Complete blood count – a very common procedure, which is carried out in order to determine the pathological processes occurring in the body. Clinical blood test – a fairly quick and informative diagnostic method that allows the doctor to determine the cause of the symptoms that the patient complains about by changes in the composition of the blood. Of course, it is better to entrust the interpretation of a general blood test to a specialist, however, knowing the main indicators and their norms, you can independently determine whether you are healthy or not.
Deciphering the complete blood count – important points
In our time deciphering a complete blood count is possible even online – the patient simply enters the indicators available to him and receives the necessary interpretation. However, it is better to entrust this responsible matter to the attending physician. The procedure itself is not complicated and is prescribed in the following cases:
- for the purpose of determining a course of treatment;
- in case of scheduled medical examination;
- before vaccination;
- to identify contraindications.
The only precondition for blood sampling is to abstain from food prior to blood donation, as the food consumed may affect the results. And inaccurate results can lead to incorrect selection of the course of treatment, which will lead to patient dissatisfaction, additional costs and an extension of the treatment period.
Before donating blood for a general analysis, you should not eat at least 3 hours before blood sampling.
Blood is taken from a finger after treating the finger of the left hand with alcohol, making an incision a couple of millimeters deep on the fingertip and collecting blood with a pipette.
If blood from a vein is required for analysis, after processing the inside of the elbow bend, the vein is punctured with a hollow needle, with which blood is drawn into a special container.
Indicators that are taken into account when deciphering the complete blood count
Before proceeding with the decoding of a complete blood count, you need to know what this or that indicator means. So, the indicators of the general blood test are as follows:
- hemoglobin (Hb) – serves to transport oxygen to the cells and carbon dioxide to the lungs;
- erythrocytes (RBC) – transport hemoglobin, with which their functions are closely related;
- color score (MCHC) – shows how erythrocytes are saturated with hemoglobin;
- reticulocytes (RTC) – immature erythrocytes;
- platelets (PLT) – are responsible for blood clotting and healing of damaged tissues;
- thrombocrit (PST) – ratio of blood and platelets;
- ESR (ESR) – erythrocyte sedimentation rate;
- leukocytes (WBC) – protect the body from pathogens and cellular decay products;
- leukocyte formula – the number of each type of leukocyte in the blood;
- plasma cells – participate in the production of antibodies.
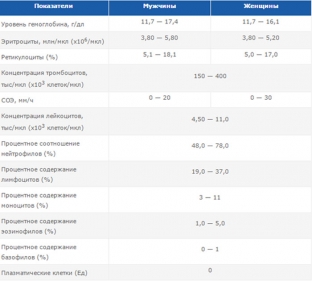
The norms of the indicated indicators for adults:
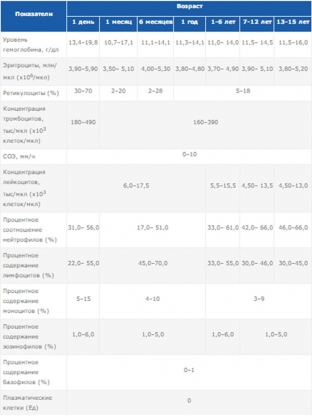
Norms for children:
What do abnormalities indicate
Deviations of analysis indicators from the specified norms can occur for various reasons: both serious and completely harmless. For example, elevated white blood cells may indicate a bacterial infection, leukemia, or cancer, but may also be the result of surgery, intense physical activity. A decrease in the level of leukocytes may be due to a lack of vitamins, a viral disease. ESR may increase before menstruation, from the fifth week of pregnancy and after childbirth (from 4 weeks).
If you suspect any serious illness, your doctor will perform additional tests to help make a diagnosis.
When deciphering the results of a general blood test, the doctor compares various indicators, which allows him to draw a conclusion about the patient's state of health. Remember that self-diagnosis in this case is excluded. If you have any doubts that your test results have been correctly interpreted, it is best to seek the advice of another qualified professional.






Add a comment