In industrialized countries, nearly one in three people will experience an allergic reaction at some point in their lives, and one in ten children will suffer from atopic dermatitis.
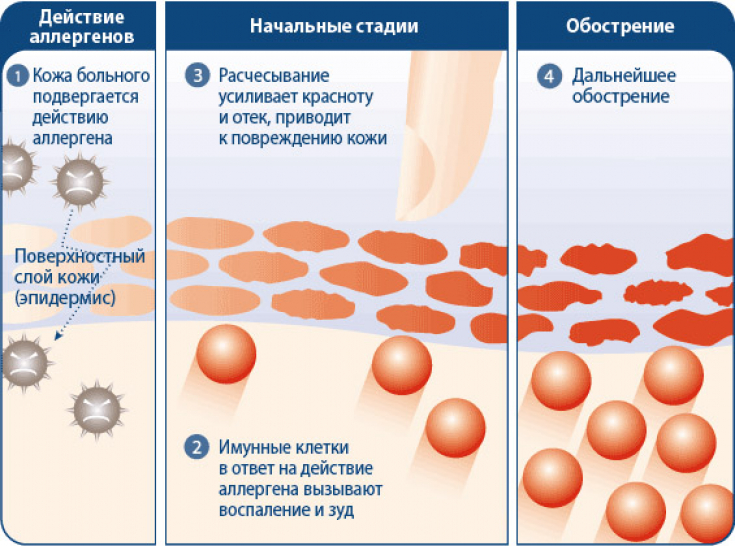
T cells play an important role in the immune response, they are a vital aspect of the body's resistance to infection. However, if they are not controlled, pathological autoimmune reactions can develop, and previously "defender cells" will start attacking the body itself or harmless substances such as allergens.
On estet-portal.com read about the recent discovery of scientists regarding the role of salt in the pathogenesis of allergic diseases, including atopic dermatitis.
Can salt cause atopic dermatitis
Recent studies have shown that salt appears to play an important role in causing hypersensitivity reactions. A team of German researchers demonstrated in cell cultures that sodium ions can induce an increase in Th2 cell production. These immune cells are active in allergic diseases such as atopic dermatitis.
Scientists have found that patients with atopic dermatitis have an increased concentration of salt in the skin.
When Th2 cells are overproduced, the production of pro-inflammatory proteins such as interleukin 4 (IL-4) and interleukin 13 (IL-13) is increased, which can lead to inflammatory skin diseases such as atopic dermatitis. Under the influence of sodium ions, a whole cascade of processes is launched leading to the development of an inadequate immune response.
Read the latest articles in Telegram
How salt affects immune cells
There are more Th2 cells in the body when exposed to sodium ions because other types of T cells can be converted to Th2 in the presence of salt. Therefore, ionic signals play a role in the generation and control of these cells.
In connection with this hypothesis, studies of the concentration of sodium in the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis were carried out. Although it is difficult to measure the concentration of ions in tissues, the scientists enlisted the help of colleagues in nuclear chemistry and physics and tested skin samples using neutron activation analysis.
The level of sodium in the affected areas of the skin with atopic dermatitis exceeded the normative values by more than 30 times. This study clearly shows that salt plays an important role in the etiology of allergic diseases.
You may also be interested in: Atopic dermatitis: causes and effective treatments
Salty environment: paradise for Staphylococcus aureus
Higher sodium levels in affected skin are also associated with increased levels of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. For these microorganisms, a salty environment is favorable for reproduction. Thus, the infection provokes the development of the inflammatory process, and causes even more severe damage to the human skin.
Staphylococcus aureus are microorganisms that thrive in saline environments, unlike other commensal bacteria.
However, scientists have not yet been able to show how and why the concentration of salt in the affected tissues increases, so it is impossible to be sure whether a low-salt diet will help in the fight against atopic dermatitis and other allergic diseases. Therefore, scientists do not stop at this discovery, but continue to search for the reasons for the increase in the concentration of sodium ions in the skin in patients with atopic dermatitis.
Read also: Is topical treatment of atopic dermatitis effective







Add a comment