Self-harm or pathomimia (English self-harm) – manifestation of auto-aggression, which is manifested by conscious or unconscious injury to oneself.
Many believe that self-mutilation – just a way to get attention. In fact, this behavior is often caused by a number of psychogenic factors and may be indicative of mental disorders.
Self-destructive manifestations usually look like ulcers, hematomas, erosions, as well as excoriated acne. Sometimes a skin disease is simulated so believably that self-harm is very difficult to distinguish from real-life dermatological diseases.
Read on estet-portal.com about the causes and symptoms of pathomymia, as well as about the treatment of mental disorders.
Patomimia Manifestation: Our Bad Habits Are Not Groundless
The most common form of pathomimia is the so-called neurotic excoriations — damage resulting from repeated scratching of the skin by the patients themselves. This phenomenon is also defined by the concepts of "psychogenic excoriations"; or "compulsive scratching of the skin".
More often (52-92%) neurotic excoriations occur in women. The dermatological picture of neurotic excoriations is extremely diverse: from minor abrasions to deep excoriations with bloody crusts or deep scars.
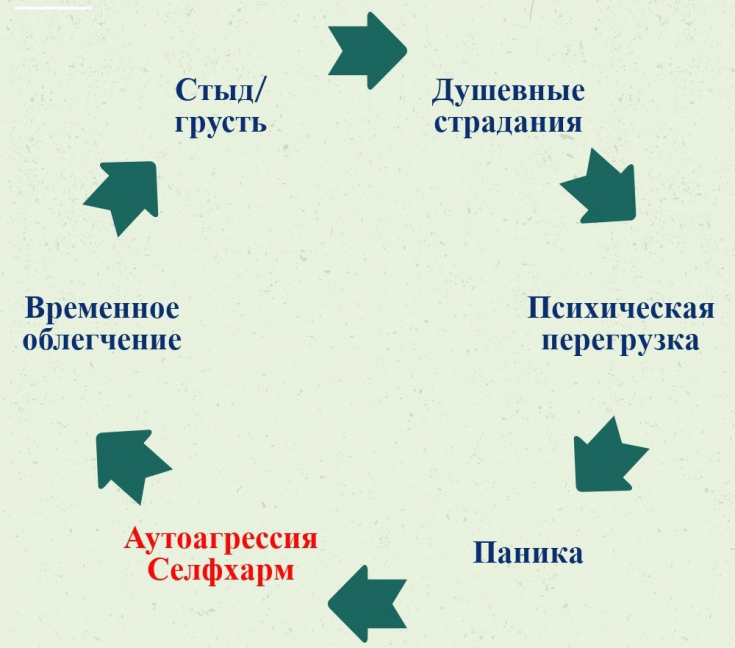
Self-damaging skin diseases include:
• dermatomania (the desire to damage the skin, its appendages, mucous membranes);
• trichotillomania (compulsive hair pulling);
• onychophagia (nail biting);
• cheilophagia (lip biting);
• dermatotlasia (biting the skin around the nail bed).
Self-harm – this is a clear psychological or mental problem, so you should not turn a blind eye to such behavior and think that it will pass by itself.
Psychological causes of self-harm: triggers
In the pathogenesis of pathomimia, as a rule, mechanisms of autoaggression lie. Autoaggression – a way for an individual to cope with difficult emotional experiences, to cope with pain and strong emotions.
Everyone has their own reasons: the loss of a loved one, toxic relationships, rejection in the family or society, and so on.
Self-harm can also be a sign of various pathologies of the psyche: depression, post-traumatic syndrome, hysterical personality disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, organic brain damage, alcoholism, drug addiction, emotional instability, autism, oligophrenia, schizophrenia.
Scientists distinguish three main components of the formation of pathomime:
1. frustration: restraining one's emotions and aggression;
2. traumatic situation: accumulation of aggression due to external objects;
3. an internal need to resolve the conflict.
Also, self-harm can be a call from loved ones to draw attention to themselves, which often occurs in adolescence.How to help loved ones with depression : 5 important rules
Symptoms of pathomimia: everything is visible on the face – demonstrative self-harm
Often, patients disguise pathomymia as various dermatological diseases. However, there are several reliable signs of self-harm:
• constant appearance of new skin wounds;
• location of mutilations in easily accessible places;
• negative response of a person to medical care and denial of self-harm;
• subjective state of a person: anxiety, poor sleep, phobias, feeling of inferiority.
The manifestations of pathomimia are varied: some patients pull out hair, burn, scratch the skin until it bleeds, or make deep cuts. Often patients deliberately injure themselves or do it quietly, claiming that they are sick with something.
Existential crisis: what it is and how to overcome it
In the presence of persistent self-harm, first of all, it is necessary to consult a specialist: a dermatologist, a psychotherapist and a psychoanalyst. Drug treatment consists of a course of drugs that have anti-inflammatory and healing effects. Physiotherapeutic methods are also used: paraffin therapy, electrophoresis, laser therapy. In parallel, psychotropic drugs, antidepressants or sedatives are prescribed. It all depends on the severity of the patient's condition. The most important task – identify the psychological cause of auto-aggressive behavior and eliminate traumatic factors.
Psychotherapy can be very lengthy, because a person with pathomimia often does not want to immediately make contact and solve problems.
During such a period, it is important to provide maximum support and show understanding to a person, because self-harm – this is a cry for help. Such people need to learn to love and accept themselves completely, no matter what.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Psychology" section. You may also be interested in:
Feelings of Fear and Anxiety: Coping in 5 Steps






Add a comment