Hypertrophy of fat pads, especially in the face and neck area, violate the proportions of beauty, therefore, require treatment.
Phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholic acid are the most commonly used solutions for injectable lipolysis.
Sodium deoxycholate is currently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration.
This article on estet-portal.com describes the correct and safe use of lipolysis solutions, patient selection methods, dose selection, and a summary of post-treatment care and complications of the procedure.
- Deoxycholic Acid for Injectable Lipolysis
- Mechanism of action of injectable lipolytics
- Algorithm of injection lipolysis procedure
- Possible side effects of injectable lipolyfor
Deoxycholic acid for injectable lipolysis
Demand for injectable lipolysis is growing steadily as the population is overweight.
Effective fat reduction in the face and neck should help people achieve a better appearance and desired shape of the face and neck.
In Italy, in the late 1980s, Dr. Sergio Maggiori began using phosphatidylcholine for xanthelasma infiltration with satisfactory results.
In 1995, a Brazilian dermatologist, Dr. Patricia Ritts, injected herself with phosphatidylcholine while self-treating bags under her eyes.
Sodium deoxycholate is currently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) for the reduction of persistent submental fatra.
Read the latest articles in Telegram!
Mechanism of action of injectable lipolytics
Phosphatidylcholine is the most important and essential phospholipid in the human body.
It facilitates the emulsification of fat, allowing fat to be absorbed and transported.
After subcutaneous injections of phosphatidylcholine into adipose tissue, adipocytes rupture, and phosphatidylcholine enhances the secretion of triglycerol-rich lipoproteins.
Deoxycholic acid is a component of human bile acid that plays a vital role in the emulsification and digestion of fat in the intestine.
Deoxycholic acid physically destroys the cell membrane of adipocytes, causing cell death, and relatively low protein tissues such as fat are more susceptible to the cytolytic effects of deoxycholic acid than relatively high protein tissues such as skin and muscle.
The clinical efficacy and safety of deoxycholic acid has been established by several studies.
Deoxycholic Acid Injection was approved in 2015 as a first-in-class injectable for submental fat lipolysis.
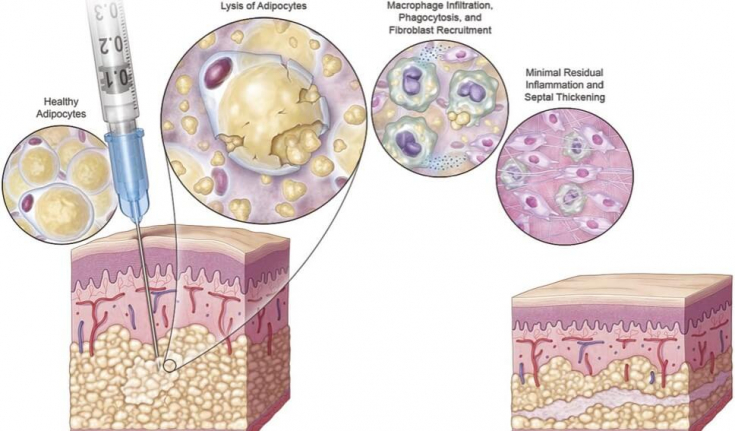
Mechanism of action of deoxycholic acid: After injection, the adipocyte wall is destroyed, which leads to inflammatory cell necrosis and a decrease in the size of adipocytes, after which fibroblasts migrate and stimulate, which leads to to collagen accumulation
Reviewing the literature, it can be seen that various variable combinations of both deoxycholic acid and phosphatidylcholine have been tried.
Some standard combinations are as follows:
- Lipostabil contains phosphatidylcholine (50mg/ml) together with deoxycholic acid, sodium hydroxide, sodium chloride, α-tocopherol, benzyl alcohol and ethanol.
- Kybella contains deoxycholic acid (10 mg/ml).
- GeoLysis contains deoxycholic acidtu (10 mg/ml).
Injectable lipolysis: what the doctor should remember
Algorithm of injection lipolysis procedure
Persistent submental fat or double chin is the only on-label indication for lipolytics.
However, these drugs are widely used by doctors in other areas: for the correction of local fat deposits in the face and body.
The results of these readings are variable and the methods are not standardized.
The patient is assessed by analyzing the severity of submental fat frontally and in profile.
The submental fat is located in front of the platysma muscles.
Thus, before marking the injection site, the patient is asked to contract the platysma muscle to palpate fat (to do this, the patient needs to open their mouth wide and say "Eee").
After marking the submental fat, several injection points are marked 1 cm apart in a grid pattern.
Another important anatomical landmark is the lower border of the mandible with an antagonal notch (a bony landmark in the anterior part of the masticatory muscle that approximates the position of the marginal mandibular nerve).
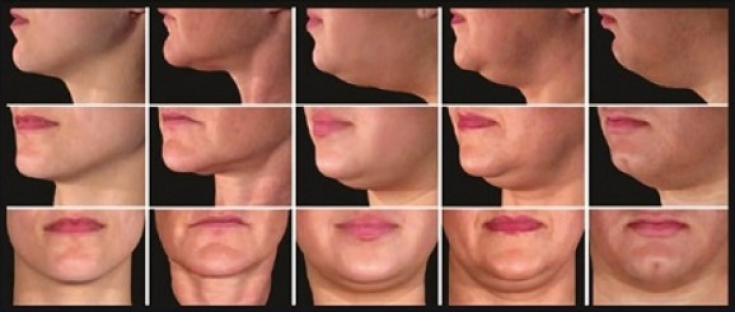
Deoxycholic acid is injected into the submental fat using a 1 ml syringe and a fine needle (usually 30 G and 13 mm). Usually, 3-5 ml of deoxycholic acid is administered per session.
Typically, three to five sessions are required, with a 4 week interval between two sessions. After the procedure, topical antibiotics are prescribed.
can be used effectively to relieve discomfort after lipolysis. Patients are instructed not to massage the treated area for the next 48 hours
Ultrasonic liposuction (lipolysis) — non-surgical method of getting rid of fat Possible side effects of injectable lipolysis
According to statistics, the majority of patients who have resorted to injection lipolysis to reduce a double chin are very
satisfied with the result.The most common side effects of — it is
discomfort, swelling and pain,which will disappear with time. Swelling and pain after injections of deoxycholic acid alone can last up to 10-14 days, while discomfort after injections of a combination of deoxycholic acid and phosphatidylcholine usually lasts no more than a week.
You may also experiencebruising
due to vascular damage after the procedure.
Clinically, this can lead to an asymmetrical smile. This complication can be avoided with correct injection technique.
Skin ulceration: superficial injections may result in ulceration.
Deoxycholic Acid is a first-in-class injectable for the reduction of submental fat and provides a minimally invasive alternative to liposuction and surgery.
Victor Yushchenko: Laser lipolysis and liposuction — procedures that optimally complement each other







Add a comment