You lose your hair every day – and this is normal, because each hair has its own life cycle. But if there are more tufts of hair on the comb than usual, you should consult a dermatologist. It will help determine why your hair is falling out more, what form of hair loss you have, and what treatment options are available. Bernd Mones, world-famous stylist, hair designer, head of Hair Studio by Bernd Monés and Orisen
Diagnostic methods for hair loss
Hormonal-hereditary (androgenic) hair loss is often diagnosed quite clearly by the degree of thinning of the hairs or by the pattern of baldness.
Local hair loss can also be seen by its characteristic features: well-defined bald spots on the head with smooth skin where the hair has been lost.
When diffuse scalp hair loss occurs, the doctor will investigate the causes more closely to understand why this is happening. A blood test will help determine a possible metabolic abnormality or nutritional deficiency.

For basic diagnosis, four important laboratory parameters are examined:
- hemoglobin level in the blood - indicates that the patient is anemic; this is often the cause of iron deficiency;
- - ferritin level – this value gives information about the iron content in the body;
- - TSH value - indicates the likely presence of a thyroid disease;
- - erythrocyte sedimentation rate or other inflammatory parameters (eg, white blood cell count) - may indicate the presence of a chronic inflammatory disease.
In addition, there are various other tests and some studies that indicate the possible causes of hair loss, help to more accurately study the nature and assess the extent of baldness.
The most important instrumental diagnostics
The use of special devices and techniques enables the doctor to more accurately determine the causes of hair loss and the development of scalp diseases, and make assumptions about the prospects for treatment.
Epilations test (pull test): a pull test is performed on several areas of the head: the doctor takes a small tuft of hair with his fingers and pulls it lightly. He does it in different places and in different directions. This method helps to establish how easily the hair is separated from the scalp and gives a rough idea of the intensity of hair loss.

Trichogramma makes it possible to study the hair roots. Hair goes through different phases in their life (cycles): growth - or anagen, rest - or catagen, and telogen – fallout stage. With the help of a trichogram, you can evaluate how much of the hair is currently at each of the stages. This study provides an opportunity to determine the intensity of hair loss.
To make a trichogram, approximately 20 to 50 hairs are removed from the patient with tweezers in the direction of growth. The hair roots are examined under a microscope to determine what stage of the cycle they are in. In total, more than 80 percent of the hair should be in the growth stage and less than 20 percent in the shedding stage. The remaining few percent of the hair is usually in the transitional phase.
The method of extracting the hair in this case is important for the study. Some patients, fearing pain during the extraction of hair with tweezers, bring to the doctor the hair that remains on their comb after combing. For a trichogram, they are worthless, as they are all clearly in the fall-out phase.
TrichoScan is a special computer program in which the following parameters can be determined using digital photography:
hair density per square centimeter;
hair thickness;
The rate of hair growth over time.
This helps in assessing the pattern of hair loss. In addition, a comparison of the condition of the hair can of course be recorded before and after the treatment. It shows how well the prescribed treatment affects hair growth. With this diagnostic method, the hair is not removed. However, it is necessary that one or two areas of the head be shaved and a small area of the skin should be dyed.
After three days, the regrown hair is photographed at a high magnification that the software allows. The program helps to calculate the rate of hair growth and their number at different stages of development: in the anagen phase, the hair grows at a certain rate, and in the telogen phase, the hair does not show growth.
Biopsy – analysis of tissue samples of the scalp. It does not give a complete diagnostic and correct clinical picture of hair loss, because it allows you to analyze hair loss in certain areas of the head, and this is not sufficient to classify the causes of hair loss. The method is used, for example, in cases of suspected cicatricial alopecia. This is permanent hair loss due to inflammation of the scalp and subsequent scarring.
Scalp biopsy usually takes two small tissue samples. This is such a deep cut to "catch" the hair follicles in their entirety. The samples are analyzed in the laboratory in more detail.
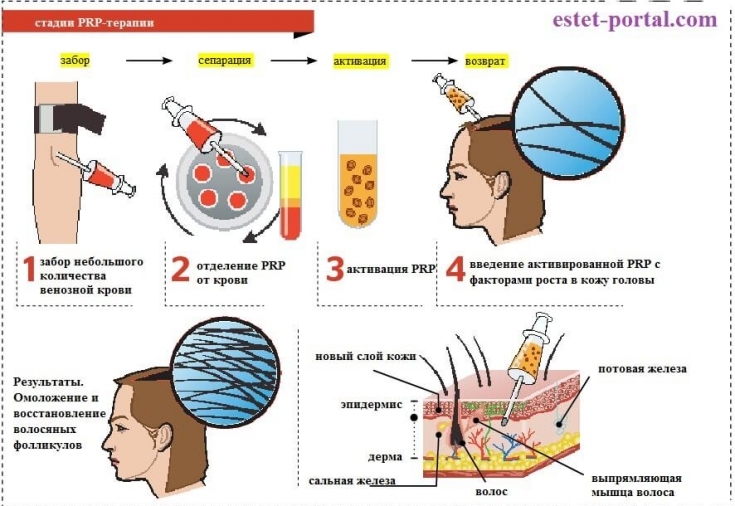
What to do if you notice hair loss
If thinning of hair on the head begins, many people ask: what helps with hair loss? Most hair loss treatments are designed for hormonal hereditary alopecia.
The common feature of all such remedies is that their effect develops over several months and is not permanent. This means that after stopping the medication, hair loss returns. In general, the success of drug therapy for hair loss is difficult to assess – one specific remedy helps, the other does not.
Types of drug therapy
Finasteride was originally known as a drug for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia and was prescribed only for an enlarged prostate.
Later, doctors discovered that some patients who took finasteride had improved hair growth. After that, companies developed their own hair loss products based on finasteride.
Finasteride – these are so-called 5α-reductase inhibitors, i.e.: they block the 5α-reductase enzyme, which converts the normally male sex hormone testosterone into its active form, dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Because the hereditary sensitivity of the hair roots in androgenetic alopecia is caused primarily by DHT, finasteride may stop the progression of hair loss in affected men. Sometimes after taking the drug, the hair on the head becomes thick again.
Prescription drug and is used in the form of tablets (1 mg). High dose tablets (5mg) are only available for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Use: men with hormonal hereditary hair loss.
Side effects: Finasteride may, in rare cases, reduce subjective sexual desire (libido).
The effectiveness of the drug does not affect other functions of the body. Small amounts of the drug can pass into seminal fluid. However, these amounts are not sufficient to harm the unborn child of a pregnant partner.
For women, however, this drug is not suitable because in pregnant women or women of childbearing age, potential harm to the fetus cannot be ruled out. In addition, studies have shown that finasteride does not have a beneficial effect on hormonal hereditary hair loss in women.
Alfatradiol - (Alfatradiol), 17α-estradiol is a similar endogenous female sex hormone, which, unlike finasteride, has only a small hormonal effect. Crucial for its use as a hair repair agent is its inhibitory effect on the 5α-reductase enzyme. Like finasteride, 17α-estradiol thus prevents the conversion of testosterone to active dihydrotestosterone.
17α-estradiol is available by prescription as a hair tincture.
Usage: Men and women with hormonal hereditary hair loss.
Side effects: The alcohol in the tincture may cause local skin reactions such as itching and redness.
Minoxidil, like finasteride, was originally conceived to treat a different condition, high blood pressure.
Here, too, an increase in hair growth is observed as a side effect. Subsequently, researchers developed a minoxidil-containing tincture for people suffering from hair loss. The exact mechanism of action of this topical agent is not known, but it may include, among other things, increased blood flow to the scalp.
Minoxidil is available by prescription: hair tinctures - there are 5% solutions for men and 2% solutions for women. In tablets, the drug is used only as antihypertensive drugs.
Usage: Men and women with hormonal hereditary hair loss.
Side effects: The most likely to cause problems with the hair tincture are local skin reactions such as itching, redness, and flaking of the skin.
Less common side effects are systemic, i.e. those that affect the whole body: This happens, for example, in rare cases - causes dizziness, heart palpitations and low blood pressure.
In some patients, hair loss temporarily increases a few weeks after the start of treatment. The reason is believed to be that the hair mass in the shedding (telogen) phase is "pushed out" by intensely renewed hair entering the anagen phase. The effect is seen as a response to minoxidil.
Studies have shown that products containing the active ingredient minoxidil are likely to have an effect on hair growth, but may not completely stop hair loss.

Antiandrogens can sometimes help women with hormonal hair loss. These are substances that prevent the action of testosterone (or DHT) by blocking its receptors. Experts believe that this mechanism of action can stop hair loss, but there is still no scientific evidence for this.
Antiandrogens are found in some hormonal drugs and contraceptives (eg, chlormadinone acetate, cyproterone acetate, dienogest) and are taken as tablets.
Use: women with hormonal hereditary hair loss.
Side effects: possible symptoms include fatigue, lack of energy, and loss of sexual desire.
Women of childbearing age who are suffering from hair loss should take antiandrogen and estrogen combinations for prophylaxis.
The fact is that androgens can lead to the "feminization" of the male fetus. Estrogens, on the other hand, should activate actions against hair loss: this increases the amount of the so-called sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG). As a result, more testosterone accumulates in the blood. However, the hair follicle can only receive free testosterone.
Smokers are not recommended to take sex hormone preparations because they increase the risk of blood clots (thrombosis, embolism).
Hair transplantation has the best effect on hormonal hereditary hair loss. The transplant takes advantage of the fact that the hair follicles at the back of the head are not sensitive to testosterone and therefore do not fall out.
Small pieces of tissue with hair follicles from the occipital region are transplanted into bald spots on the crown of the head. The disadvantage of hair transplantation is that the result usually does not look as natural as in the case of successful treatment of hair loss with drugs (finasteride, minoxidil) that prevent the loss of one's own hair.
Diffuse hair loss treatment is effective when the cause is removed. It may be thyroid dysfunction, responsible for increased hair loss, then you should deal with the disease in the first place.
If your hair loss is caused by certain medications, your doctor will tell you if you can switch to another medication. It happens that nutritional deficiencies cause diffuse hair loss - these are changes in diet, due to which essential nutrients (such as zinc, vitamins, protein) are not delivered to the hair. Then a change in diet may fix the problem.
Since the hair follicles remain intact in alopecia areata, in principle, the hair is completely restored on its own. Although there are various therapeutic approaches, their effectiveness is questionable.
For less severe cases, doctors prescribe zinc (in the form of effervescent tablets). In addition, if necessary, in severe cases, the doctor recommends glucocorticoids to achieve improvement. They are applied externally or internally, like hair tinctures or cream, like tablets.
Hair Loss: What You Can Do For Yourself
Hair loss in women often becomes a serious cosmetic problem for them, because hair is at the first place in assessing the health and attractiveness of a person.
Many try to solve the problem with caffeine-containing hair loss shampoos, immune stimulants or dietary supplements. All such products promise to return hair by stimulating blood circulation in the scalp. For most of these agents, evidence of effectiveness has not yet been accepted.
Hormonal-hereditary hair loss is never completely reversible, with the help of cosmetics it can, at most, – slow down or hide.
The right haircut can hide bald spots or areas of thinning hair. It is recommended to leave a length of 3:57 centimeters at the top of the head, and the areas of the ears and neck should be left free.
If you can't get a hair transplant, you can try using a hair replacement. To date, there are wigs and pieces made of natural and synthetic hair in different shapes and colors that can be fixed on the head - temporarily or permanently.
With many similar hair substitutes, you can even swim. In any case, you can get professional advice at Hair Studio by Bernd Monеs.
Hair loss: when the loss is accompanied by mental stress
Whether male or female, the most important factors for mental well-being are considered to be awareness of hair loss and acceptance of oneself in this condition. Those who have stable self-esteem may not equate hair loss with loss of external attractiveness, since changes in appearance do not affect their personal inner strength.
However, some need help to gain self-confidence, teach them to calmly look at the world even with a bald head. Anyone who believes that hair loss weighs him down emotionally should not be afraid to seek psychological help.
 Therapy for self-esteem
Therapy for self-esteem
You should seek professional psychological support if:
- hair loss is taking away your enjoyment of life;
-
You often feel insecure about your hair loss; - You have become avoidant of certain situations and activities;
- You feel like an outsider because of your hair loss;
- You are afraid that others will notice your hair loss;
- You are worried that you will not be able to find a partner due to hair loss or that your partner is moving away from you;
- You feel shy about losing your hair during sex;
- Hair loss prevents you from communicating with other people.
- With the support of a psychotherapist, you can learn how to get rid of fears and negative emotions associated with hair loss. Believe me, you are not disfigured, you just have little hair or even none at all. If your hair loss is not related to illness, you can simply remember the comfort associated with feeling your physical health and forget that you have little hair.
Source estet-portal.com






Add a comment