Potassium and sodium – minerals that are common in the cells of our body and are involved in the same biochemical processes, but with the opposite effect. Ideally, they should balance each other. However, nowadays there is a trend towards an excess of sodium in the human body. Of course, it is necessary to maintain the vital activity of cells, like potassium. However, if the balance of these elements is disturbed (in conditions of excess sodium and potassium deficiency), the well-being of the whole organism, especially the cardiovascular system and the brain, is at risk. Estet-portal.com will tell you how to maintain a healthy balance of potassium and sodium in the body.
Causes and dangers of potassium and sodium imbalance
The balance of potassium and sodium is necessary to ensure the normal functions of the body. A normal sodium to potassium ratio helps maintain healthy bones and normal blood pressure.
The levels of these minerals can be regulated through nutrition.
The body tends to retain sodium (via the renin-angiothesin-aldosterone system) and use up potassium. That is why it is easier for the body to survive the lack of sodium than its excess. In the event of a decrease in the level of sodium in the body, the adrenal glands (or rather, the adrenal cortex) begin to produce the hormone aldosterone, under the influence of which the kidneys begin to absorb the available sodium again.
Potassium is constantly excreted in the urine, especially under stress. This feature of the organism is explained by evolutionary features – ancient people did not have access to table salt that we are used to, so their body learned to retain this mineral. Hunters could do without salt, while farmers experienced a shortage of salt, but received enough potassium from fresh vegetables and fruits. Thus, there is no mechanism for storing potassium by the body.
In modern conditions, things are exactly the opposite: we add salt to any dish, use it in the form of various additives, and the amount of raw vegetables and fruits containing potassium in the diet of a modern person has significantly decreased. Constant stressful situations only exacerbate the problem, as they contribute to the excretion of potassium and the accumulation of sodium.
What is the danger of excess sodium?
Possessing a diuretic effect, potassium promotes the excretion of excess salt that does not benefit the body, while sodium contributes to the accumulation of metabolic products and water retention.
- Hypertension – one of the consequences of the imbalance of potassium and sodium towards the latter. The peoples who consume mainly raw plant foods are practically unaware of the problem of high blood pressure, which cannot be said about the inhabitants of megacities.
- Excess sodium in the body is associated with a 73% increased risk of death from any disease compared to the minimum content of this mineral.
Proper intake of potassium prevents:
- kidney and gallstones;
- lime deposits in joints and vessels.
Potassium deficiency symptoms:
- fatigue;
- severe leg cramps;
- muscle weakness;
- breathing difficulties;
- cardiac arrhythmias;
- constipation;
- nausea;
- swelling;
- Infrequent urination.
How to restore the balance of potassium and sodium in the body?
The best way to raise your potassium levels in your body is to eat fresh, plant-based foods. And the more intense the physical and mental loads, the more a person consumes salt, the greater the need for potassium.
The optimal ratio of sodium and potassium in food – 1:2–1:4.
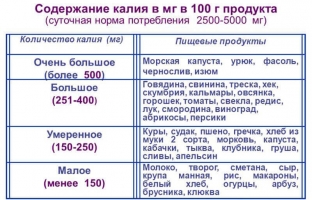
Sodium and potassium are involved in the same biochemical processes, but they perform opposite functions. Violation of the balance of these elements is fraught with malfunctions of entire body systems. The main way to maintain a healthy ratio of these elements is nutrition. The balance of potassium and sodium is achieved through the inclusion of raw (unprocessed) plant foods in the diet.






Add a comment