Bronchoadenitis – this is a lesion of the intrathoracic lymph nodes, it is a manifestation of the primary tuberculosis complex. Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic nodes is rarely a consequence of a primary complex.
The symptomatology of bronchoadenitis directly depends on which nodes are affected - tracheal, tracheobronchial, bronchopulmonary, bifurcation or lateral aortic. Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic lymph nodes is most common in childhood. How is tuberculous bronchoadenitis diagnosed? What is the difficulty in diagnosing and why?
Types and forms of tuberculous bronchoadenitis
There are such forms of tuberculosis of the lymph nodes: infiltrative, tumor-like and small - when no changes are detected on the x-ray in the direct projection, they are visible on the CT or lateral x-ray. Recently, just such a variant of bronchoadenitis has been found quite often.
The infiltrative form is very difficult to distinguish from the tumor-like form, therefore it is proposed to distinguish the hyperplastic form, caseous and indurative by morphological changes.
- The hyperplastic form is characterized by the presence of reversible changes, since the lymph node contains lymphoid tissue and epithelioid humps.
- In the caseous form, the knot is a caseoma. This is the most severe form of bronchoadenitis.
- The indurative form is characterized by the growth of fibrous tissue.
What symptoms of bronchoadenitis development should alert?
The presence of bronchoadenitis is manifested by an increase in temperature to 38-390C, which may soon decrease slightly and remain subfebrile. Children begin to sweat profusely at night for no particular reason, their appetite disappears and a cough develops that resembles whooping cough. Cough worries at night, at first it is dry, and then sputum begins to be coughed up.
In connection with the vaccination of children, chemoprophylaxis, hospitalization and long-term treatment of patients with active forms of tuberculosis, the clinical manifestations of lymph node involvement in tuberculosis become more and more erased over the years. All symptoms of bronchoadenitis are mild and rarely forced to see a doctor.
The role of radiography in the process of diagnosing bronchoadenitis
It is very difficult to diagnose bronchoadenitis, as the process develops in the depth of the chest. Therefore, nothing can be detected percussion, dry rales can be heard auscultatively, which is unlikely to give reason to suspect tuberculosis. Thus, only a chest x-ray makes it possible to diagnose the process.
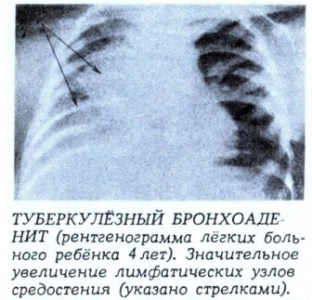 In this case, the examination should be carried out not only in the direct projection, but also in the lateral and posterior, since the shadow of the lymph nodes can hide behind the shadow of the heart. Of great importance in the diagnosis of bronchoadenitis is tomography of the tracheobronchial tree. To avoid unnecessary exposure of children, tomography is performed only in the presence of convincing clinical symptoms and in the absence of any pathologies on the chest x-ray.
In this case, the examination should be carried out not only in the direct projection, but also in the lateral and posterior, since the shadow of the lymph nodes can hide behind the shadow of the heart. Of great importance in the diagnosis of bronchoadenitis is tomography of the tracheobronchial tree. To avoid unnecessary exposure of children, tomography is performed only in the presence of convincing clinical symptoms and in the absence of any pathologies on the chest x-ray.
Pi X-ray examination revealed a shadow in the lung tissue and displacement of the mediastinal organs to the side of atelectasis. This is a symptom of Goltzknecht – Jacobson. Hilar bronchiectasis and atelectasis that remain are sometimes an indication for surgery.
Associated symptoms and consequences of bronchoadenitis. How can the process end?
Tuberculous bronchoadenitis is most often unilateral. In rare cases, the nodes are affected on both sides, when perifocal inflammation of the lung tissue develops with the development of a butterfly symptom. In patients with tuberculous bronchoadenitis, there may be signs of compression of the mediastinal organs, which is accompanied by a complication of the passage of food.
In the general blood test, such changes are observed - leukocytosis, accelerated ESR and lymphopenia with caseous pneumonia.
The consequence of tuberculous bronchoadenitis may be sclerosis of the lung root, resulting in the formation of hilar bronchiectasis, which can provoke pulmonary bleeding. Such changes in the lungs can only be detected by bronchography or bronchoscopy.






Add a comment