
Therefore, retinoids are used to reduce the manifestations of photoaging, acne, hyperkeratosis, wrinkles and other dermatological problems. For this purpose use:
- retinol esters;
- retinol;
- retinaldehyde;
- oxiretinoids.
The Retinoid Cascade Method used in the MEDICARE Retinoid Care Program provides retinoid action at different levels of the dermal-epidermal junction:
- retinyl palmitate normalizes the structure of the skin, smoothes wrinkles, stimulates cell renewal and collagen synthesis, and also helps fight acne;
- retinyl acetate increases the level of collagen and elastin, accelerates the process of getting rid of dead cells;
- All-trans retinol restores skin density, stimulates collagen synthesis, increases hydration and improves skin texture.
Retinoids affect the growth of epithelial cells, their differentiation and functional activity.
Benefits of combining carboxytherapy and cascade retinoids
Retinoids not only stimulate the synthesis of new collagen, but also inhibit the destruction of existing collagen fibers under the influence of external factors.
The effect of retinoids on the skin depends on the level of activity of the enzymes responsible for the metabolism of retinoids in the skin. The targeted action of enzymes is ensured by the absence of protein metabolites in the skin.
Maximum results with minimal irritation are achieved by combining carboxyteration and a retinoid cascade.
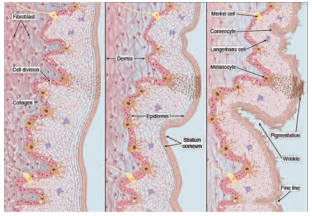
The effect of carboxytherapy and retinoids is provided by the following mechanisms:
- wrinkle reduction – the result of enhancing the ability of the epidermis to retain moisture, stimulating the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans, transforming growth factor beta, procollagen and collagen;
- reducing skin dryness – the result of accelerated epidermal renewal, achieved by accelerated maturation of keratinocytes;
- hyperpigmentation reduction – the result of accelerated cell renewal of the epidermis.
The course of retinoids allows you to restore barrier epidermal lipids, consisting mainly of free fatty acids and ceramides.
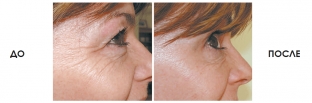
The use of a combination of carboxytherapy and retinoids provides excellent results: restoration of skin elasticity and tone, its natural protective functions, smoothing wrinkles, reducing hyperpigmentation and acne, improving skin structure and color. For information about the scheme for the combined use of retinoids and carboxytherapy, as well as answers to all your questions, you can get from MEDICARE.







Add a comment