Pigmentation occurs in many people, especially those with fair, sensitive skin. And some types of pigmentation have become popular in the beauty industry, and, moreover, freckles are an undeniable trend in the modeling business today.
However, not in all cases, pigmentation is a purely aesthetic highlight, sometimes they can hide danger and manifest serious diseases of the endocrine and cardiovascular system.
On estet-portal.com read about the causes of hypo- and hyperpigmentation, what disorders they may indicate, and what methods are used to combat them.
Pathological and physiological conditions of the body that provoke the appearance of pigmentation
Pigment spots appear under the influence of various endogenous and exogenous factors.
The main ones are:
• the influence of ultraviolet radiation (excessive insolation);
• hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause, oral contraceptives);
• diseases of the hepatobiliary system (cholestasis);
• endocrine disorders (hyperthyroidism);
• genetic mutations (albinism);
• disturbances in the work of the adrenal glands (Addison's disease);
• toxicodermia;
• vitamin deficiency;
• cellular aging.
Follow us on Instagram!
Before prescribing treatment, it is imperative to exclude possible serious diseases and conduct a thorough examination.
Mechanisms underlying hyperpigmentation
Any pigmentation is an uneven distribution of melanin pigment in the epidermis. It is known that melanocytes, long-lived dendritic cells with a slow division cycle, are responsible for its production.
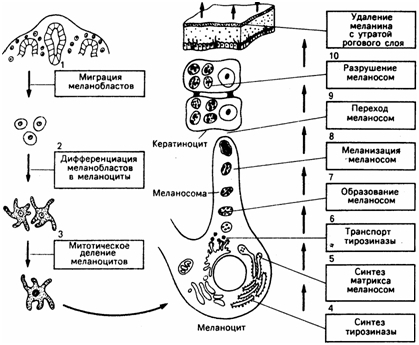
The enzyme tyrosinase activates the oxidation of tyrosine, resulting in the formation of melanin – our protection against burns and overheating.
With the help of melanosomes, the pigment melanin enters the cells of keratinocytes.
Keratinocytes – the main component of the epidermis (more than 80%). These cells are actively involved in the distribution of "brown pigment", on which the color of human skin depends. xxxx>
Main pathogenetic mechanisms of changes in skin pigmentation
There are several main pathogenetic mechanisms that underlie skin pigmentation disorders, namely:1. Cell aging
Pathogenesis consists in disruption of the melanin-producing apparatus, that is, in its "aging", as a result of which patches appear with hyper or hypopigmentation.
2. Cell DNA damage
As in the first case, the function of melanocytes is impaired due to changes in the genetic material of the cell.
Most often, DNA damage occurs under the influence of ultraviolet radiation and in the presence of the Mc1r gene ("red hair gene").
When the genetic material of the cell is damaged, areas of hypopigmentation appear, for example, with vitiligo or leukoderma.
As a result of the influence of melanin-stimulating hormones (melanotropin, MSH) on the pituitary gland during pregnancy or medication, an excess of pigment is released.
4. Lack of fatty acids
The transport of melanin along the dendritic processes is disrupted due to their shortening and loss of flexibility.
Effective methods to combat skin pigmentation
When studying the problem of age spots, it becomes obvious that it is not too easy to influence the intracellular process of melanin production, especially due to aging or genetic changes in the skin.
But there are still effective treatments, such as:
• antioxidant therapy;
• use of tyrosinase inhibitors;
• use of UV blockers; • laser peeling;
• fractional photothermolysis;
•
skin whitening
;• application of fatty acids (omega-3), vitamins (A and C).
The treatment program is developed individually depending on the phototype and characteristics of the patient's skin. After any procedure to eliminate pigmentation, it is necessary to use sunscreen and monitor the condition of the skin. You may also be interested in: Skin Lightening Vitamin C






Add a comment