Precancerous lesions may be optional or obligatory. Obligate precancer is an early oncological pathology, which tends to turn into cancer over time. In contrast, facultative precancerous diseases do not always develop into cancer, but require very careful monitoring. At the same time, the longer the treatment of an optional precancerous condition is delayed, the higher the likelihood of developing a malignant tumor. Find out in the article which ailments are precancerous conditions.
Precancerous diseases: types and causes of development
The presence of a precancerous background does not at all indicate that it will definitely turn into cancer. So, precancerous diseases turn into malignant only in 0.1 – 5% of cases. Diseases that fall under the category of precancerous include almost all chronic inflammatory processes.
There are 3 categories of precancerous diseases:
- precancerous diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- precancerous skin diseases;
- precancerous diseases of the genital organs in women.
Precancerous diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
The probable cause of cancer development is chronic gastritis, especially its anacid form. Atrophic gastritis poses a great danger, in this case the incidence of cancer is 13%.
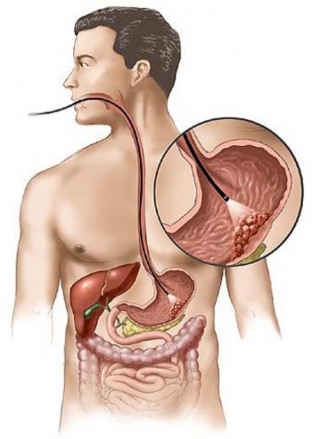 Menetrier's disease (tumor-simulating gastritis) is also a precancerous disease – this disease in 8-40% of cases is the cause of stomach cancer.
Menetrier's disease (tumor-simulating gastritis) is also a precancerous disease – this disease in 8-40% of cases is the cause of stomach cancer.
The probability of a stomach ulcer turning into a malignant state depends on its size and location. The risk increases if the ulcer diameter exceeds 2 cm.
Precancerous pathology of the stomach includes gastric polyps, especially a group of adenomatous diseases more than 2 cm – here the possibility of transition to a malignant state is & nbsp; 75%.
Diffuse polyposis is an obligate precancer – in almost 100% of cases, this precancerous disease develops into cancer. This disease is transmitted genetically and degeneration into a malignant state occurs at a young age.
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are facultative precancers and should be treated conservatively.
Precancerous skin conditions
They can transform into malignant tumors:
- nevi;
- chronic radiation damage to the skin;
- late radiation dermatitis;
- actinic keratoses;
- senile keratosis and atrophy;
- trophic ulcers, chronic ulcerative and vegetative pyoderma, which persist for a long time;
- ulcerative and warty form of lichen planus;
- scar changes in the skin in the foci of erythematous and tuberculous forms of lupus
- limited precancerous hyperkeratosis of the red border of the lips, keloids.
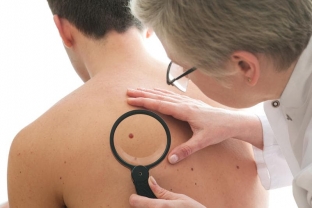
Dubreu's precancerous melanosis, pigmented actinic keratoses, epidermal-dermal borderline nevus are highly prone to malignancy.
In 5-6% of cases, carcinomas develop from scars resulting from burns. Benign epithelial tumors prone to becoming malignant are cutaneous horn (12-20% of cases) and keratoacanthoma (17.5%).
Although the chances that warts and papillomas will turn into malignant changes are quite small, there are still a number of cases when cancer develops from them.
Precancerous diseases of the female genital organs
The cervix is most often affected, in second place – ovaries, further – vagina and external genitalia. At the same time, cervical polyps rarely degenerate into cancer, as they are accompanied by bloody discharge, which is why they are quickly diagnosed and removed in a timely manner.
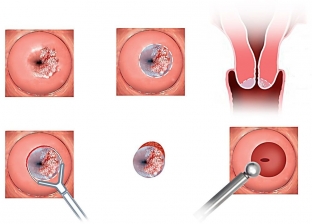
Erosion can be present in a woman for months and even years and does not manifest itself in any way. If cervical erosion exists for a long time and is not treated, it can cause the development of a tumor. The main cause of cervical and uterine cancer is the human papillomavirus.
Ovarian cysts in the early stages in women are asymptomatic and can only be detected during a gynecological examination. Any recognized cyst must be removed.
Vaginal cancer develops due to leukoplakia. In women who neglect hygiene, leukoplakia turns into ulcers, which in the future can become the basis for the development of cancer. In the advanced stages, treatment is difficult, especially if you refuse to see a doctor regularly. It should be borne in mind that vaginal cancer is more dangerous than cervical cancer, so all chronic diseases of the vagina must be treated in a hospital setting.
Cancer is often the cause of neglect of one's health and in many cases it is possible to prevent its development through regular check-ups with doctors. In order to prevent such an outcome, one should be especially attentive to any deterioration in well-being and visit specialists in time.






Add a comment