The brain coordinates the work of the whole organism, therefore, a violation of its functions inevitably entails concomitant malfunctions in the work of the constituent elements of our body. A rather dangerous reaction of the body to injury, infection or excessive stress is cerebral edema. This condition develops quite quickly, so it is important to suspect a violation in time and contact a specialist in order to promptly carry out diagnostic measures, determine the cause of the edema and ways to effectively eliminate a potentially dangerous problem.
Cerebral edema: methods for diagnosing pathology
It is important to understand that it will not be possible to diagnose cerebral edema on your own, for this, specialists use the following methods:
- CT and MRI of the brain;
- measurement of intracranial pressure;
- lumbar puncture;
- examination of the fundus;
- neurological examination;
- collection and analysis of anamnesis.
The body reacts with cerebral edema to the impact of damaging factors.
Cerebral edema is accompanied by an increase in ICP, as the cells and intercellular space of the brain are rapidly filled with fluid. As a result, the volume of the brain increases.
Next we will look at:
- causes of occurrence and classification of GM edema;
- symptoms of GM edema;
- treatment and possible complications of GM edema.
Causes and classification of cerebral edema
The most common factors causing cerebral edema are:
- Injuries:
- alarms;
- blows to the head;
- falls.
- Ischemic stroke.
- Hemorrhagic stroke.
- Infectious diseases, most often:
- encephalitis;
- meningitis;
- toxoplasmosis;
- subdural abscess.
- Tumours.
- Climbing to a height of more than 1500 m above sea level (often found among climbers).
In newborns, the cause of the described pathology is most often the trauma received during childbirth.
Types of cerebral edema:
- local, diffuse and generalized (in the lesion, in one hemisphere and in both hemispheres, respectively);
- swelling of the brainstem, blood vessels or substance of the brain;
- vasogenic, cytotoxic, ischemic, interstitial;
- postoperative, post-traumatic, toxic, neoplastic, inflammatory, epileptic, ischemic, hypertensive, neuroendocrine.
Symptoms that indicate the presence of cerebral edema
Symptoms increase in severity as intracranial pressure increases. So, in the initial stages of cerebral edema, the following symptoms can warn:
- headaches, which can be quite severe;
- dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- partial impairment or complete loss of vision;
- irregular breathing;
- fainting;
- brief convulsions;
- loss of ability to navigate in space;
- memory lapses;
- speech difficulty;
- neck stiffness;
- swallowing disorder;
- discoordination;
- in severe cases – coma.
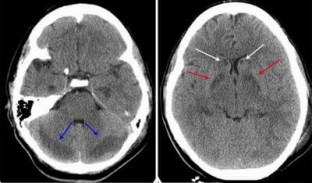
If you suspect cerebral edema, which occurs on the basis of the above symptoms and possible injuries or infections, you should urgently seek medical help.
Treatment of cerebral edema and possible consequences
If the cause of cerebral edema is a slight jar or a change in height, in most cases no special treatment is required – after a while, the brain returns to normal on its own.
The pathology treatment method is chosen by the doctor after establishing the cause of cerebral edema and the patient's condition. The main goal of treatment is to restore the oxygen supply to the nerve cells. Available pathology elimination methods:
- Oxygen therapy (administration of oxygen to improve brain nutrition).
- Hypothermia (decrease in body temperature).
- Medicated treatment (may be aimed at combating the disease that caused the swelling).
- Ventriculostomy (removal of excess fluid through a special catheter to reduce ICP).
- Intravenous infusion (to eliminate pressure surges and improve blood circulation in the brain).
The consequences of cerebral edema depend on the degree of development of the pathology, the timeliness of diagnosis and treatment. Most patients experience headaches, suffer from sleep disorders, forgetfulness, absent-mindedness, and depression. Violations of communication skills and physical activity are not excluded, in severe cases, paralysis and even death occur. That is why estet-portal.com urges in no case to ignore the potential signs of edema and seek medical help in a timely manner.






Add a comment