Hyaluronic acid injections are considered a safe and effective method of periorbital correction, which provides good results in filling the nasolacrimal and nasopharyngeal sulci. Despite a number of advantages of HA, the hydrophilicity of the gel can cause edema, which usually resolves within a few days after injection. However, sometimes the edema may persist for a long time, in particular after correction of the infraorbital sulci. The estet-portal.com article presents a clinical case from the practice of Ricardo Augusto Sandoval Vasques, Kelly Park, Katherine Braunlich and Shino Bay Aguilera.
- Clinical case description: prolonged swelling after filling the nasomalar sulcus with HA filler
- Possible causes of prolonged swelling under the eyes after andhyaluronic acid injections
Clinical case description: prolonged swelling after filling the nasopharynx with HA filler
A 61-year-old female patient came to the authors' clinic with complaints of dark circles and furrows under her eyes. During the consultation, the authors proposed to correct the pronounced nasolacrimal and nasopharyngeal sulcus with fillers based on hyaluronic acid.
During procedure, the patient was injected with 1 ml of filler based on stabilized hyaluronic acid at a concentration of 20 mg/ml with lidocaine 0.3%.
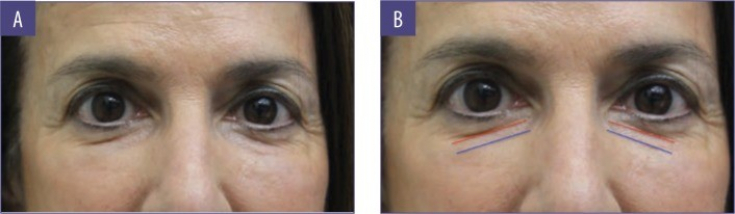
Photo 1: patient during initial consultation: red line – nasolacrimal sulcus, blue – nasopharynx
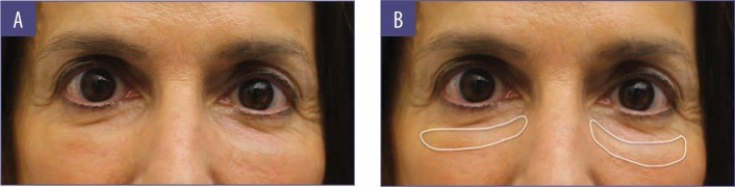
Photo 2: 1 year after hyaluronic acid filler injections; the area of the most pronounced edema is marked in white
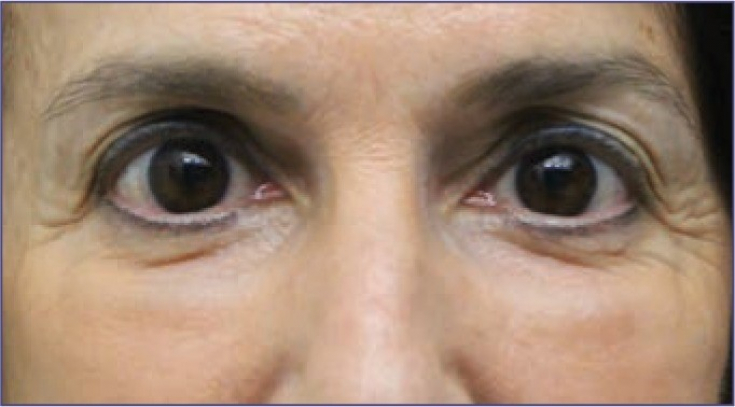
Photo 3: female patient 19 months after hyaluronic acid filler injections
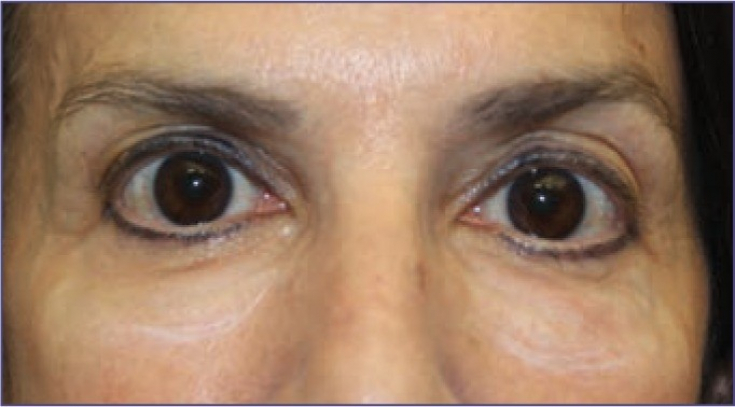
Photo 4: patient 25 months after hyaluronic acid injections
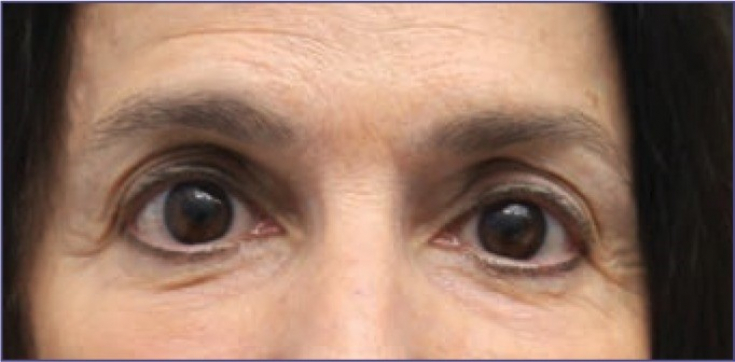
Photo 5: patient 31 months after hyaluronic acid injections
The patient tolerated the procedure well, with no immediate complications. However, after a few months, the woman developed edema under the eyes, most pronounced in the area of the nasopharyngeal sulcus. A year later, the patient reported the problem to the doctor. 18 months after the filler injections, the patient came to the doctor's office and, after a consultation, decided on further follow-up. Only 19 months after the initial correction, she agreed to hyaluronidase injections.
Follow us on Facebook!
In the area of the most pronounced edema, 5 units (0.05 ml) of hyaluronidase were injected on both sides of the face. After that, there was immediately a visible improvement.
After 25 months after the initial procedure, the patient returned to the doctor with complaints of moderate swelling. After that, she was injected with 2 more units (0.02 ml) of hyaluronidase on both sides of the face in the same area, followed by improvement.
After 31 months after correction, the edema decreased significantly and the patient refused further therapy.
Possible causes of prolonged swelling under the eyes after hyaluronic acid injections
In this case, prolonged swelling under the eyes after the filler could be formed due to several factors:
- anatomical features of the patient;
- hydrophilic properties of selected HA filler;
- Introduction Techniques.
- elasticity;
- viscosity;
- cohesiveness;
- cross stitching.
(mg/ml) is proportional to the amount of cross-linked (insoluble) and free (soluble) hyaluronic acid. Cross-linked HA resists enzymatic degradation and provides longer lasting correction results, while free HA is easily degraded. Hyaluronic acid – viscoelastic gel:
Viscosity – the ability of HA to deform during injection;
- elasticity – the ability to restore its original shape.
- Fillers with a high
(G’) show more resistance to movement and therefore retain their shape better. Fillers with a high modulus of elasticity are ideal for deep insertion for lifting purposes, but are less suitable for areas with high muscle activity. Cross-linking HA increases gel density, modulus of elasticity, and gel cohesion.
Cohesiveness– internal adhesive force that binds the cross-linked HA. The higher the cohesiveness, the better the filler retains its shape. Fillers with low cohesiveness, respectively, give a smaller lifting effect. This is important to consider when choosing the depth of injection of the drug. Low cohesiveness can also lead to fragmentation of the HA and increase the effect of gravity on the product. Filler injection technique
When augmenting the infraorbital region with a HA filler, a specific insertion technique must be followed. The filler should be injected
below the ligament that supports the orbicular muscle of the eye, otherwise gel migration and prolonged swelling after the filler is injected under the eyes. There are various
HA injection techniques to correct the nasopharynx. Injections into the correct anatomical region – an important rule of any insertion technique. Using a cannula, the doctor can feel the resistance of the suspensory ligament and avoid incorrect injection of the drug. In general, the technique that minimizes the amount of filler injected is considered optimal.
In the present case, the patient persisted with prolonged edema despite in-depth knowledge of anatomy, the clinical experience of the practitioner, and the correct choice of HA filler for the target anatomy.
In order to choose the ideal filler for correcting the problem area, it is necessary to take into account its rheological properties, which affect the result of contouring.
Therefore, the authors suggest that prolonged swelling may behigh hydrophilicity of the selected filler
, which can lead to increased gravitational pull, migration of the product to unwanted areas and / or long-term attraction of water, which entails the development of edema . However, the exact cause of this complication is unknown. To avoid such complications, the authors recommend using homogeneous, non-dispersed cohesive gels based on low-concentration hyaluronic acid for the correction of the nasolacrimal and nasopharyngeal sulci.
Adapted from J Clin Aesthet DermatolMore interesting videos on our







Add a comment