In winter we prefer to eat more and sit in front of the TV. As a result, we quickly gain extra pounds. And it's not even that the cold weather is not conducive to long walks. This is due to our biological clock, which goes astray due to lack of sunlight. It is its deficiency that causes a lack of some and an overabundance of other hormones.
This imbalance affects our condition: we become less active and more often complain of fatigue. This condition can be adjusted if you know how to properly set the internal clockwork.
- Biological clock in winter: low hormone levels
- Biological clock in winter: excess melatonin
- Biological clock in winter: just add water
- Biological clock in winter: your lungs don't get enough oxygen
- Biological clock in winter: protect yourself from the cold
Biological clock in winter: low hormone levels
In winter, the level of serotonin, dopamine and beta-endorphin in the blood drops rapidly. The deficiency of these hormones affects our condition: we think more slowly and get tired faster.
Subscribe to our page on Facebook!
Lack of serotonin is especially affected. This hormone is actively involved in the regulation of blood pressure and body temperature, in the processes of blood coagulation. It also stimulates the central and peripheral nervous system. If this does not happen, then we become depressed.

Winter depression affects about 20% of people, mostly women. They are four times more likely than men.
Subscribe to our page on Instagram!
Lack of sunlight also affects the insufficient formation of vitamin D in the body. It is he who promotes the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, which affects bone strength and dental health. It also regulates the secretion of insulin and reduces the level of bad cholesterol in the blood.
What to do? Phytotherapy will help. The light emitted during such procedures does not contain UV radiation, so it does not burn or harm the eyes. For the same purpose, you can visit the solarium.
Contraindications for herbal medicine:
- diabetes mellitus;
- hyperthyroidism;
- conjunctiva and other
eye diseases. Biological clock in winter: excess melatonin
We sleep more in winter than in summer. This is due to — the sleep hormone melatonin, which increases as soon as it gets dark. If it is light outside, its level drops, and we feel a surge of energy. In winter, the days are short, so the high production of melatonin is maintained around the clock. As a result, during the day we often sleep on the go, and at night, on the contrary, we suffer from
insomnia. High levels of this hormone also affect the internal organs. For example, it suppresses the function of the thyroid gland, which secretes less thyroxine (T4). Lack of them leads to a slowdown in metabolism and weight gain.
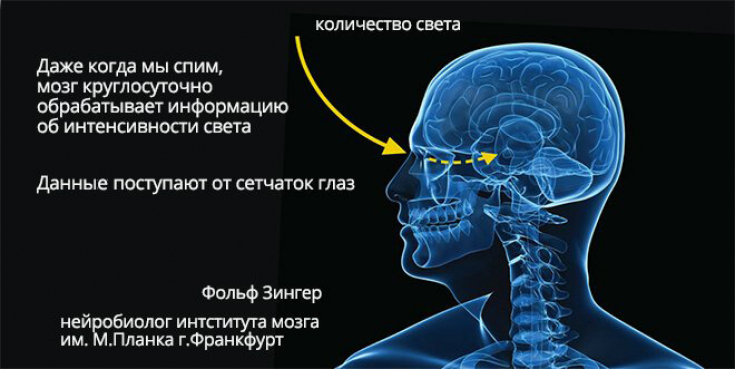
What should I do?
- Drink a cup of green tea with guarana or a glass of freshly squeezed citrus juice. It will give you strength.
Keep the bedroom temperature below 18°C.
Make sure your dinner diet includes carbohydrates (porridge, pasta, banana) and protein (cottage cheese, fish, lean white meat). This will support- melatonin production. Biological clock in winter: just add water
In winter, the skin loses moisture almost twice as fast as in summer. This happens because of the cold temperature outside and the warm — in room. As a result, the skin becomes dry and prone to irritation.
Lack of water
in the body affects chronic fatigue. The fact is that the blood thickens, flows more slowly, and nutrients enter all the cells of the body more slowly.
Drying of the mucous membrane leads to a weakening of the immune system. The body is less able to defend itself against the attacks of pathogens.
Drink at least 2 liters of fluid daily. It is best that it be mineral water, green or fruit tea. Eat soups, they also supply water to the body.
Don't forget about cosmetics that protect the skin fromdrying and frost. - Biological clock in winter: your lungs lack oxygen The biggest threat to the lungs is chemically polluted air. The content of these impurities especially increases in winter, when there are no natural filters, such as plant leaves.
in large cities, the oxygen content in the air drops to 18%. That is, it only covers the minimum needs of a person.
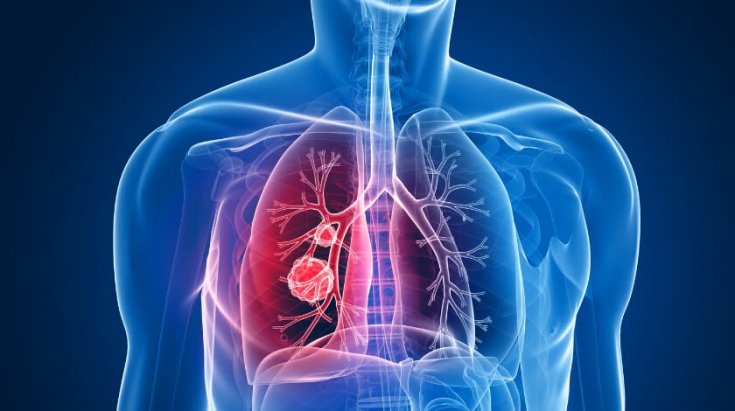 In addition, low temperatures cause spasm of blood vessels, worsening blood supply. This means that the distribution of oxygen throughout the body is worse.
In addition, low temperatures cause spasm of blood vessels, worsening blood supply. This means that the distribution of oxygen throughout the body is worse.
What to do?
Ventilate the premises more often.
-
Stay outside every day.
Do aerobic exercises. They increase lung capacity, accelerate blood circulation and thus improve blood oxygenation. Skiing, running - , swimming,
- on an exercise bike also contribute to this. Biological clock in winter: protect yourself from the cold Our body protects itself from the cold in winter in various ways. Sweating is reduced and, at the same time, metabolism is accelerated to release more energy. This protects against hypothermia, but can also lead to an increase in toxins, in particular due to the fact that in winter we eat more fatty foods.

Dress warmly, according to the weather. Don't forget the scarf and hat.
- Eat little but often. Make sure that your menu includes vegetables and cereals from whole grains. This will help cleanse the
body
. - See more important and useful information on YouTube:






Add a comment