The formation of stones in the prostate often becomes one of the established diagnoses of middle-aged and elderly men. The prostate gland is a very important organ for men's health, which, unfortunately, often gives men a lot of trouble, since the prostate gland loses its function with age and can undergo hyperplastic changes. The pathological process in the prostate creates favorable conditions for the formation of calculi in it, which must be eliminated in a timely manner in order to return the man to his male health.
Main symptoms and treatments for prostate stones
Stones in the prostate are formed as a result of a long-term chronic inflammation of the prostate gland, that is, they are one of the complications of chronic prostatitis. In most cases, there are multiple prostate calculi, the size of which can vary from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. Finding and removing stones from the prostate gland is necessary as early as possible, since their long-term location in the prostate leads to its gradual atrophy.
Stones in the prostate:
- what are the symptoms of stones in the prostate;
- methods for diagnosing stones in the prostate gland;
- the main methods of treatment of stones in the prostate.
What are the symptoms of prostate stones
Since stones in the prostate are formed against the background of chronic prostatitis, the symptoms of this pathology are superimposed on the clinical picture of the inflammatory process. Prostate calculi are manifested by the following symptoms:
- constant dull pain in the perineum and sacral region, which increases during intercourse, driving on rough roads, or during bowel movements;
- frequent, painful, and difficult urination;
- Hamaturia may occur in severe cases;
- Hemospermia is the presence of blood in the semen.
In some patients, the disease has a latent course, patients may not present any complaints and calculi in the prostate are found incidentally during a routine examination or as a result of a plain radiography of the pelvis.
Methods for diagnosing stones in the prostate gland
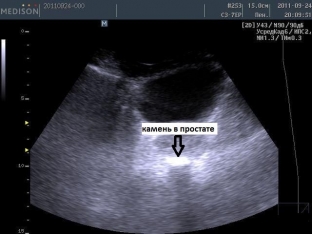
The diagnostic process of stones in the prostate gland is based on the data of digital rectal examination and instrumental diagnostic methods. During palpation of the prostate gland, the stones in it are determined in the form of strong formations; if they are close to each other, crepitus may be noted during palpation. Plain x-ray shows dense shadows behind or above the pubic symphysis. Informative is also an ultrasound examination of the prostate with a filled bladder, which allows you to accurately determine the size, number and location of stones. Stones on ultrasound are defined as clear echopositive prostate masses with acoustic shadowing.
Basic Treatments for Prostate Stones
The treatment of prostate stones in most cases is limited to conservative methods of therapy. Patients are prescribed only anti-inflammatory therapy to eliminate chronic prostatitis. To date, the following methods for removing stones from the prostate are also widely used:
- transurethral endoscopic prostate surgery;
- laser crushing of stones;
- electroresection of the prostate gland;
- remote shock wave lithotripsy.
Open surgery is performed only when an abscess of the prostate is formed in order to empty it. In most cases, with timely therapy, the prognosis for the patient is favorable.






Add a comment