Timely diagnosis of syphilis in the early stages of infection is difficult due to the absence of acute manifestations of the disease. But there are characteristic signs in the form of specific erosions and ulcers that affect the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, as well as damage to the lymph nodes typical of syphilis, which makes it possible to correctly classify the symptoms and begin treatment already in the primary stage of the disease.
Features of trophic disorders in syphilis
The incubation period, or the period from the moment of infection with syphilis to the appearance of a hard chancre, is on average 21-24 days.
Under the influence of trophic disorders of the epidermis caused by vascular lesions characteristic of syphilis, necrosis occurs in the center of the infiltrate and erosion develops. In some cases, tissue decomposition is observed, which begins from the surface of the element, as with the development of erosion, penetrates to a great depth and forms a primary ulcer. Most often, primary syphiloma is found in the form of erosion or ulcers ranging in size from a grain to a little finger nail or a 1-kopeck coin, of a regular round or oval shape. The bottom of the erosion is often smooth, as if polished, the boundaries are clear. The color of syphiloma is usually red – like freshly cut meat. Another shade may be typical – gray, dirty gray, dark, which depends on the film-like pseudo-diphtheria plaque, which adheres tightly to the bottom. Such erosions seem to be covered with a layer of "spoiled fat". The edges of the syphiloma either lie on the same level with the surrounding skin and the bottom of the erosion, or gradually, as in a deep saucer, descend to the center of its bottom (saucer-shaped primary erosion). The discharge of uncomplicated primary syphiloma is serous. The presence of a seal at the bottom of a primary syphiloma is the most characteristic, almost pathognomonic symptom.
Current of primary syphilis
The peculiarities of the clinical course of primary syphilis in modern conditions should also include an increase in the localization of pathological lesions in the oral cavity. Primary syphiloma, located on the upper or lower lip, has the form of erosion or more often an ulcer covered with a crust.
The form of syphiloma may also be different. Developing at the site of a former linear abrasion or crack, scratching, as well as in skin folds, erosion can take an oval shape (chancres of zaeda, chancres of the tongue).
Chancre-amygdalite in syphilis
There are three forms of tonsil chancre: erosive, ulcerative and anginal (amygdalite). The clinical picture of the first two varieties is characterized by the presence of a hard, painful chancre, which can be mistaken for a banal sore throat. Only the third form is considered atypical, in which erosion or ulcers are absent or not detected during external examination, and only an increase in the tonsils is noted. To establish the correct diagnosis, attention is paid to the following signs: unilateral enlargement of the tonsil, its pastosity, the absence of widespread redness, and the presence of submandibular and cervical lymphadenitis, which is often painful. The anterior cervical lymph nodes may be enlarged.
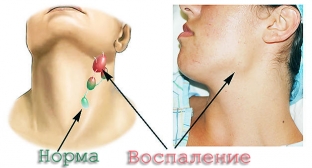
Associated bubo (sclerodenitis) with syphilis
Regional lymphadenitis is an integral part of the primary period of syphilis. The localization of concomitant sclerodenitis always corresponds to the location of the chancre and the direction from the last lymphatic vessels. The altered lymph nodes are enlarged to the size of a bean, a small plum, a pigeon's egg, sometimes larger, dense, not connected either to each other, or to the surrounding fiber, or to the skin, and therefore mobile, have an ovoid shape and are not painful. It is characteristic that not one lymph node is enlarged, but a group (“pleiad”) nodes, and one of them is usually larger.







Add a comment