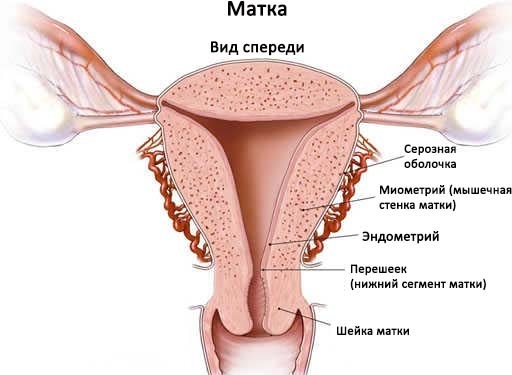
Studying your body, you must have come across such a concept as the endometrium. But not many people know what it is. It is the inner lining of the uterus, which is supplied with blood vessels. It also lines the cavity of the genital muscular organ. This mucosal layer is very important for women's health. After all, with his participation, menstruation occurs. But the main function of the mucous membrane is that it creates favorable conditions for the conception of a baby. In this article, the editors of estet-portal.com will share with you information regarding physiological changes and endometrial thickness. You will also find out what pathologies are common among women of reproductive age.
Cyclic changes in the lining of the uterus
The endometrium grows and then flakes off. These are very important physiological processes by which the reproductive system of a woman works like clockwork. By its nature, the mucosa is sensitive to hormones. In the first phase of the menstrual cycle, estrogen acts on the endometrium. This hormone promotes the growth of endometrial glands, as well as the growth and development of follicles that produce estrogens and regenerate the epithelium.
In the last phase of the cycle, under the influence of progesterone, the mucosa becomes thicker and richer in glands. At the same time, it is richly supplied with blood. All this creates favorable conditions for the normal fertilization of the egg and its further attachment to the wall of the uterus.
If pregnancy does not occur, the hardened endometrium flakes off and exits the uterus along with menstrual flow.
After the end of menstruation, a new menstrual cycle begins. At the same time, in the uterine mucosa, with the participation of a deeper endometrium, recovery processes occur after the rejection of the upper layer. And when pregnancy occurs, the endometrium is not rejected. This phenomenon is prevented by hormonal processes occurring in the body.
What is the normal thickness of the endometrium
The thickness of the endometrium is very important for pregnancy. Under the influence of female sex hormones, it changes during the menstrual cycle, like the lining of the uterus itself. Each phase of the cycle has its own layer thickness. You can determine it using ultrasound.
Below is the norm for the thickness of the endometrium in a particular period of the menstrual cycle:
• 5-7 days of cycle – 3-6mm, average is 5mm.
• 8-10 days of cycle – there is a thickening of the endometrium up to 8 mm. It can vary from 5 to 10 mm.
• 11-14 cycle days – the mucosa thickens up to 11 mm. Variations are possible from 7 to 14 mm.
• 15-18 cycle days – the thickness of the endometrium ranges from 10-16 mm. Average – 11 mm.
• 19-23 cycle days – mucosal thickness maximum – 14 mm, can vary from 10 to 18 mm.
• 24-27 cycle days – there is a slight decrease to 12 mm. There may be fluctuations of 10-17mm.
In order for the fertilized egg to safely attach to the body of the uterus, the optimal layer thickness should be 7 mm.
If there are deviations from the norm, this indicates the presence of pathology. Below we will consider what diseases exist, and also find out the causes of their occurrence.
Hyperplasia: thickening of the lining of the uterus
When the endometrium grows too fast, it becomes thicker than usual. This condition of the mucous membrane is called hyperplasia. This disease is benign. It occurs in two forms:
• Simple – there are many glandular cells that provoke cystic formations. It can be glandular or fibrous tumors. There are also mixed polyps.
• Atopic – a progressive form of the disease in which the structure of the tissue changes. In most cases, adenomatosis is malignant.
Hyperplasia may be asymptomatic. But often the pathology makes itself felt through the following signs:
• Violation of menstrual cycle – it becomes either shorter or longer.
• Profuse bleeding with clots during menstruation.
• Change the duration of "critical days".
• Small bleeding a couple of days before the start of menstruation.
• The appearance of blood during sex.
There are many causes of hyperplasia. The disease can cause:
• excess estrogens and lack of progesterone;
• late abortion;
• constant stress;
• surgery on the endocrine gland;
• inflammatory processes of the genital organs;
• Sexually transmitted infections.
Most often, hyperplasia occurs in women suffering from diabetes mellitus and arterial hypertension, as well as those who take contraceptives containing estrogens for a long time.
If there are no symptoms of pathology and there is no infertility, treatment of hyperplasia is not carried out. And in all other cases, the doctor prescribes hormonal drugs or an operation in which the layer of the endometrium is removed. In a particularly serious condition of the patient, a complete removal of the uterus may be required. Comprehensive treatment is also possible, which includes surgery and supportive hormonal therapy.
Hypoplasia: the presence of a "thin" endometrial layer
If the upper or lower uterine mucosa is underdeveloped, it remains thin throughout the cycle. This pathology is called hypoplasia. At the initial stage, it practically does not manifest itself.
The disorder is usually detected by a gynecologist during an examination. In general, hypoplasia is characterized by the following characteristic symptoms:
• presence of pain during menstruation;
• irregular cycle;
• short-term "critical days";
• scanty menses;
• lack of orgasm;
• insufficient hairline of the external genitalia.
The thin endometrium prevents the fertilized egg from attaching to the uterine wall. Often this pathology leads to infertility.
"Culprits" hypoplasia can be both hormonal disruptions and various diseases of the genital organs. The following factors also lead to such a pathology:
• inflammatory processes in the uterus;
• abortions;
• impaired blood supply to the tissues of the uterus;
• heredity;
• Ovarian surgery.
Violation of the lining of the uterus is not always treatable. But if you turn to a gynecologist in a timely manner, the chances of recovery increase. So, obstetrician-gynecologists prescribe to the patient estrogen in high dosage and aspirin in small doses. Acupuncture is also sometimes used for treatment, which improves blood circulation in the pelvis.
Endometrium – an important part of the female body. If a pathology of this mucous membrane is detected, it is necessary to carry out therapy. And the sooner the better. In this way, you will not only preserve your health, but also increase the chances of getting pregnant and bearing a healthy baby.
See also: Profuse periods: a cause for concern or a sign of illness






Add a comment