You must have noticed that people living together not only partially adopt each other's habits, but also become similar to each other. So, it is assumed that the reason for this similarity lies in the mirror neurons. In addition, there is a theory that it is this type of neurons that is responsible for a person's ability to empathize. Estet-portal.com will tell you what mirror neurons are and how they are related to the ability of humans and animals to empathize (empathy).
Mirror neurons – the key to empathy and understanding?
In the 1990s, Italian scientists, while observing the cerebral cortex of monkeys, discovered an interesting pattern: the same motor neuron fired in a monkey not only when she herself took food, but also in the process of observing similar actions of another monkey. This phenomenon interested scientists, because the ability to put oneself in the place of a fellow is inherent in people. Mirror neurons called a certain set of cells that "mirror" are activated when observing certain movements of another person (animal).
It is also interesting that mirror neurons only respond to certain types of actions that we can predict from past experience. For example, they do not react to the usual movement of the hand. But if we see a person who feels pain, is about to eat something delicious or drink cold water on a hot day, we understand at the synaptic level what the person is going to do next. Moreover, we often want to do the same.
Tune in to the "wave" another person is possible not only with the help of sight: sounds, smells, tactile sensations also contribute to this phenomenon.
Mirror neurons – healthy criticism of an interesting theory
The theory that it is thanks to mirror neurons that we are capable of empathy is quite attractive and logical. For example, we see how bad a person is, mirror neurons are activated, we automatically “tune in” to on his wave and partially adopt the feelings of a person. And since mirror neurons are connected to other areas of the brain that send messages to all parts of the body, we are able to "synchronize" with another person, even physiological indicators: breathing, blood pressure, heart rate. In addition, emotional contagion is also associated with mirror neurons – those. the occurrence of identical or similar emotions perceived by another person in a certain situation.
This is why, as some experts suggest, autistics and psychopaths are not able to empathize with others – their mirror neuron function is impaired. The same is said about patients with schizophrenia.
Critics of the theory about the key role of mirror neurons in understanding the actions and emotions of other people believe that the conclusions of the theory are too global and have not yet been confirmed.
The fact is that tracking and explaining the activity of mirror neurons in the human brain is not so simple. Therefore, James Kilner and Roger Lemon of University College London studied in detail 25 scientific papers that analyze records of mirror cell activity in monkeys. These records indicate the presence of motor cells, the properties of which are similar to mirror ones in:
- frontal lobes of the brain that control movement;
- in the parietal lobe.
However, some of these cells are only capable of mirror reaction when observing a living being; others are capable of such a response to video-recorded movements. It is also observed that some mirror neurons respond to a small number of specific movements, while other groups of neurons respond to a wider range of movements or even to the sounds that accompany such movements. Some cells are able to suppress activity while observing certain movements.
It is also noted that the angle of observation and the possibility of receiving an award – factors affecting the activity of mirror neurons in monkeys. Such features indicate, most likely, that mirror neurons – only part of a complex system of brain activity that specialists have yet to understand.
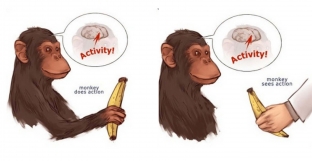
D. Kilner and R. Lemon believe that experiments with monkeys are not enough to fully understand the work and functions of mirror neurons, and it is impossible to conduct similar experiments on humans. The only human study of this kind indicates the presence of mirror neurons in the temporal lobe and frontal cortex of the human brain. There are many types of mirror neurons that have yet to be proven to exist and have functional significance in humans.






Add a comment