Intestinal Flu — mysterious disease. Many know it personally, and some suffer repeatedly and yet don not know that such a disease doesn exist
What is colloquially referred to as the "stomach flu" is actually part of a larger group of illnesses caused by rotaviruses and noroviruses. These microorganisms, in contrast to the "normal" flu, affect not the respiratory organs, but the gastrointestinal tract.
But when the first symptoms of intestinal flu appear, treatment requires the same attention as a respiratory infection. Because seasonal and intestinal flu are united not only by their viral nature, but and high probability of complications.
- Symptoms of the intestinal flu: the main signs of the disease
- Treatment of intestinal flu: basic principles of therapy
Symptoms of the intestinal flu: the main signs of the disease
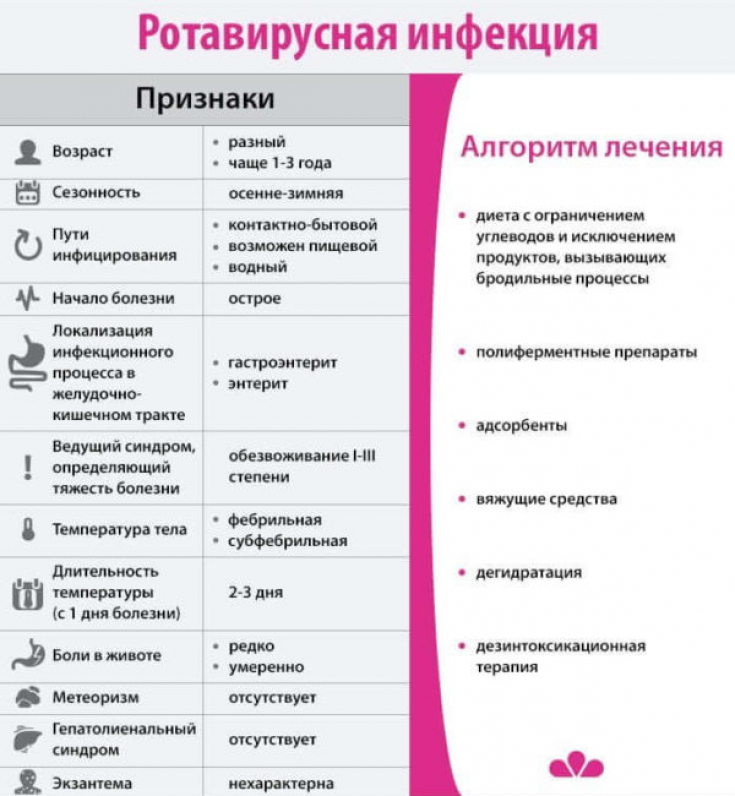
The onset of the disease is always acute: the transition from feeling good to poor health can occur within 1-2 hours The first symptom of intestinal flu — an increase in body temperature to & nbsp; 38.5-39.5 ° C, after which other manifestations of the disease begin:
-
Vomiting. It is not associated with food intake, and in on the first day it is uncontrollable — the patient vomits very often, even if the stomach is empty.
-
Diarrhea. This symptom only comes on 2 or 3 days. At first, defecation is normal, but then the stool becomes liquid, the feces are foamy, with a characteristic unpleasant odor. The frequency of urges can reach 5-7 times hours.
-
Symptoms of intoxication. Body aches, severe headache, severe loss of appetite or its complete absence, nausea — these signs point to viral intoxication.
Read also: Top 5 Unexpected Places Where Germs & Bacteria Are Waiting for You
From the description of the symptoms, you can understand why rota- and norovirus infections are called intestinal flu — they manifest themselves in the same way as food poisoning. But in the latter case, the body temperature usually remains normal or slightly lower, which is completely atypical for intestinal flu.

This disease most often affects children of the first 3 years of life and old people — their immune system has its “weaknesses”, as a result of which the disease can deal a heavy blow to health. It is these categories of patients that need the earliest possible start of treatment.
Treatment of intestinal flu: basic principles of therapy
In many cases, recovery occurs on its own, between 3 and 7 days from the onset of the disease. But this applies only to patients whose immunity is strong enough, and the general state of health is not worsened by any chronic pathologies. Otherwise, intestinal flu can lead to severe complications, and the most likely — dehydration.
Therefore, in all situations when the disease proceeds rapidly, and the patient is in the high-risk group due to age or health condition, it is necessary to start treatment immediately as soon as the disease has declared itself.
Complex therapy includes:
-
Consumption of large amounts of liquid. In case of severe diarrhea and vomiting, it is necessary to replenish the loss of water with the help of unsweetened fruit drinks, mineral water, electrolyte solutions.
-
Antiemetics. Vomiting, which in the first few hours is in the nature of a cleansing process, subsequently only increases dehydration and greatly worsens the patient's well-being. To eliminate this symptom, the doctor prescribes drugs that suppress the gag reflex.
-
Anti-diarrheals. These are prescribed if the diarrhea lasts more than 1 days and is debilitating.
-
Enterosorbents. These drugs, passing through the intestines and, not being absorbed into blood, absorb toxins and viruses, which reduces the overall level of intoxication.
-
Antipyretics. Drugs of this group are prescribed if the body temperature exceeds 38.5° in adults and 38.0° in children who do not tolerate fever.
Read also: Winter is coming: how to protect yourself from diseases
Depending on the peculiarities of the course of the disease and the general health of the patient, the doctor may supplement the treatment with other drugs and methods.
In the process of therapy, it is important to follow a diet — the diet should consist of boiled and mashed vegetables, lean meat, cereal soups, and any foods that promote fermentation and gas formation (cabbage, legumes, pastries, sweets) should be excluded from it.
Treatment of young children or patients with a severe course of the disease is carried out in a hospital setting. This allows you to control all vital signs and conduct intensive therapy aimed at eliminating dehydration and preventing other complications.
Read also: Protection against flu: popular myths and good advice
You might be interested: Perfect belly in 5 minutes!






Add a comment